The Fossil Record
... 1 teaspoon of soil ≈ 1 billion bacteria 1 billion bacteria ÷ 200 bacteria/1 mutation = ...
... 1 teaspoon of soil ≈ 1 billion bacteria 1 billion bacteria ÷ 200 bacteria/1 mutation = ...
2nd Semester Review The second semester test covers Meiosis
... Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
... Physiology: Digestive System, Circulatory System and Respiratory System, and Ecology. This list will help you prepare. You should also look over all the review documents that you have in your workbook for these units. ...
Name_____________________ Date__________ Class
... substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic mat ...
... substituted with (or exchanged for) a different nucleotide that may result in an altered sequence of amino acid during translation. occurs when a DNA gene is damaged or changed in such a way as to alter the genetic message carried by that gene. is a type of mutation involving the loss of genetic mat ...
Chapter 4 Heredity and Evolution
... Recessive conditions: cystic fibrosis, TaySachs disease, sickle cell anemia, and albinism. ...
... Recessive conditions: cystic fibrosis, TaySachs disease, sickle cell anemia, and albinism. ...
Lecture 2 PSY391S John Yeomans
... Why Use Genes? • Behavior = Genes <=> Environment • Psychologists have studied environmental effects on behavior best for a century. • Human genome project now gives us all the genes. What an opportunity! • Most of these genes are found in lower animals such as mice. • Behavioral effects of single ...
... Why Use Genes? • Behavior = Genes <=> Environment • Psychologists have studied environmental effects on behavior best for a century. • Human genome project now gives us all the genes. What an opportunity! • Most of these genes are found in lower animals such as mice. • Behavioral effects of single ...
Reproduction and Genetics Vocabulary
... a structure in the cell nucleus that has DNA; each chromosome has many genes ...
... a structure in the cell nucleus that has DNA; each chromosome has many genes ...
Station 2: Genetic Drift
... 2. If the amount of pollution decreased and the environment recovered, what effect would that have on the moth phenotype? ...
... 2. If the amount of pollution decreased and the environment recovered, what effect would that have on the moth phenotype? ...
1 - Spokane Public Schools
... c.) Fossils show a record of organisms in the past. A slow change in the fossils with many transitional forms as one moves upward through the sedimentary rock strata supports the concept of gradualism, while abrupt discontinuities in the fossil record are more supportive of the concept of punctuated ...
... c.) Fossils show a record of organisms in the past. A slow change in the fossils with many transitional forms as one moves upward through the sedimentary rock strata supports the concept of gradualism, while abrupt discontinuities in the fossil record are more supportive of the concept of punctuated ...
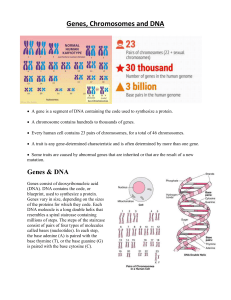
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A gene is a segment of DNA containing the code used to synthesize a protein. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more t ...
... A gene is a segment of DNA containing the code used to synthesize a protein. A chromosome contains hundreds to thousands of genes. Every human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more t ...
Pop.GeneticsandEvolution
... genes frequently move in and out of populations • Sometimes males will leave when they mature to form their own group ...
... genes frequently move in and out of populations • Sometimes males will leave when they mature to form their own group ...
All life is based on the same genetic code
... The increase is due at least in part to the age-related accumulation of The increase is due ...
... The increase is due at least in part to the age-related accumulation of The increase is due ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following statements are true or false ...
... II. State whether the following statements are true or false ...
Selective Breeding – the purposeful breeding of plants and animals
... breeding of plants and animals for specific traits. Evolution – gradual changes in a species over time, that leads to the development of new species. Competition – struggle for survival between members of the same species, as well as between different species. Homologous Structures – similar body st ...
... breeding of plants and animals for specific traits. Evolution – gradual changes in a species over time, that leads to the development of new species. Competition – struggle for survival between members of the same species, as well as between different species. Homologous Structures – similar body st ...
Evolution: A Change In A Population
... A. Population- a group of individuals belonging to the same species in a given area B. Species- group of populations whose individuals can interbreed and produce fertile offspring C. Population Genetics - study of kinds of number of genes in a populations D. Evolution- generation to generation chang ...
... A. Population- a group of individuals belonging to the same species in a given area B. Species- group of populations whose individuals can interbreed and produce fertile offspring C. Population Genetics - study of kinds of number of genes in a populations D. Evolution- generation to generation chang ...
Population Genetics - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 1) Large population 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
... 1) Large population 2) No mutation 3) No gene flow (no immigration or emigration) 4) Random mating (no mating preference for particular phenotype) 5) No natural selection (all genotypes have an = chance of surviving & reproducing) ...
Population Genetics - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... **So why study population genetics? Why use the H-W Theorem? 1) shows how genetics is related to evolution; 2) provides a benchmark genetic equilibrium against which change can be noted; 3) permits an estimation of gene frequencies; especially useful in estimating the number of carriers of lethal ...
... **So why study population genetics? Why use the H-W Theorem? 1) shows how genetics is related to evolution; 2) provides a benchmark genetic equilibrium against which change can be noted; 3) permits an estimation of gene frequencies; especially useful in estimating the number of carriers of lethal ...
Notes Unit 5 Part 2
... frequency of alleles for a population, then we say the population is ________________ or changing B. HOW Populations Evolve (Sources of Evolutionary Change): a. Natural Selection: evolution that occurs when _____________ selects the best _____________ individuals to survive If the ________________ ...
... frequency of alleles for a population, then we say the population is ________________ or changing B. HOW Populations Evolve (Sources of Evolutionary Change): a. Natural Selection: evolution that occurs when _____________ selects the best _____________ individuals to survive If the ________________ ...
Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as
... Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as one pair from each of our parents, which means that the sperm and egg receive 23 chromosomes through a complex process of cell division called as the meiosis. 2. Where is DNA found? Ans. Most of the DNA in a human cell is found in ...
... Ans. Our cell contains 23 pairs of chromosome and it is inherited as one pair from each of our parents, which means that the sperm and egg receive 23 chromosomes through a complex process of cell division called as the meiosis. 2. Where is DNA found? Ans. Most of the DNA in a human cell is found in ...
Evolution
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • Frequency of alleles in a stable population will not change over time – Very large population – Population is isolated – Mutations don’t alter gene pool – Random mating – All individuals are equal in reproductive success ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • Frequency of alleles in a stable population will not change over time – Very large population – Population is isolated – Mutations don’t alter gene pool – Random mating – All individuals are equal in reproductive success ...
Final Exam Review - Blue Valley Schools
... What is a homologous structure? How do homologous structures help support the idea of common ancestry? What is a vestigial structure? What do they tell us about the evolutionary history of organisms? Natural Selection How do we summarize natural selection? 1. Variation exists among individuals withi ...
... What is a homologous structure? How do homologous structures help support the idea of common ancestry? What is a vestigial structure? What do they tell us about the evolutionary history of organisms? Natural Selection How do we summarize natural selection? 1. Variation exists among individuals withi ...