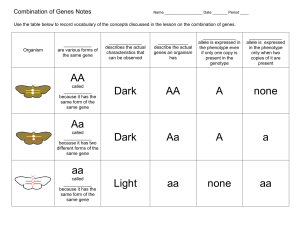
CH 3 GENETICS - TEST – GIFT GUIDE HINTS due
... Offspring = the “children” of parents. Some mutations are passed to offspring Order = refers to the sequence of DNA code letter (ATCG) that leads to the order (sequence) of amino acids that make up proteins Phenotype = the phenomena or physical traits of an organism that are usually visible to the h ...
... Offspring = the “children” of parents. Some mutations are passed to offspring Order = refers to the sequence of DNA code letter (ATCG) that leads to the order (sequence) of amino acids that make up proteins Phenotype = the phenomena or physical traits of an organism that are usually visible to the h ...
Genetics Summative Assessment review sheet
... Genetics Summative Assessment (Thursday, May 7th , 2104) Important Vocabulary: Genetics heredity allele trait Phenotype genotype purebred hybrid Mutation chromosome gene DNA Nurture nature co-dominance genetic disorder Asexual reproduction ...
... Genetics Summative Assessment (Thursday, May 7th , 2104) Important Vocabulary: Genetics heredity allele trait Phenotype genotype purebred hybrid Mutation chromosome gene DNA Nurture nature co-dominance genetic disorder Asexual reproduction ...
Document
... 5.5 Gene Interaction Occurs When Genes at Multiple Loci Determine a Single Phenotype • Duplicate recessive epistasis Albinism in freshwater snail Physa heterostroha can result from the presence of either of two recessive alleles at two different loci. P1 aaBB X AAbb ...
... 5.5 Gene Interaction Occurs When Genes at Multiple Loci Determine a Single Phenotype • Duplicate recessive epistasis Albinism in freshwater snail Physa heterostroha can result from the presence of either of two recessive alleles at two different loci. P1 aaBB X AAbb ...
Blank Jeopardy - Hazlet Township Public Schools
... The difference between a sex-linked traits and genetic traits ...
... The difference between a sex-linked traits and genetic traits ...
NB 100:Heredity
... Ex: Free earlobes = E Tall height = T Recessive allele – its trait is hidden if the dominant allele is present Ex: Attached earlobes; Short pea plant Write as lowercase letter of dominant allele Ex: ...
... Ex: Free earlobes = E Tall height = T Recessive allele – its trait is hidden if the dominant allele is present Ex: Attached earlobes; Short pea plant Write as lowercase letter of dominant allele Ex: ...
Genetics - Georgia Highlands College
... • Meiosis produces haploid gametes from diploid cells – Aa mother = A or a eggs ...
... • Meiosis produces haploid gametes from diploid cells – Aa mother = A or a eggs ...
Evolution of Populations
... • Usually a dominant and recessive • Only two distinct phenotypes can be shown ...
... • Usually a dominant and recessive • Only two distinct phenotypes can be shown ...
Traits_Disorders_Teacher
... 4. Pedigree analysis can help one determine human genotypes. 5. Harmful recessive genetic traits can persist in the population through carriers 6. Genetic testing will become more widespread. ...
... 4. Pedigree analysis can help one determine human genotypes. 5. Harmful recessive genetic traits can persist in the population through carriers 6. Genetic testing will become more widespread. ...
How does probability relate to genetics?
... Each allele is _______________ of the other, and no two alleles are __________ to each other When two events are ____________ of each other, the probability that both events will occur can be calculated using the ___________ ________ The probability of two or more outcomes occurring is equal to the ...
... Each allele is _______________ of the other, and no two alleles are __________ to each other When two events are ____________ of each other, the probability that both events will occur can be calculated using the ___________ ________ The probability of two or more outcomes occurring is equal to the ...
Genetics Pre/Post Test
... c. The chromosomes in a pair contain very different genetic information. d. Each of the chromosomes contains one copy of circular DNA. 13. DNA and RNA are _____. ...
... c. The chromosomes in a pair contain very different genetic information. d. Each of the chromosomes contains one copy of circular DNA. 13. DNA and RNA are _____. ...
