here - WordPress.com
... Both versions of adaptationism have been resoundingly rejected by modern evolutionary biologists. Due to their intuitive appeal, constant policing is required on this front, especially in the social sciences. - Darwinian evolution: the primary mechanism to explain most or all adaptation (i.e. match ...
... Both versions of adaptationism have been resoundingly rejected by modern evolutionary biologists. Due to their intuitive appeal, constant policing is required on this front, especially in the social sciences. - Darwinian evolution: the primary mechanism to explain most or all adaptation (i.e. match ...
POPULATION GENETICS Learning Objectives • Define Population
... constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences. ...
... constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences. ...
0.-intro-to-biopsych..
... left temporal lobe impact behavior and/or cognitive functioning Neuroscience: interdisciplinary study brain relationship to psychological processes ◦ Key difference: interdisciplinary (may involve computer science, chemists, linguists, anthropologists, etc ...
... left temporal lobe impact behavior and/or cognitive functioning Neuroscience: interdisciplinary study brain relationship to psychological processes ◦ Key difference: interdisciplinary (may involve computer science, chemists, linguists, anthropologists, etc ...
Chapter 27: Evolution of Life
... Genetic drift refers to changes in allele frequencies of a gene pool due to chance; genetic drift has a much larger effect in a small population. The founder effect occurs when a few individuals leave the original population and begin a new population. A bottleneck effect is seen when much of a popu ...
... Genetic drift refers to changes in allele frequencies of a gene pool due to chance; genetic drift has a much larger effect in a small population. The founder effect occurs when a few individuals leave the original population and begin a new population. A bottleneck effect is seen when much of a popu ...
lesson Plans - Lemon Bay High School
... and artificial selection on the conclusions and answer genetic makeup of a ...
... and artificial selection on the conclusions and answer genetic makeup of a ...
Natural Selection
... Artificial Selection: the process by which humans change a species by breeding it for ...
... Artificial Selection: the process by which humans change a species by breeding it for ...
Goal 3
... Mutations are changes in DNA coding and can be deletions, additions, or substitutions. Mutations can be random and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or chemical exposure. Describe how mutations change amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) ...
... Mutations are changes in DNA coding and can be deletions, additions, or substitutions. Mutations can be random and spontaneous or caused by radiation and/or chemical exposure. Describe how mutations change amino acid sequence, protein function, phenotype. Only mutations in sex cells (egg and sperm) ...
Gene Technology - Manasquan Public Schools
... An average adult male liger can weigh over 900 pounds. An adult male Siberian tiger can grow to an average weight of 500 pounds, An adult African lion can average 450 pounds. The reproductive process that creates a liger leaves out the growth inhibitor gene present in the male lion and the female ti ...
... An average adult male liger can weigh over 900 pounds. An adult male Siberian tiger can grow to an average weight of 500 pounds, An adult African lion can average 450 pounds. The reproductive process that creates a liger leaves out the growth inhibitor gene present in the male lion and the female ti ...
Chapter 23 Notes
... • Uses population genetics as the means to track and study evolution. • Looks at the genetic basis of variation and natural selection. ...
... • Uses population genetics as the means to track and study evolution. • Looks at the genetic basis of variation and natural selection. ...
Speciation - WordPress.com
... neighbouring populations • Gene mutations occur at a constant and low rate, some are beneficial and result in increasing the organisms reproductive success. This mutation will therefore be passed on. • An accumulation of mutations can occur, which could mean that if the population was reintroduced t ...
... neighbouring populations • Gene mutations occur at a constant and low rate, some are beneficial and result in increasing the organisms reproductive success. This mutation will therefore be passed on. • An accumulation of mutations can occur, which could mean that if the population was reintroduced t ...
Natural Selection
... a. Some individuals are more “fit” for the environment or for life in general ex. Resistance to disease ...
... a. Some individuals are more “fit” for the environment or for life in general ex. Resistance to disease ...
Modern Genetics Notes
... Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes are called autosomes. The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosomes, which are indicated by X for females and Y for males. ...
... Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. 22 pairs of homologous chromosomes are called autosomes. The 23rd pair is called the sex chromosomes, which are indicated by X for females and Y for males. ...
Population - Perry Local Schools
... • Uses population genetics as the means to track and study evolution. • Looks at the genetic basis of variation and natural selection. ...
... • Uses population genetics as the means to track and study evolution. • Looks at the genetic basis of variation and natural selection. ...
01 Microevolution Unique Gene Pools and
... Genes can be duplicated and occasionally the duplication moves a gene from one chromosome to another. Each gene will accumulate different mutations altering the protein that is subsequently synthesized. Myoglobin is a protein that binds with oxygen in the muscles. This gene has been duplicated and m ...
