Review and Non-Mendelian Genetics
... answer the question 2. Guinea pig coat color is determined by a single gene. The allele for black coat color is dominant to brown. In a cross between two black-haired guinea pigs, 20 offspring are born. If both parents were heterozygous, probability would predict that approximately how many of the 2 ...
... answer the question 2. Guinea pig coat color is determined by a single gene. The allele for black coat color is dominant to brown. In a cross between two black-haired guinea pigs, 20 offspring are born. If both parents were heterozygous, probability would predict that approximately how many of the 2 ...
heredity The passing of traits from parents to offspring. fertilization
... An organism that has 2 different alleles for a trait; an organism that is heterozygous for a particular trait. ...
... An organism that has 2 different alleles for a trait; an organism that is heterozygous for a particular trait. ...
1 - Acpsd.net
... 14. True Breeding: One that is homozygous for a trait (self pollinating) purebreeding Hybrid: one of each allele, heterozygous Ex. Hh 15. Male and female parts are located in the same plant, multiple offspring, fairly short generation times, traits are easy to tell apart. 16. Autosomal traits- found ...
... 14. True Breeding: One that is homozygous for a trait (self pollinating) purebreeding Hybrid: one of each allele, heterozygous Ex. Hh 15. Male and female parts are located in the same plant, multiple offspring, fairly short generation times, traits are easy to tell apart. 16. Autosomal traits- found ...
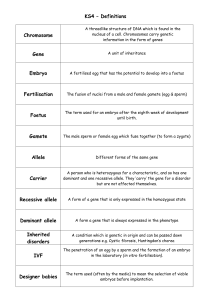
Definitions
... The penetration of an egg by a sperm and the formation of an embryo in the laboratory (in vitro fertilisation). ...
... The penetration of an egg by a sperm and the formation of an embryo in the laboratory (in vitro fertilisation). ...
7.2
... incomplete dominance, where the heterozygous phenotype is somewhere between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. The heterozygous phenotype is a third, distinct phenotype. • Codominance: In codominance, two alleles of a gene are completely and separately expressed, and both p ...
... incomplete dominance, where the heterozygous phenotype is somewhere between the homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive phenotypes. The heterozygous phenotype is a third, distinct phenotype. • Codominance: In codominance, two alleles of a gene are completely and separately expressed, and both p ...
Unit_biology_2_Genetic_variation
... Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: a) Sexual reproduction gives rise to variation because, when gametes fuse, one of each pair of alleles comes from each parent. b) In human body cells, one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes carries the genes that deter ...
... Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding of how science works: a) Sexual reproduction gives rise to variation because, when gametes fuse, one of each pair of alleles comes from each parent. b) In human body cells, one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes carries the genes that deter ...
Genetics Lesson 5 ALL vocabulary
... 15. blended inheritance – the idea that offspring inherit a blend of parental traits. 16. co-dominance- both alleles affect the offspring’s phenotype is separate and distinct ways (human blood types) 17. complete dominance- when on allele is expressed over the other 18. incomplete dominance- bo ...
... 15. blended inheritance – the idea that offspring inherit a blend of parental traits. 16. co-dominance- both alleles affect the offspring’s phenotype is separate and distinct ways (human blood types) 17. complete dominance- when on allele is expressed over the other 18. incomplete dominance- bo ...
Name
... 6. There are 100 students in a class. Ninety-six did well in the course whereas four blew it totally and received a grade of F. Sorry. In the highly unlikely event that these traits are genetic rather than environmental, if these traits involve dominant and recessive alleles, and if the four (4%) re ...
... 6. There are 100 students in a class. Ninety-six did well in the course whereas four blew it totally and received a grade of F. Sorry. In the highly unlikely event that these traits are genetic rather than environmental, if these traits involve dominant and recessive alleles, and if the four (4%) re ...
Genetics - Liberty Union High School District
... covered or masked when paired with a dominant trait. ...
... covered or masked when paired with a dominant trait. ...
Mendel Notes
... Today these factors are called “genes” Different forms of a gene are called “alleles” ...
... Today these factors are called “genes” Different forms of a gene are called “alleles” ...
