Darwin and His Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
... 1) Mutations- changes in the DNA sequence can result in new traits 2) Sexual Reproduction- New combinations of traits can be created in gametes due to crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis. The wide variety of gametes created will join together to make diverse offspring. ...
... 1) Mutations- changes in the DNA sequence can result in new traits 2) Sexual Reproduction- New combinations of traits can be created in gametes due to crossing over and independent assortment during meiosis. The wide variety of gametes created will join together to make diverse offspring. ...
Nutrition and Gene Expression Jan 29, 2015
... Problems in newborns from simple mutations are less common. The mutation rate is very low: the genes that a child inherits usually only differ at about 100 base pairs, from the genes in the parental DNA. Most of those sequence changes are harmless. ...
... Problems in newborns from simple mutations are less common. The mutation rate is very low: the genes that a child inherits usually only differ at about 100 base pairs, from the genes in the parental DNA. Most of those sequence changes are harmless. ...
Molecular Genetics Outcome Checklist
... _____ I can explain how, in general, restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology ca ...
... _____ I can explain how, in general, restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules into smaller fragments based on a specific nucleotide sequence, leaving “sticky ends”. _____ I understand the purpose and function of ligases. _____ I can explain how restriction enzymes, ligases, and other DNA technology ca ...
PPT file - University of Evansville Faculty Web sites
... Eukaryotes Linkage and genetic diversity ...
... Eukaryotes Linkage and genetic diversity ...
Classification: What`s in a Name
... Taxon - a group of organisms at any particular level in this system ...
... Taxon - a group of organisms at any particular level in this system ...
1 - Genetic Alliance
... The human genome (total composition of genetic material within a cell) is packaged into larger units known as chromosomes—physically separate molecules that range in length from about 50 million to 250 million base pairs. Human cells contain two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each paren ...
... The human genome (total composition of genetic material within a cell) is packaged into larger units known as chromosomes—physically separate molecules that range in length from about 50 million to 250 million base pairs. Human cells contain two sets of chromosomes, one set inherited from each paren ...
Ch 2-6
... What is a dichotomous key? An aid that is used to identify organisms and that consist of the answers to a series of questions. Define adaptation. Characteristics that improve an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment. What are the 3 kinds of adaptations? 1. Obtaini ...
... What is a dichotomous key? An aid that is used to identify organisms and that consist of the answers to a series of questions. Define adaptation. Characteristics that improve an individual’s ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment. What are the 3 kinds of adaptations? 1. Obtaini ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. The likelihood that an event may or may not take place is called probability. 12. What is the probability that a child w ...
... 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. The likelihood that an event may or may not take place is called probability. 12. What is the probability that a child w ...
Section B: Causes of Microevolution CHAPTER 23 THE
... individuals in a larger population are drastically reduced by a disaster. • By chance, some alleles may be overrepresented and others underrepresented among the survivors. • Some alleles may be eliminated altogether. • Genetic drift will continue to impact the gene pool until the population is large ...
... individuals in a larger population are drastically reduced by a disaster. • By chance, some alleles may be overrepresented and others underrepresented among the survivors. • Some alleles may be eliminated altogether. • Genetic drift will continue to impact the gene pool until the population is large ...
Organismal Biology/23B-CausesOfMicroevolution
... generation until the population grew large enough for sampling errors to be minimal. • Founder effects have been demonstrated in human populations that started from a small group of colonists. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... generation until the population grew large enough for sampling errors to be minimal. • Founder effects have been demonstrated in human populations that started from a small group of colonists. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
If you have BRCA in the family (England and Wales)
... Genetic Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations: “Genetic testing will be offered in specialist genetic clinics to a person with no personal history of breast or ovarian cancer if their combined BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carrier probability is 10% or more and an affected relative is unavailable for tes ...
... Genetic Testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations: “Genetic testing will be offered in specialist genetic clinics to a person with no personal history of breast or ovarian cancer if their combined BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carrier probability is 10% or more and an affected relative is unavailable for tes ...
