26. During interphase each chromosome replicates to two
... 31. The fraction of chromosomes a sperm or egg has? __________________________ 32. The organelle that houses the genetic material? __________________________ 33. The smallest unit able to perform the basic functions of life __________________________ 34. Any change made to the DNA molecule? ________ ...
... 31. The fraction of chromosomes a sperm or egg has? __________________________ 32. The organelle that houses the genetic material? __________________________ 33. The smallest unit able to perform the basic functions of life __________________________ 34. Any change made to the DNA molecule? ________ ...
Chapters 10 and 11 - Cellular Reproduction, Meiosis and Genetics
... 20. The “matching” chromosomes from each parent in a human karyotype are _homologous chromosomes. 21. During meiosis, what happens to the chromosome number? Reduced by half 22. The physical appearance of an organism is its _phenotype__. 23. . gametes are haploid / diploid definitions: 24. heterozygo ...
... 20. The “matching” chromosomes from each parent in a human karyotype are _homologous chromosomes. 21. During meiosis, what happens to the chromosome number? Reduced by half 22. The physical appearance of an organism is its _phenotype__. 23. . gametes are haploid / diploid definitions: 24. heterozygo ...
Study Questions – Chapter 1
... was mapped, it took less than a year to find the gene. What had changed that made such a big difference in the timelines of these two projects? 16. What information can help evaluate the list of potential candidate genes located in the region to which a gene has been mapped? 17. How can an animal mo ...
... was mapped, it took less than a year to find the gene. What had changed that made such a big difference in the timelines of these two projects? 16. What information can help evaluate the list of potential candidate genes located in the region to which a gene has been mapped? 17. How can an animal mo ...
Biological ideas relating to genetic modification
... Deoxyribonucleic acid. A molecule found in the nucleus of a cell which codes for an individuals genetic make up. ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid. A molecule found in the nucleus of a cell which codes for an individuals genetic make up. ...
Propionic-Acidemia-G.. - Propionic Acidemia Foundation
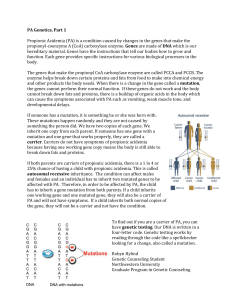
... enzyme helps break down certain proteins and fats from food to make into chemical energy and other products the body needs. When there is a change in the gene called a mutation, the genes cannot perform their normal function. If these genes do not work and the body cannot break down fats and protein ...
... enzyme helps break down certain proteins and fats from food to make into chemical energy and other products the body needs. When there is a change in the gene called a mutation, the genes cannot perform their normal function. If these genes do not work and the body cannot break down fats and protein ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide D6
... 2. The _________________ states that factors for different traits on different genes are independent of one another. 3. A ___________ is a plant pure for a specific trait. 4. A _________________ occurs between individuals with 2 contrasting traits. 5. A ______________ is the actual alleles that are ...
... 2. The _________________ states that factors for different traits on different genes are independent of one another. 3. A ___________ is a plant pure for a specific trait. 4. A _________________ occurs between individuals with 2 contrasting traits. 5. A ______________ is the actual alleles that are ...
Clone
... Hybridization: crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both *produces hybrids that are hardier than parents *ex. Corn, mules Inbreeding – mating between closely related individuals. Risks: because genetically similar, recessive alleles causing genetic defects appear more often ...
... Hybridization: crossing dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both *produces hybrids that are hardier than parents *ex. Corn, mules Inbreeding – mating between closely related individuals. Risks: because genetically similar, recessive alleles causing genetic defects appear more often ...
Chapter 6, Section 3: Advances in Genetics
... cows so that the cows produce the protein responsible for blood clotting in their milk. The protein is then extracted and used to treat hemophiliacs. Genes have also been inserted into plant DNA which enables plants to survive in cold temperatures or in poor soil. Some genetically engineered plant ...
... cows so that the cows produce the protein responsible for blood clotting in their milk. The protein is then extracted and used to treat hemophiliacs. Genes have also been inserted into plant DNA which enables plants to survive in cold temperatures or in poor soil. Some genetically engineered plant ...
Punnetts 2
... • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, s ...
... • Because males have only one X chromosome, they show all the traitsgenes on that X. Females have two X’s, so they have two chances to get a gene that is good, and can show the good trait. Example: If females, have one gene on an X for colorblindness, and one gene on the other X for normal vision, s ...
Mendel chp 5 notes
... EX. Polydactyly- (extra fingers or toes) iii. variably expressive – intensity varies in different people 1. some people may have an extra digit on every extremity or some may just have a partial digit on one extremity h. Pleiotropy - one gene (protein) controls several functions or has more than one ...