Extending Mendelian Genetics for two or more genes
... The gene for pigment deposition is said to be epistatic to the gene that codes for black or brown pigment ...
... The gene for pigment deposition is said to be epistatic to the gene that codes for black or brown pigment ...
Introduction to Genetics
... genetic makeup • Example: • Mom’s allele → “T” (dominant) • Dad’s allele → “t” (recessive) ...
... genetic makeup • Example: • Mom’s allele → “T” (dominant) • Dad’s allele → “t” (recessive) ...
Unit 3.4 Inheritance
... 4. The specific position on a homologous chromosome of a gene ___________________________ 5. Having two different alleles at a locus ______________________________ 6. A heritable factor that controls a specific characteristic. ________________________________ 7. The characteristic on an organism. __ ...
... 4. The specific position on a homologous chromosome of a gene ___________________________ 5. Having two different alleles at a locus ______________________________ 6. A heritable factor that controls a specific characteristic. ________________________________ 7. The characteristic on an organism. __ ...
laid the foundation of genetics through his work on garden peas
... Identify the trait from the given pair of alleles : If purple flower (P) is dominant to white flower (p). ...
... Identify the trait from the given pair of alleles : If purple flower (P) is dominant to white flower (p). ...
Notes 5-1 & 5-2
... If a gene has both dominant alleles, it is homozygous dominant (TT) If a gene has both recessive alleles, it is homozygous recessive (tt) If a gene has 1 dominant and 1 recessive allele, it is heterozygous (Tt) ...
... If a gene has both dominant alleles, it is homozygous dominant (TT) If a gene has both recessive alleles, it is homozygous recessive (tt) If a gene has 1 dominant and 1 recessive allele, it is heterozygous (Tt) ...
Document
... – the degree to which the dominant gene is expressed is called penetrance • Tay Sachs is a disease that causes fat accumulation in the neural tissues of children leading to death in the homozygous individual. The disease is due to the loss of function of a needed enzyme. – Although the allele for th ...
... – the degree to which the dominant gene is expressed is called penetrance • Tay Sachs is a disease that causes fat accumulation in the neural tissues of children leading to death in the homozygous individual. The disease is due to the loss of function of a needed enzyme. – Although the allele for th ...
Problem Set 1 1. Name 4 important differences between mitosis and
... genotypes have gooey earwax. On Paradise Island there are 100 people, 25 of whom have gooey earwax. Assuming Hardy–Weinberg conditions, what is the frequency of the c allele on Paradise Island? ...
... genotypes have gooey earwax. On Paradise Island there are 100 people, 25 of whom have gooey earwax. Assuming Hardy–Weinberg conditions, what is the frequency of the c allele on Paradise Island? ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide D6
... 14. A _______________ occurs between individuals with one pair of contrasting traits. 15. A ____________ is a segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a trait. 16. _______________ mask other traits. 17. When both alleles are different an organism is _________________. 18. _____________________ o ...
... 14. A _______________ occurs between individuals with one pair of contrasting traits. 15. A ____________ is a segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a trait. 16. _______________ mask other traits. 17. When both alleles are different an organism is _________________. 18. _____________________ o ...
Ch 9.3 SR
... codominance incomplete dominance traits allele a. __________ are segments of DNA that carry hereditary instructions and are found on chromosomes. b. Different forms of a single gene are called __________. c. __________ is when a recessive and a dominant trait mix or blend. d. In horses, when a pure ...
... codominance incomplete dominance traits allele a. __________ are segments of DNA that carry hereditary instructions and are found on chromosomes. b. Different forms of a single gene are called __________. c. __________ is when a recessive and a dominant trait mix or blend. d. In horses, when a pure ...
Genetics Study Guide 2013
... 22) What phenotypic ratio do you get when you cross two heterozygous organisms? 23) Huntingdon’s disease is a fatal disorder characterized by progressive deterioration of the nervous system. The symptoms of this disease usually begin to develop in middle age. It is caused by a dominant allele (H). A ...
... 22) What phenotypic ratio do you get when you cross two heterozygous organisms? 23) Huntingdon’s disease is a fatal disorder characterized by progressive deterioration of the nervous system. The symptoms of this disease usually begin to develop in middle age. It is caused by a dominant allele (H). A ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.