Chapter 9 - Mantachie High School
... Trait—in genetics, a category within which alternate characteristics, such as height and eye color, can be observed Codominance—an inheritance relationship in which neither of two alleles of the same gene totally masks the other; both alleles for a gene are expressed (designated as RR’) Complete do ...
... Trait—in genetics, a category within which alternate characteristics, such as height and eye color, can be observed Codominance—an inheritance relationship in which neither of two alleles of the same gene totally masks the other; both alleles for a gene are expressed (designated as RR’) Complete do ...
STAAR REVIEW—GENETICS, NATURAL SELECTION
... ARTIFICIAL SELECTION/ SELECTIVE BREEDING —CATEGORY 4 Genetics: The study of heredity Gregor Mendel: The father of genetics Alleles: Genes that code for different versions of a trait (represented by capital and lower case letters) Chromosomes: Specific location of the inherited traits (genes) ...
... ARTIFICIAL SELECTION/ SELECTIVE BREEDING —CATEGORY 4 Genetics: The study of heredity Gregor Mendel: The father of genetics Alleles: Genes that code for different versions of a trait (represented by capital and lower case letters) Chromosomes: Specific location of the inherited traits (genes) ...
Introduction to Genetics Notes
... RecessiveAn organism with a recessive allele will exhibit that form only when the dominant allele for the trait is not present. ...
... RecessiveAn organism with a recessive allele will exhibit that form only when the dominant allele for the trait is not present. ...
Mendelian Genetics continued..
... Also in guinnea pigs, black eyes are dominant to red eyes. A male guinnea pig that is heterozygous for both traits is crossed with a female that is long haired and red eyed. What are the expected phenotypes of their offspring and in what proportion? ...
... Also in guinnea pigs, black eyes are dominant to red eyes. A male guinnea pig that is heterozygous for both traits is crossed with a female that is long haired and red eyed. What are the expected phenotypes of their offspring and in what proportion? ...
Egg Genetics Vocab. Notes
... chromosomes (each chromosome has a matching pair. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, so 46 chromosomes total.) • Pairs of chromosomes have matching genes, therefore, genes also come in pairs, (2). • Not all genes in a pair are identical! – Ex.) There is one gene pair that controls flower color in ...
... chromosomes (each chromosome has a matching pair. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, so 46 chromosomes total.) • Pairs of chromosomes have matching genes, therefore, genes also come in pairs, (2). • Not all genes in a pair are identical! – Ex.) There is one gene pair that controls flower color in ...
Introduction to Genetics
... The allele for axial flowers (A) in peas is dominant to the allele for flowers borne terminally (a). What phenotypic ratios would you expect among the offspring of a cross between a known heterozygous axialflowered plant and one whose flowers are ...
... The allele for axial flowers (A) in peas is dominant to the allele for flowers borne terminally (a). What phenotypic ratios would you expect among the offspring of a cross between a known heterozygous axialflowered plant and one whose flowers are ...
Genetics and Heredity Study Guide
... Vocabulary you need to know for the test: heredity trait genetics fertilization purebred hybrid gene allele probability punnett square homozygous heterozygous codominance multiple alleles carrier genetic disorder Cystic Fibrosis Sickle-Cell Disease Hemophilia Down Syndrome Pedigree Karyotype ...
... Vocabulary you need to know for the test: heredity trait genetics fertilization purebred hybrid gene allele probability punnett square homozygous heterozygous codominance multiple alleles carrier genetic disorder Cystic Fibrosis Sickle-Cell Disease Hemophilia Down Syndrome Pedigree Karyotype ...
Allele - West Ada
... Phenotype - An organism’s physical appearance or visible traits. What can be seen. (ex: freckles, curly hair) Genotype - An organisms genetic makeup or allele combination. What can not be seen. (ex: AA, Aa, aa) Allele – 2 forms of a gene, 1 from each parent. (ex: AA, Aa, aa) Allele = Alphabet ...
