Evolution
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • Frequency of alleles in a stable population will not change over time – Very large population – Population is isolated – Mutations don’t alter gene pool – Random mating – All individuals are equal in reproductive success ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium • Frequency of alleles in a stable population will not change over time – Very large population – Population is isolated – Mutations don’t alter gene pool – Random mating – All individuals are equal in reproductive success ...
Introduction to BST775: Statistical Methods for Genetic Analysis I
... • Types of DNA variation • The process of gene mapping • Types of studies ...
... • Types of DNA variation • The process of gene mapping • Types of studies ...
Genetic Variation within Populations
... A man spoke frantically into the phone, "My wife is pregnant and her contractions are only two minutes apart!" "Is this her first child?" the doctor asked. "No!" the man shouted, "This is her husband!" ...
... A man spoke frantically into the phone, "My wife is pregnant and her contractions are only two minutes apart!" "Is this her first child?" the doctor asked. "No!" the man shouted, "This is her husband!" ...
Evolution of populations
... b. amino acid Δ makes no difference 4. may be beneficial or detrimental 5. may be lethal ...
... b. amino acid Δ makes no difference 4. may be beneficial or detrimental 5. may be lethal ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... sequences that detect the complementary base sequences found in the disease- causing allele ...
... sequences that detect the complementary base sequences found in the disease- causing allele ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
Mossburg AP Biology Unit 2 Test Review
... 7. Given the calculations from question #4, what is the frequency of the homozygous recessive individuals in the population? Homozygous dominate? Heterozygous? 8. ___________ are selected for and ___________ evolve in the process of evolution. 9. Explain the five agents of evolutionary change. 10. W ...
... 7. Given the calculations from question #4, what is the frequency of the homozygous recessive individuals in the population? Homozygous dominate? Heterozygous? 8. ___________ are selected for and ___________ evolve in the process of evolution. 9. Explain the five agents of evolutionary change. 10. W ...
Natural Selection Essential Questions
... Many different organisms increase the ________________ that at least some will survive a major environmental ________________ Many organisms increase the “________________” that NATURE “________________” from 17. What is gene flow? The movement of ________________ from one ________________ to ...
... Many different organisms increase the ________________ that at least some will survive a major environmental ________________ Many organisms increase the “________________” that NATURE “________________” from 17. What is gene flow? The movement of ________________ from one ________________ to ...
23.4 a closer look at natural selection
... cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest natural selection? ...
... cline. What external factors might produce a cline? Why does the existence of a cline suggest natural selection? ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
Practice final exam
... 12. Microevolution, or evolution at its smallest scale, occurs when a. an individual's traits change in response to environmental factors. b. a community of organisms changes due to the extinction of several dominant species. c. a new species arises from an existing species. d. a population's allele ...
... 12. Microevolution, or evolution at its smallest scale, occurs when a. an individual's traits change in response to environmental factors. b. a community of organisms changes due to the extinction of several dominant species. c. a new species arises from an existing species. d. a population's allele ...
Ecology
... Factors that restrict the process of natural selection, and why they do. How genetic variation is maintained in populations, and why small populations are of particular concern in that regard. Evidence that is necessary for us to conclude that: 1) evolution has occurred; 2) natural selection has occ ...
... Factors that restrict the process of natural selection, and why they do. How genetic variation is maintained in populations, and why small populations are of particular concern in that regard. Evidence that is necessary for us to conclude that: 1) evolution has occurred; 2) natural selection has occ ...
There is no scantron with the webpage version of the THQ. Mark
... frequencies have high fitness, the result is a. directional selection. b. stabilizing selection. c. disruptive selection d. genetic drift Figure 17–2 shows highest fitness toward the center of the curve. When individuals with an average form of a trait have the highest fitness, the result is a. not ...
... frequencies have high fitness, the result is a. directional selection. b. stabilizing selection. c. disruptive selection d. genetic drift Figure 17–2 shows highest fitness toward the center of the curve. When individuals with an average form of a trait have the highest fitness, the result is a. not ...
Microevolution: Unique Gene Pools
... black coat color and b for white coat color. • Selection acts on phenotype because differential reproduction and success depends on phenotype not genotype. • Natural selection “selects”/”favors” individuals, but only populations evolve. ...
... black coat color and b for white coat color. • Selection acts on phenotype because differential reproduction and success depends on phenotype not genotype. • Natural selection “selects”/”favors” individuals, but only populations evolve. ...
Insects and genetics
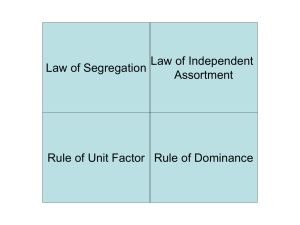
... 5. Mendel's law of segregation states that alternative forms of a particular factor (gene) remain discrete during the reproductive process; his second law, the law of independent_ assortment, states that different factors are inherited independently of one another. 6. Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan? Use ...
... 5. Mendel's law of segregation states that alternative forms of a particular factor (gene) remain discrete during the reproductive process; his second law, the law of independent_ assortment, states that different factors are inherited independently of one another. 6. Who was Thomas Hunt Morgan? Use ...
Chapter 17 Review ppt
... is reduced to one tenth of its original number. By chance, the average moose that remain are larger than the average moose in the original population. This change in the population’s gene pool is known as the bottleneck effect ...
... is reduced to one tenth of its original number. By chance, the average moose that remain are larger than the average moose in the original population. This change in the population’s gene pool is known as the bottleneck effect ...
Chapter 23.1 Questions 1. Define microevolution. 2. What are the
... 2. Chance events that cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from one ...
... 2. Chance events that cause allele frequencies to fluctuate unpredictably from one ...
History of Genetics
... • (almost) all inheritance is based on DNA: the sequence of ACGT nucleotides encodes all instructions needed to build and maintain an organism. • A chromosome is a single DNA molecule together with other molecules (proteins and RNA) needed to support and read the DNA. • A gene is a specific region o ...
... • (almost) all inheritance is based on DNA: the sequence of ACGT nucleotides encodes all instructions needed to build and maintain an organism. • A chromosome is a single DNA molecule together with other molecules (proteins and RNA) needed to support and read the DNA. • A gene is a specific region o ...
Glossary of Genetic Terms
... Cloned DNA -- any DNA fragment that passively replicates in the host organism after it has been joined to a cloning vector. Deletion -- the loss of a segment of the genetic material from a chromosome. Deletion mapping -- the use of overlapping deletions to localize the position of an unknown gene on ...
... Cloned DNA -- any DNA fragment that passively replicates in the host organism after it has been joined to a cloning vector. Deletion -- the loss of a segment of the genetic material from a chromosome. Deletion mapping -- the use of overlapping deletions to localize the position of an unknown gene on ...
Slides
... Non-adaptive Evolution: Gene Flow Gene Flow • Transfer of alleles from one population to ...
... Non-adaptive Evolution: Gene Flow Gene Flow • Transfer of alleles from one population to ...
Diversity of Life
... characteristics and can interbreed with one another to produce fertile offspring. • Species that interbreed share a common gene pool (all genes, including all the different alleles, of all of the individuals in a population). • Because of the shared gene pool, a genetic change that occurs in one ind ...
... characteristics and can interbreed with one another to produce fertile offspring. • Species that interbreed share a common gene pool (all genes, including all the different alleles, of all of the individuals in a population). • Because of the shared gene pool, a genetic change that occurs in one ind ...