Huntington`s disease is an example of a genetic disorder caused by
... alleles, what is the genotype of an individual a. with PKU? b. that appears normal but could pass the trait on? c. that is normal? 8. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by a recessive allele located on the X chromosome. a. In the space provided, draw a Punnett square that shoes how two unaffected ...
... alleles, what is the genotype of an individual a. with PKU? b. that appears normal but could pass the trait on? c. that is normal? 8. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by a recessive allele located on the X chromosome. a. In the space provided, draw a Punnett square that shoes how two unaffected ...
Royal family pedigree following the hemophilia allele
... chromosomes act the same regardless of your sex- autosomal. The 23rd pair are sex chromosomes Females are XX (inherit an X from each parent) Males are XY (inherit X from mom and Y from dad). Genes found on either the X or Y chromosomes are called sex-linked. ...
... chromosomes act the same regardless of your sex- autosomal. The 23rd pair are sex chromosomes Females are XX (inherit an X from each parent) Males are XY (inherit X from mom and Y from dad). Genes found on either the X or Y chromosomes are called sex-linked. ...
4.3 Theoretical Genetics Define the following: Genotype Gene
... d. Explain why human females can be homozygous or heterozygous for sex-linked genes, where males cannot. ...
... d. Explain why human females can be homozygous or heterozygous for sex-linked genes, where males cannot. ...
Alleleswoyce10notebook
... The different forms (often dominant and recessive) of a gene are known as alleles (uh LEELZ). Dominant alleles are shown with a capital letter. Recessive alleles are shown with a lowercase letter. ...
... The different forms (often dominant and recessive) of a gene are known as alleles (uh LEELZ). Dominant alleles are shown with a capital letter. Recessive alleles are shown with a lowercase letter. ...
Inheritance of Sex
... - when heterozygous and dominant homozygous phenotypes are identical Incomplete dominance: - phenotype of F1 hybrids is between phenotypes of parental varieties Codominance: - when two dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways ...
... - when heterozygous and dominant homozygous phenotypes are identical Incomplete dominance: - phenotype of F1 hybrids is between phenotypes of parental varieties Codominance: - when two dominant alleles affect the phenotype in separate, distinguishable ways ...
Genetics Guided Notes
... If a disease is ___________________, both parents have to pass on a mutated allele to the offspring o Those who are heterozygous (Aa) are ____________, meaning they have the mutated allele and can pass it on, but are ____________ themselves ...
... If a disease is ___________________, both parents have to pass on a mutated allele to the offspring o Those who are heterozygous (Aa) are ____________, meaning they have the mutated allele and can pass it on, but are ____________ themselves ...
Lecture 4 pdf
... • unknown genetic background • long generation time • small family size • no environmental control To look for Mendelian inheritance patterns, employ the use of large pedigrees – large family trees showing relationships and phenotypes pedigree analysis – try to infer genotypes and hence inheritance ...
... • unknown genetic background • long generation time • small family size • no environmental control To look for Mendelian inheritance patterns, employ the use of large pedigrees – large family trees showing relationships and phenotypes pedigree analysis – try to infer genotypes and hence inheritance ...
Early beliefs about Heredity and Gregory Mendel
... Important Terms used in Genetics Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism. More specifically, it refers to the actual alleles that an organism contains for a specific trait. One allele for each trait is inherited from each parent. Phenotype: The outward appearance of an organism. This refers to t ...
... Important Terms used in Genetics Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism. More specifically, it refers to the actual alleles that an organism contains for a specific trait. One allele for each trait is inherited from each parent. Phenotype: The outward appearance of an organism. This refers to t ...
Genetics Exam Study Guide
... 16. What is a dihybrid cross? Do you know how to set one up? How to figure out the possible gamete combinations from a parent’s genotype? 17. What is polygenic inheritance? How does this lead to continuous variation, and what is continuous variation? 18. What is pleiotropy? ...
... 16. What is a dihybrid cross? Do you know how to set one up? How to figure out the possible gamete combinations from a parent’s genotype? 17. What is polygenic inheritance? How does this lead to continuous variation, and what is continuous variation? 18. What is pleiotropy? ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.