... Phenotype - An organism’s physical appearance or visible traits. What can be seen. (ex: freckles, curly hair) Genotype - An organisms genetic makeup or allele combination. What can not be seen. (ex: AA, Aa, aa) Allele – 2 forms of a gene, 1 from each parent. (ex: AA, Aa, aa) Allele = Alphabet ...
Hardy-Weinberg Practice Problems
... 2. The delta – 32 mutation, a recessive gene, gives humans protection from HIV infection. The allele frequency in a town in Sweden is 20%. a. What percent of the population have two copies of the gene and are therefore immune to ...
... 2. The delta – 32 mutation, a recessive gene, gives humans protection from HIV infection. The allele frequency in a town in Sweden is 20%. a. What percent of the population have two copies of the gene and are therefore immune to ...
Epistasis is not dominance.
... Effects of one gene override or mask the phenotype of a second gene. Epistasis is not dominance. Compare the definitions: Epistasis: One gene masks the expression of a different gene for a different trait Dominance: One allele masks the expression of another allele of the same gene ...
... Effects of one gene override or mask the phenotype of a second gene. Epistasis is not dominance. Compare the definitions: Epistasis: One gene masks the expression of a different gene for a different trait Dominance: One allele masks the expression of another allele of the same gene ...
Chapter 4
... same locus on homologous chromosomes and govern the same trait. Because they are different, their action may result in different expressions of that trait. The term is often ...
... same locus on homologous chromosomes and govern the same trait. Because they are different, their action may result in different expressions of that trait. The term is often ...
Review for Heredity Unit
... 11. Different forms of a characteristic like blue eyes are _____________________ 12. When more than one allele is dominant as in blood types. ___________________ 13. The area of science that studies heredity is ______________________ ...
... 11. Different forms of a characteristic like blue eyes are _____________________ 12. When more than one allele is dominant as in blood types. ___________________ 13. The area of science that studies heredity is ______________________ ...
genetic study guide/quiz
... 2. He used ______ plants to study heredity. Garden pea plants reproduce sexually, which means they use the process of _________ to produce haploid ____________, also called male and female sex cells. The male gamete in peas forms in the ________ and the female gamete forms in the female reproductive ...
... 2. He used ______ plants to study heredity. Garden pea plants reproduce sexually, which means they use the process of _________ to produce haploid ____________, also called male and female sex cells. The male gamete in peas forms in the ________ and the female gamete forms in the female reproductive ...
Unit 7 Heredity: Chp 11 Non-Mendelian Genetics Notes
... Simple Mendelian Inheritance = controlled by dominant and recessive paired alleles. Many inheritance patterns are more complicated than those in Pea plants. ...
... Simple Mendelian Inheritance = controlled by dominant and recessive paired alleles. Many inheritance patterns are more complicated than those in Pea plants. ...
Genetics Quiz- Matching, Short answer
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
... 1. Explain the difference between dominant and recessive alleles. For example, if I have brown eyes what would the allele look like. ...
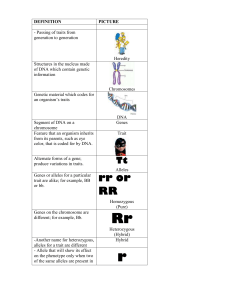
definition - Humble ISD
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
Basic Genetics Notes
... • Purple flower allele (R) is dominant over white flower allele (r) • So the genotype of RR = purple flower Rr = purple flower ...
... • Purple flower allele (R) is dominant over white flower allele (r) • So the genotype of RR = purple flower Rr = purple flower ...
Who Is My Mommy?
... 2. Allele: different forms of a gene. You get one allele for each gene from each parent. 3. Genotype: an organisms genetic makeup or allele combinations. Ex. AA, Bb ...
... 2. Allele: different forms of a gene. You get one allele for each gene from each parent. 3. Genotype: an organisms genetic makeup or allele combinations. Ex. AA, Bb ...
Genetics and Heredity
... Contains the genes that code for inherited traits Stored in the nucleus of an organisms cells ...
... Contains the genes that code for inherited traits Stored in the nucleus of an organisms cells ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.