LEARNING ACTIVITY 2.3 Matching: Patterns of Genetic Inheritance
... A. Traits in which many genes influence the characteristics in question. B. Alleles are imprinted, or chemically marked, in such a way that one member of the pair is activated, regardless of its makeup. C. Refers to each form of a gene. D. When heterozygous individuals with just one recessive allele ...
... A. Traits in which many genes influence the characteristics in question. B. Alleles are imprinted, or chemically marked, in such a way that one member of the pair is activated, regardless of its makeup. C. Refers to each form of a gene. D. When heterozygous individuals with just one recessive allele ...
Genetics Vocabulary
... Both alleles from your parents are the same Either both dominant (BB) or recessive (bb) ...
... Both alleles from your parents are the same Either both dominant (BB) or recessive (bb) ...
Genetics - Biology Junction
... 3. Another word for a heterozygous genotype 4. Shows a 3:1 ratio of phenotypes 5. Occurs whenever both alleles for a gene are expressed 6. Generation of all hybrids produced by crossing two pure organisms 7. Plant studied by Gregor Mendel 10. Study of how characteristics are transmitted from parents ...
... 3. Another word for a heterozygous genotype 4. Shows a 3:1 ratio of phenotypes 5. Occurs whenever both alleles for a gene are expressed 6. Generation of all hybrids produced by crossing two pure organisms 7. Plant studied by Gregor Mendel 10. Study of how characteristics are transmitted from parents ...
Mendel`s Laws and Genetics Quiz
... 1. The two versions of a gene for a characteristic are called a) genotypes. b) phenotypes. c) alleles. d) chromosomes. ...
... 1. The two versions of a gene for a characteristic are called a) genotypes. b) phenotypes. c) alleles. d) chromosomes. ...
BW 180-182
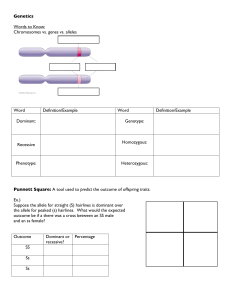
... Allele: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Homozygous: _______________________________________________________________________________________ Heterozygous: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Allele: _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Homozygous: _______________________________________________________________________________________ Heterozygous: ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Beyond Dominant and Recessive alleles
... Against Mendel’s principle….. Some alleles are neither dominant nor ...
... Against Mendel’s principle….. Some alleles are neither dominant nor ...
Study Guide for Test
... Patterns of Inheritance a. Simple Dominance b. Incomplete Dominance c. Codominance d. Mutliple Alleles i. Blood Typing e. Sex-linked traits ...
... Patterns of Inheritance a. Simple Dominance b. Incomplete Dominance c. Codominance d. Mutliple Alleles i. Blood Typing e. Sex-linked traits ...
Genetics - Easy Plan Book
... • Everyone has two alleles. One from mom and one from dad. • Purebred – is if both alleles are exactly the ...
... • Everyone has two alleles. One from mom and one from dad. • Purebred – is if both alleles are exactly the ...
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
... Law of Segregation: during ______________ formation (MEIOSIS) pairs of alleles _____________ and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete forma ...
... Law of Segregation: during ______________ formation (MEIOSIS) pairs of alleles _____________ and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete forma ...
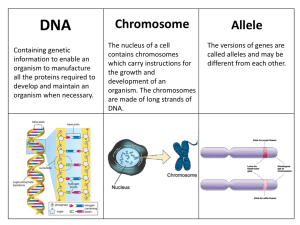
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... which consist of a sugar, a triphosphate and a base. There are 4 bases A – Adenine C – Cytosine G - Guanine T – Thymine ...
... which consist of a sugar, a triphosphate and a base. There are 4 bases A – Adenine C – Cytosine G - Guanine T – Thymine ...
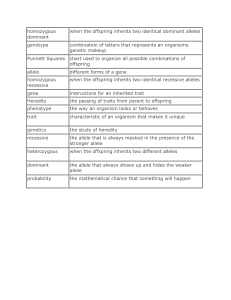
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... combination of letters that represents an organisms genetic makeup ...
... combination of letters that represents an organisms genetic makeup ...
Genetics Unit: 1. Heredity- the passing of traits from parent to young
... Phenotype- physical characteristics (ex. tall or short) Phenotypic Ratio- the proportion of phenotypes for a particular cross Homo or Homeo- same Homozygous- organism that has 2 identical alleles for a trait (ex. TT or tt) Hetero- different Heterozygous- organism that has 2 different alleles for a t ...
... Phenotype- physical characteristics (ex. tall or short) Phenotypic Ratio- the proportion of phenotypes for a particular cross Homo or Homeo- same Homozygous- organism that has 2 identical alleles for a trait (ex. TT or tt) Hetero- different Heterozygous- organism that has 2 different alleles for a t ...
Dominance (genetics)

Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of one gene, in which the effect on phenotype of one allele masks the contribution of a second allele at the same locus. The first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. For genes on an autosome (any chromosome other than a sex chromosome), the alleles and their associated traits are autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Dominance is a key concept in Mendelian inheritance and classical genetics. Often the dominant allele codes for a functional protein whereas the recessive allele does not.A classic example of dominance is the inheritance of seed shape, for example a pea shape in peas. Peas may be round, associated with allele R or wrinkled, associated with allele r. In this case, three combinations of alleles (genotypes) are possible: RR, Rr, and rr. The RR individuals have round peas and the rr individuals have wrinkled peas. In Rr individuals the R allele masks the presence of the r allele, so these individuals also have round peas. Thus, allele R is dominant to allele r, and allele r is recessive to allele R. This use of upper case letters for dominant alleles and lower caseones for recessive alleles is a widely followed convention.More generally, where a gene exists in two allelic versions (designated A and a), three combinations of alleles are possible: AA, Aa, and aa. If AA and aa individuals (homozygotes) show different forms of some trait (phenotypes), and Aa individuals (heterozygotes) show the same phenotype as AA individuals, then allele A is said to dominate or be dominant to or show dominance to allele a, and a is said to be recessive to A.Dominance is not inherent to an allele. It is a relationship between alleles; one allele can be dominant over a second allele, recessive to a third allele, and codominant to a fourth. Also, an allele may be dominant for a particular aspect of phenotype but not for other aspects influenced by the same gene. Dominance differs from epistasis, a relationship in which an allele of one gene affects the expression of another allele at a different gene.