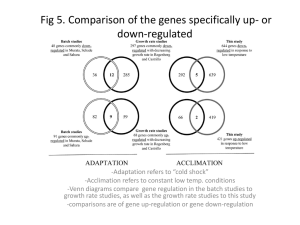
Genetics Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle Across
... 2. the division of sex cells (results in 4 different haploid cells) 3. this type of reproduction involves 2 parents 4. a variety of different genes and traits 5. location on a chromosome that codes for a certain trait 7. _____ chromosomes are chromosome pairs, one from each parent, that are similar ...
... 2. the division of sex cells (results in 4 different haploid cells) 3. this type of reproduction involves 2 parents 4. a variety of different genes and traits 5. location on a chromosome that codes for a certain trait 7. _____ chromosomes are chromosome pairs, one from each parent, that are similar ...
Evolution as Genetic Change
... effects on phenotypes. Each of these can be represented by the type of curve that would result from a graph. 1. Directional selection- individuals at one end have higher fitness than those in the middle or at the opposite end. 2. Stabilizing selection- individuals in the center have greater fitness ...
... effects on phenotypes. Each of these can be represented by the type of curve that would result from a graph. 1. Directional selection- individuals at one end have higher fitness than those in the middle or at the opposite end. 2. Stabilizing selection- individuals in the center have greater fitness ...
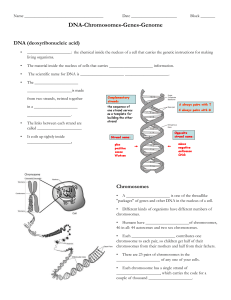
DNA-Chromosomes-Genes-Genome student notesheet
... • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
... • Each chromosome has a single strand of _____________________, which carries the code for a couple of thousand _____________________. ...
Notes Unit 4 Part 8
... if the mutation occurs in ____________, birth defects can occur if the mutation occurs in ____________, cancer may occur mutagens = factors in the _______________ that cause mutations to occur e.g. carcinogen = mutagens that specifically cause _________ e.g. Types of Mutations: A. Gene Mutat ...
... if the mutation occurs in ____________, birth defects can occur if the mutation occurs in ____________, cancer may occur mutagens = factors in the _______________ that cause mutations to occur e.g. carcinogen = mutagens that specifically cause _________ e.g. Types of Mutations: A. Gene Mutat ...
Lesson 5 Mechanisms of evolution - Blyth-Biology11
... • Not all evolutionary changes are the result of natural selection • Evolution can occur due to catastrophic events • Mutation is the ultimate source of variation in an individual’s gene pool ...
... • Not all evolutionary changes are the result of natural selection • Evolution can occur due to catastrophic events • Mutation is the ultimate source of variation in an individual’s gene pool ...
GENETIC VARIATION - anderson1.k12.sc.us
... Population: group of individuals of same species that live in same area ...
... Population: group of individuals of same species that live in same area ...
Document
... three. Create a phylogenetic tree to represent the relationship between these species. ...
... three. Create a phylogenetic tree to represent the relationship between these species. ...
Study guide key - Mayfield City Schools
... the change in allele frequencies that occur over time within a population 2. What is macroevolution? evolution on a scale of separated gene pools. Macroevolutionary studies focus on change that occurs at or above the level of species, in contrast with microevolution, which refers to smaller evolutio ...
... the change in allele frequencies that occur over time within a population 2. What is macroevolution? evolution on a scale of separated gene pools. Macroevolutionary studies focus on change that occurs at or above the level of species, in contrast with microevolution, which refers to smaller evolutio ...
Modeling Multiple-Allele Genes in NetLogo
... Modeling Multiple-Allele Genes in NetLogo By Max Harmony and Haven Mills Jim Lyons, mentor ...
... Modeling Multiple-Allele Genes in NetLogo By Max Harmony and Haven Mills Jim Lyons, mentor ...
Lecture Six: Causes of Evolution
... Somewhere in ancient West Africa, a mutation of the gene coding for normal hemoglobin (in humans) occurred. It was recessive. We'll call it h, and the normal version of the gene is H. If two copies of the mutant gene are inherited, the person getting those copies will have a disease called Sickle Ce ...