... Genes can be duplicated and occasionally the duplication moves a gene from one chromosome to another. Each gene will accumulate different mutations altering the protein that is subsequently synthesized. Myoglobin is a protein that binds with oxygen in the muscles. This gene has been duplicated and m ...
Gene pool
... of all known animals, and I have taken some pains to estimate its probable minimum rate of natural increase: it will be under the mark to assume that it breeds when thirty years old, and goes on breeding till ninety years old, bringing forth three pairs of young in this interval; if this be so, at t ...
... of all known animals, and I have taken some pains to estimate its probable minimum rate of natural increase: it will be under the mark to assume that it breeds when thirty years old, and goes on breeding till ninety years old, bringing forth three pairs of young in this interval; if this be so, at t ...
1. Two subfields of cultural anthropology include
... Matching People (2 pts each) Match the following individuals with their related theories and/or ideas. Each has only one correct response. 21. Georges Cuvier ...
... Matching People (2 pts each) Match the following individuals with their related theories and/or ideas. Each has only one correct response. 21. Georges Cuvier ...
Slide 1
... reaction to the environment. When it changes or a new environment becomes available, which individuals are most fit will also change. There is no planning by individual organisms or populations. Things change accidentally, then the best of those accidents stick around through generations because the ...
... reaction to the environment. When it changes or a new environment becomes available, which individuals are most fit will also change. There is no planning by individual organisms or populations. Things change accidentally, then the best of those accidents stick around through generations because the ...
Student notes for selection lecture
... What are their five conditions for equilibrium? Give examples of what can happen if they are disrupted. Stress to the students that Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium is only achieved if: 1. No net mutations occur; alleles remain the same If there are mutations totally new alleles are produced in a popula ...
... What are their five conditions for equilibrium? Give examples of what can happen if they are disrupted. Stress to the students that Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium is only achieved if: 1. No net mutations occur; alleles remain the same If there are mutations totally new alleles are produced in a popula ...
Human Growth and Development Genetics
... person’s ability to learn something and then apply this knowledge to new problems and experiences. ...
... person’s ability to learn something and then apply this knowledge to new problems and experiences. ...
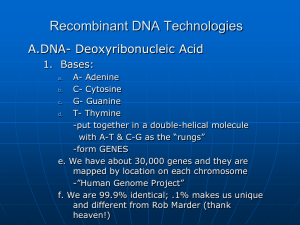
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... 1. Organisms with foreign DNA spliced into it 2. Examples: a. Bacteria- make chemicals that we need 1) insulin (rather than from a dead pig’s organ) 2) fertilizers 3) hormones 4) nutrasweet (phenylalanine- watch out PKU people) 5) Spider silk for manufacturing b. Plants 1) Resist frost (Arctic floun ...
... 1. Organisms with foreign DNA spliced into it 2. Examples: a. Bacteria- make chemicals that we need 1) insulin (rather than from a dead pig’s organ) 2) fertilizers 3) hormones 4) nutrasweet (phenylalanine- watch out PKU people) 5) Spider silk for manufacturing b. Plants 1) Resist frost (Arctic floun ...
Microevolution involves the evolutionary changes within a population.
... therefore called directional selection. ...
... therefore called directional selection. ...
People Pieces
... sequences. The genome is the entire DNA of an organism. In 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed. This provided the actual sequence, or spelling, of the human DNA. Research is continuing to understand the actual details of the genes, as well as the function of each gene. Researchers are ...
... sequences. The genome is the entire DNA of an organism. In 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed. This provided the actual sequence, or spelling, of the human DNA. Research is continuing to understand the actual details of the genes, as well as the function of each gene. Researchers are ...
“What is that, where is it found and why can it live there
... Characteristics are passed on from one generation to the next. In sexual reproduction both parents contribute to the features of the offspring. Information, embedded in the DNA molecules that make up the chromosomes in the sperm and ovum nuclei, determines these features through the production of sp ...
... Characteristics are passed on from one generation to the next. In sexual reproduction both parents contribute to the features of the offspring. Information, embedded in the DNA molecules that make up the chromosomes in the sperm and ovum nuclei, determines these features through the production of sp ...
Final Exam Review Donnelly Part Answers
... also have a higher resistance to malaria than do people with normal red blood cells. Limits of natural selection 1. Selection can only act on existing variation in a population. 2. Evolution is limited by historical constraints. 3. Adaptations are usually compromises. 4. Natural selection interacts ...
... also have a higher resistance to malaria than do people with normal red blood cells. Limits of natural selection 1. Selection can only act on existing variation in a population. 2. Evolution is limited by historical constraints. 3. Adaptations are usually compromises. 4. Natural selection interacts ...