Evolution as Genetic Change
... Evolution as Genetic Change • Natural selection acts on phenotypes, survival and reproduction determine which alleles are inherited, changing relative frequencies of alleles in a population over time. • Thus evolution is any change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a population’s gene pool ...
... Evolution as Genetic Change • Natural selection acts on phenotypes, survival and reproduction determine which alleles are inherited, changing relative frequencies of alleles in a population over time. • Thus evolution is any change in the relative frequencies of alleles in a population’s gene pool ...
ppt version
... The environment presents many different challenges to an individual’s ability to reproduce Organisms tend to produce more offspring than their environment can support; thus, individuals of a species often compete with one another to survive Individuals within a population that are better able to cop ...
... The environment presents many different challenges to an individual’s ability to reproduce Organisms tend to produce more offspring than their environment can support; thus, individuals of a species often compete with one another to survive Individuals within a population that are better able to cop ...
ANTHR1 - Physical Anthropology
... b. ribosomes d. alleles 19. Without considering the use of drugs, in a malarial environment, which hemoglobin genotype would provide the LEAST resistance to malaria? a. AA c. SS b. AS d. AS and SS 20. Ribosomes are important because they a. are the cell's energy centers c. make DNA b. convert food i ...
... b. ribosomes d. alleles 19. Without considering the use of drugs, in a malarial environment, which hemoglobin genotype would provide the LEAST resistance to malaria? a. AA c. SS b. AS d. AS and SS 20. Ribosomes are important because they a. are the cell's energy centers c. make DNA b. convert food i ...
THINK ABOUT THESE………………
... Can you be certain of the genotype of individual 5 in Figure 14–13? Explain. Most likely homozygous dominant because if he were heterozygous we would expect half of the offspring to have attached ...
... Can you be certain of the genotype of individual 5 in Figure 14–13? Explain. Most likely homozygous dominant because if he were heterozygous we would expect half of the offspring to have attached ...
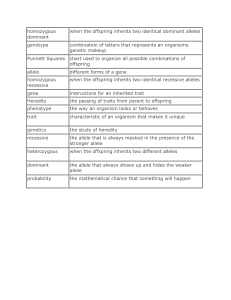
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
Genetics review sheet VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary
... VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary section will be fill in the blank with a word bank 1. gene ...
... VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary section will be fill in the blank with a word bank 1. gene ...
Gene Frequency and Natural Selection
... was very small, only at about 4%. Through each generation the mutation escalates all the way to 32% in the fifth generation. We ran out of time to complete the 6th generation, but my guess is that the mutation would have increased about 5%. As you can see, as the trait BB increases, the other traits ...
... was very small, only at about 4%. Through each generation the mutation escalates all the way to 32% in the fifth generation. We ran out of time to complete the 6th generation, but my guess is that the mutation would have increased about 5%. As you can see, as the trait BB increases, the other traits ...
Natural Selection - Unit Timeline
... and composition of a prey population • Predict potential changes in a prey population over successive generations • Collect and analyze data to test predictions • Express ratios and use graphs to represent the data gathered during the simulations ...
... and composition of a prey population • Predict potential changes in a prey population over successive generations • Collect and analyze data to test predictions • Express ratios and use graphs to represent the data gathered during the simulations ...
Document
... of genes on different chromosomes – the effect of the traits may be additive or pleiotrophic – skin color is additive with at least 3 genes inherited on 3 different locus and different genes – gives us a distribution of skin color instead of dark brown, tan, or white ...
... of genes on different chromosomes – the effect of the traits may be additive or pleiotrophic – skin color is additive with at least 3 genes inherited on 3 different locus and different genes – gives us a distribution of skin color instead of dark brown, tan, or white ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 13. What is the probability that a child will be male? 50% or 1 in 2 14. In a punnett square, what does each square represent? possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross 15. Visible characteristics are called traits (I would also accept phenotype). 16. The actual gene make ...
... 13. What is the probability that a child will be male? 50% or 1 in 2 14. In a punnett square, what does each square represent? possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross 15. Visible characteristics are called traits (I would also accept phenotype). 16. The actual gene make ...