Chapter 16: The Evolution of Populations
... Single- Gene and Polygenetic traits 14. Is the following sentence true or false. ?The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends upon how many genes control the trait 15. Is the following sentence true or false? Most traits are controlled by a ...
... Single- Gene and Polygenetic traits 14. Is the following sentence true or false. ?The number of phenotypes produced for a given trait depends upon how many genes control the trait 15. Is the following sentence true or false? Most traits are controlled by a ...
7.1 Solutions File
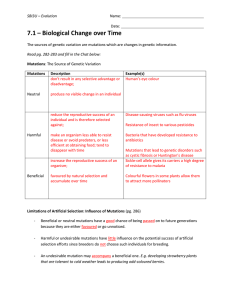
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
... The sources of genetic variation are mutations which are changes in genetic information. Read pg. 282-283 and fill in the Chat below: Mutations: The Source of Genetic Variation Mutations ...
Extending Mendelian Genetics for two or more genes
... Polygenic inheritance – an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character ...
... Polygenic inheritance – an additive effect of two or more genes on a single phenotypic character ...
Name
... _____ 17. If a mutation introduces a new skin color in a lizard population, which factor might determine whether the frequency of the new allele will increase? a. how many other alleles are present b. whether the mutation makes some lizards more fit for their environment than other lizards c. how ma ...
... _____ 17. If a mutation introduces a new skin color in a lizard population, which factor might determine whether the frequency of the new allele will increase? a. how many other alleles are present b. whether the mutation makes some lizards more fit for their environment than other lizards c. how ma ...
Evolution as Genetic Change
... o how does natural selection or change in allele frequencies result in speciation? o Species – a group of organisms that breed with one another and produce fertile offspring – share a common gene pool o Gene pools of two populations must become separated for them to become new species o REPRODUCTIV ...
... o how does natural selection or change in allele frequencies result in speciation? o Species – a group of organisms that breed with one another and produce fertile offspring – share a common gene pool o Gene pools of two populations must become separated for them to become new species o REPRODUCTIV ...
Spring Exam Study Guide 2015 answers
... 93. The Galapagos finch species are an excellent example of ____________________________. What is the definition of speciation? Speciation The evolutionary process by which a new species arises 94. The combined information of all members of a particular population is the population’s ___________ ...
... 93. The Galapagos finch species are an excellent example of ____________________________. What is the definition of speciation? Speciation The evolutionary process by which a new species arises 94. The combined information of all members of a particular population is the population’s ___________ ...
Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) Scents Colours
... Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) ...
... Natural products and ecological interactions Adaptive evolution (i.e. “rapid”) ...
History of Genetics - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... transcription separated from translation sexual reproduction: 2 partners contribute equally to offspring life cycle: alternation of haploid and diploid phases (i.e. 1 vs. 2 copies of each gene and chromosome) ...
... transcription separated from translation sexual reproduction: 2 partners contribute equally to offspring life cycle: alternation of haploid and diploid phases (i.e. 1 vs. 2 copies of each gene and chromosome) ...
Chapter 16
... • Genetic outcomes also can be unpredictable after a few individuals establish a new population – Seedling on birds • It is the effect of drift when a small number of individuals start a new population. • By chance, allele frequencies of founders may not be the same as those in the original ...
... • Genetic outcomes also can be unpredictable after a few individuals establish a new population – Seedling on birds • It is the effect of drift when a small number of individuals start a new population. • By chance, allele frequencies of founders may not be the same as those in the original ...
Detection of different genes heredity
... Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell ...
... Sickle-Cell Disease is a genetic disorder that affects the blood. People with sickle-cell disease produce an abnormal form of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Sickle-shaped red blood cells cannot carry as much oxygen as normal-shaped cells. The allele for the sickle-cell ...
This exam is worth 50 points Evolutionary Biology You may take this
... dominant over sour-puss (s), tall sail (T) was dominant over short (t), and white teeth (W) were dominant over yellow (w). Assuming that these genes assort independently, in a cross between a female dimetrodon homozygous dominant for all three traits and a male homozygous recessive for these same tr ...
... dominant over sour-puss (s), tall sail (T) was dominant over short (t), and white teeth (W) were dominant over yellow (w). Assuming that these genes assort independently, in a cross between a female dimetrodon homozygous dominant for all three traits and a male homozygous recessive for these same tr ...
review_for_final_exam_jan_2016
... discuss practical and ethical issues associated with genetic engineering 3. Genetics (chapters 10 and 14): ...