... Somewhere in ancient West Africa, a mutation of the gene coding for normal hemoglobin (in humans) occurred. It was recessive. We'll call it h, and the normal version of the gene is H. If two copies of the mutant gene are inherited, the person getting those copies will have a disease called Sickle Ce ...
Genetic Engineering II
... particular piece of DNA in the test tube (rather than in living cells like E. coli). • Very useful if only have small quantities such as blood or semen. • Use temperature changes to separate the DNA strand, add primers, polymerase and ta-dah... new strand is made. ...
... particular piece of DNA in the test tube (rather than in living cells like E. coli). • Very useful if only have small quantities such as blood or semen. • Use temperature changes to separate the DNA strand, add primers, polymerase and ta-dah... new strand is made. ...
Unit Four
... However, the only thing that stays the same is that the environment changes The abiotic changes in the environment make it more likely for species mutations to be demonstrated in the population ...
... However, the only thing that stays the same is that the environment changes The abiotic changes in the environment make it more likely for species mutations to be demonstrated in the population ...
Chapter 6 Notes--EVOLUTION
... (ie: Mattson makes up a population, City of Kent makes up a population) ...
... (ie: Mattson makes up a population, City of Kent makes up a population) ...
ch 16 notes mader
... d. Assortative mating divides a population into two phenotypic classes with reduced gene exchange. e. Homozygotes for gene loci that control a trait increase, and heterozygotes for these loci decrease. f. Gene flow (gene migration) is the movement of alleles among populations by migration of breedin ...
... d. Assortative mating divides a population into two phenotypic classes with reduced gene exchange. e. Homozygotes for gene loci that control a trait increase, and heterozygotes for these loci decrease. f. Gene flow (gene migration) is the movement of alleles among populations by migration of breedin ...
Chapter 16
... than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population. ...
... than other individuals, just by chance. Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population. ...
G - bellevuebiology
... – Most mutations produce genes that are neutral (neither helpful nor harmful) – Very, very few mutations produce genes that are advantageous ...
... – Most mutations produce genes that are neutral (neither helpful nor harmful) – Very, very few mutations produce genes that are advantageous ...
Vocab table - Genetics and variation teacher
... A mutation in a chromosome where a section is removed, or in a gene, where one of the bases is removed from the sequence ...
... A mutation in a chromosome where a section is removed, or in a gene, where one of the bases is removed from the sequence ...
Chapter 12 SWBAT`s and Standards
... What did scientists discover about the relationship between genes and DNA? What is the overall structure of the DNA molecule? What happens during DNA replication? What are the three main types of RNA? What is transcription? What is translation? ...
... What did scientists discover about the relationship between genes and DNA? What is the overall structure of the DNA molecule? What happens during DNA replication? What are the three main types of RNA? What is transcription? What is translation? ...
Microevolution - Cloudfront.net
... - genetic variation - “raw materials of natural selection -unpredictable in nature -Doesn’t determine the direction of evolution -causes small changes in allele frequencies Approx. Mutation rate: One in every 100,000 genes per generation ...
... - genetic variation - “raw materials of natural selection -unpredictable in nature -Doesn’t determine the direction of evolution -causes small changes in allele frequencies Approx. Mutation rate: One in every 100,000 genes per generation ...
Unit VII Objectives Biotechnology
... bioinformatics, and genomics. 2. What is meant by the universality of the genetic code? 3. Define polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Describe what is needed for PCR to happen, its process of DNA amplification, and list several uses. 4. Describe the process of gel electrophoresis and how it is used. 5. ...
... bioinformatics, and genomics. 2. What is meant by the universality of the genetic code? 3. Define polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Describe what is needed for PCR to happen, its process of DNA amplification, and list several uses. 4. Describe the process of gel electrophoresis and how it is used. 5. ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... Mechanisms of Evolution a. Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring b. Population: a group of interbreeding species occupying a particular area c. Evolution is simply a change in the frequency of genes in a population. Evolution occurs by Natural Selection. Nat ...
... Mechanisms of Evolution a. Species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring b. Population: a group of interbreeding species occupying a particular area c. Evolution is simply a change in the frequency of genes in a population. Evolution occurs by Natural Selection. Nat ...