... EX. Polydactyly- (extra fingers or toes) iii. variably expressive – intensity varies in different people 1. some people may have an extra digit on every extremity or some may just have a partial digit on one extremity h. Pleiotropy - one gene (protein) controls several functions or has more than one ...
ch 14 RTC - WordPress.com
... into plant cells called protoplasts that have had the cell wall removed. Foreign genes transferred to crops have made the plants resistant to pests and herbicide. Plants are also being engineered to pro ...
... into plant cells called protoplasts that have had the cell wall removed. Foreign genes transferred to crops have made the plants resistant to pests and herbicide. Plants are also being engineered to pro ...
7 Self study questions
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
... 1. Explain why ORF scanning is a feasible way of identifying genes in a prokaryotic DNA sequence. 2. What modifications are introduced when ORF scanning is applied to a eukaryotic DNA sequence? 3. Describe how homology searching is used to locate genes in a DNA sequence and to assign possible functi ...
1) Give a brief explanation and examples of: Incomplete dominance
... and Human Genetic Disorders on pgs. 125 – 132 Write and Answer: ...
... and Human Genetic Disorders on pgs. 125 – 132 Write and Answer: ...
genetics 2-2
... Baldness- a sex-influenced trait which is dominant in males, recessive in females Color blindness- sex-linked genes in humans They are attached only to the Y chromosomes Hemophilia- a bleeders disease, sex-linked, attached only to the Y chromosome When you cross a horse and a mule -> a “sterile donk ...
... Baldness- a sex-influenced trait which is dominant in males, recessive in females Color blindness- sex-linked genes in humans They are attached only to the Y chromosomes Hemophilia- a bleeders disease, sex-linked, attached only to the Y chromosome When you cross a horse and a mule -> a “sterile donk ...
Genetics Webquest Worksheet
... 3. What is the four-letter DNA alphabet and what are the special rules by which the alphabet ...
... 3. What is the four-letter DNA alphabet and what are the special rules by which the alphabet ...
chapter18-20packet
... 5. a. List the multiple levels of packing in a metaphase chromosome in order of increasing complexity. ...
... 5. a. List the multiple levels of packing in a metaphase chromosome in order of increasing complexity. ...
Genetics and Intelligence
... • How do science and politics mingle in the conscious and unconscious minds of scientists? • Does ‘genetic basis for intelligence’ mean same thing as born ‘smart’ or ‘dumb’? • What is race? • What is intelligence? • Debate: Can intelligence be measured in a ...
... • How do science and politics mingle in the conscious and unconscious minds of scientists? • Does ‘genetic basis for intelligence’ mean same thing as born ‘smart’ or ‘dumb’? • What is race? • What is intelligence? • Debate: Can intelligence be measured in a ...
Leq: what is cloning and how is it done?
... Replacing a mutated gene that causes disease with a healthy copy of the gene. Inactivating, or “knocking out,” a mutated gene that is functioning improperly. Introducing a new gene into the body to help fight a disease. ...
... Replacing a mutated gene that causes disease with a healthy copy of the gene. Inactivating, or “knocking out,” a mutated gene that is functioning improperly. Introducing a new gene into the body to help fight a disease. ...
CB-Human Genetics
... C. Autosomes – the remaining 22 pairs are non-sex chromosomes D. Karyotyping - Cell biologists take photographs of cells in mitosis when the chromosomes are easy to see ...
... C. Autosomes – the remaining 22 pairs are non-sex chromosomes D. Karyotyping - Cell biologists take photographs of cells in mitosis when the chromosomes are easy to see ...
Document
... A gene is a heritable factor that consists of a length of DNA and influences a specific characteristic A gene occupies a specific position on a chromosome The various specific forms of a gene are alleles Alleles differ from each other by one or only a few bases New alleles are formed by mutation The ...
... A gene is a heritable factor that consists of a length of DNA and influences a specific characteristic A gene occupies a specific position on a chromosome The various specific forms of a gene are alleles Alleles differ from each other by one or only a few bases New alleles are formed by mutation The ...
Biotechnology Need To Know List
... How a gene marker is used to distinguish transformed bacteria When transformation of a plant cell is considered successful The relationship between genetic engineering and transgenic organisms Sex determination in humans What a pedigree allows a researcher to do Inheritance of PKU, ABO blood type, s ...
... How a gene marker is used to distinguish transformed bacteria When transformation of a plant cell is considered successful The relationship between genetic engineering and transgenic organisms Sex determination in humans What a pedigree allows a researcher to do Inheritance of PKU, ABO blood type, s ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell con ...
... 2. What is inside every cell in your body? 3. What does DNA stand for? 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell con ...