... discuss practical and ethical issues associated with genetic engineering 3. Genetics (chapters 10 and 14): ...
Evolution - Van Buren Public Schools
... shell, which is better for reaching sparse vegetation. The Isabella Island tortoise (right) has a domeshaped shell and shorter neck, which is better for the abundant, close vegetation. ...
... shell, which is better for reaching sparse vegetation. The Isabella Island tortoise (right) has a domeshaped shell and shorter neck, which is better for the abundant, close vegetation. ...
Level 2 Biology - No Brain Too Small
... the effect of crossing over and linked genes on dihybrid inheritance. Biological ideas and processes relating to factors affecting allele frequencies in a gene pool are selected from: ...
... the effect of crossing over and linked genes on dihybrid inheritance. Biological ideas and processes relating to factors affecting allele frequencies in a gene pool are selected from: ...
Level 2 Biology - No Brain Too Small
... the effect of crossing over and linked genes on dihybrid inheritance. Biological ideas and processes relating to factors affecting allele frequencies in a gene pool are selected from: ...
... the effect of crossing over and linked genes on dihybrid inheritance. Biological ideas and processes relating to factors affecting allele frequencies in a gene pool are selected from: ...
Unit 7 Review – DNA Replication, Gene Expression, and Gene
... location of various processes, molecules and enzymes involved, the role of basepairing rules, etc. How do we go from a gene to the expression of a phenotypic trait in a living organism? ...
... location of various processes, molecules and enzymes involved, the role of basepairing rules, etc. How do we go from a gene to the expression of a phenotypic trait in a living organism? ...
Evolution 2
... recombination of genes, gene flow and genetic drift can all lead to speciation. Three different types of populations may occur, they are referred to as ...
... recombination of genes, gene flow and genetic drift can all lead to speciation. Three different types of populations may occur, they are referred to as ...
The Evolution of Populations
... • Point mutations: changes in one base (eg. sickle cell) • Chromosomal mutations: delete, duplicate, disrupt, rearrange usually harmful • Sexual recombination: contributes to most of genetic variation in a population 1. Crossing Over (Meiosis – Prophase I) 2. Independent Assortment of Chromosomes ...
... • Point mutations: changes in one base (eg. sickle cell) • Chromosomal mutations: delete, duplicate, disrupt, rearrange usually harmful • Sexual recombination: contributes to most of genetic variation in a population 1. Crossing Over (Meiosis – Prophase I) 2. Independent Assortment of Chromosomes ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved i ...
... particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved i ...
Tigger/pogo transposons in the Fugu genome
... Another theme will be genome size, which involves a variety of effects. But we can think of two levels of analysis. First, there is the mechanistic question of why genomes get bigger or smaller. For example, they generally get bigger by accumulating many copies of pseudogenes or transposable elemen ...
... Another theme will be genome size, which involves a variety of effects. But we can think of two levels of analysis. First, there is the mechanistic question of why genomes get bigger or smaller. For example, they generally get bigger by accumulating many copies of pseudogenes or transposable elemen ...
BIOL 221-GENETICS
... 2. epistasis II. Genes on Chromosomes A. Evidence for genes on chromosomes 1. history of the question 2. white-eyed flies and sex determination B. Chromosomal results of mitosis and meiosis 1. events of mitosis and meiosis 2. meiosis and Mendelism C. Linkage and recombination 1. crossing over 2. det ...
... 2. epistasis II. Genes on Chromosomes A. Evidence for genes on chromosomes 1. history of the question 2. white-eyed flies and sex determination B. Chromosomal results of mitosis and meiosis 1. events of mitosis and meiosis 2. meiosis and Mendelism C. Linkage and recombination 1. crossing over 2. det ...
Natural Selection
... Main thesis: All species have descended from a common ancestor. As time went on, different lineages of organisms were modified with descent to adapt to their environments. Macroevolution is studied by examining patterns in biological populations and groups of related organisms and inferring proces ...
... Main thesis: All species have descended from a common ancestor. As time went on, different lineages of organisms were modified with descent to adapt to their environments. Macroevolution is studied by examining patterns in biological populations and groups of related organisms and inferring proces ...