Final Exam Review Sheet
... 2. Humans are now eating food from genetically modified organisms (GMOs), particularly from plants. Give five examples in which you identify the genetically engineered plant, the altered trait, and the gene construction responsible for this trait. List any concerns that opponents have expressed with ...
... 2. Humans are now eating food from genetically modified organisms (GMOs), particularly from plants. Give five examples in which you identify the genetically engineered plant, the altered trait, and the gene construction responsible for this trait. List any concerns that opponents have expressed with ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur ...
... Probability • Probability: the likelihood that an event will occur • i.e.: coin flip = ½ or 50% • Determined by: • Probability = # times expected to occur ...
Human Genetics
... Examples: Tongue rolling Earlobes Widow’s Peak Hair Whorl Dimples ...
... Examples: Tongue rolling Earlobes Widow’s Peak Hair Whorl Dimples ...
Genetics Objectives/keywords
... Genes allow for the storage and transmission of genetic information. They are a set of instructions encoded in the nucleotide sequence of each organism. Genes code for the specific sequences of amino acids that comprise the proteins that are characteristic of that organism. MA Standard 3.4 Distingui ...
... Genes allow for the storage and transmission of genetic information. They are a set of instructions encoded in the nucleotide sequence of each organism. Genes code for the specific sequences of amino acids that comprise the proteins that are characteristic of that organism. MA Standard 3.4 Distingui ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... EQ: What are some of the common disorders associated with the human ...
... EQ: What are some of the common disorders associated with the human ...
Discovery of DNA
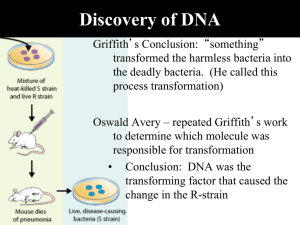
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
... Discovery of DNA Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase • Question: Are genes made of DNA or proteins? • What they knew: viruses use other organisms to reproduce Viruses only contain DNA and a protein coat. Whichever virus particle enters the cell must be the material that makes up genes (DNA). ...
Lecture 13
... ‘markers’---an array of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that characterize that region and which are frequently found in association with each other in the breeding population. The term “single nucleotide polymorphism” refers to the situation where, at a single specific nucleotide site on the ...
... ‘markers’---an array of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that characterize that region and which are frequently found in association with each other in the breeding population. The term “single nucleotide polymorphism” refers to the situation where, at a single specific nucleotide site on the ...
Final Exam Review
... Name the base that “replaces” thymine in RNA. What is transcription (describe this process)? Where in the cell does it occur? What is translation – describe this process (initiation, elongation, and termination)? Where in the cell does it occur? Chapter 17 Microevolution Define gene pool, microevolu ...
... Name the base that “replaces” thymine in RNA. What is transcription (describe this process)? Where in the cell does it occur? What is translation – describe this process (initiation, elongation, and termination)? Where in the cell does it occur? Chapter 17 Microevolution Define gene pool, microevolu ...
Slide 1
... Recessive mutation of NDP gene (X chromosome) Gene product = ‘Norrin’ is a secreted protein that is believed to affect development and maintenance of the retina (especially providing blood supply to retina). 70% are point mutations at various places in gene. Use SSCP (Single Stranded Conformation Po ...
... Recessive mutation of NDP gene (X chromosome) Gene product = ‘Norrin’ is a secreted protein that is believed to affect development and maintenance of the retina (especially providing blood supply to retina). 70% are point mutations at various places in gene. Use SSCP (Single Stranded Conformation Po ...
Genetics Study Guide
... How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
... How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE
... AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
... AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 16 OUTLINE THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE I. DNA AS THE GENETIC MATERIAL A. The search for the genetic material led to DNA: science as a process Proteins were thought to be the genetic material because: ...
Lecture 14 pdf - Institute for Behavioral Genetics
... 3. Too small a sample size Need <500,000 SNPs, <10,000 sample size to reliably detect associations ...
... 3. Too small a sample size Need <500,000 SNPs, <10,000 sample size to reliably detect associations ...
A Lite Introduction toComparative Genomics
... • SNP: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism - change in one base between two instances of the same gene • Used as genetic flags to identify traits, esp. for genetic diseases • CG goal: Identify as many SNPs as possible • Challenges – Data: need sequenced genomes from many humans along with information abo ...
... • SNP: Single Nucleotide Polymorphism - change in one base between two instances of the same gene • Used as genetic flags to identify traits, esp. for genetic diseases • CG goal: Identify as many SNPs as possible • Challenges – Data: need sequenced genomes from many humans along with information abo ...
Study Guide for Ch 5 (sec 3) and Ch 6
... 43. List the 3 kinds of mutations, and explain each one. See pictures on page 152 1. Deletion – bases are left out 2. Insertion – extra base(s) added 3. Substitution – wrong bases used (most common) – this can be harmful because it may cause a gene to produce the wrong protein. One example of this i ...
... 43. List the 3 kinds of mutations, and explain each one. See pictures on page 152 1. Deletion – bases are left out 2. Insertion – extra base(s) added 3. Substitution – wrong bases used (most common) – this can be harmful because it may cause a gene to produce the wrong protein. One example of this i ...
File - Mr. Obiechefu`s Life Science
... 43. List the 3 kinds of mutations, and explain each one. See pictures on page 152 1. Deletion – bases are left out 2. Insertion – extra base(s) added 3. Substitution – wrong bases used (most common) – this can be harmful because it may cause a gene to produce the wrong protein. One example of this i ...
... 43. List the 3 kinds of mutations, and explain each one. See pictures on page 152 1. Deletion – bases are left out 2. Insertion – extra base(s) added 3. Substitution – wrong bases used (most common) – this can be harmful because it may cause a gene to produce the wrong protein. One example of this i ...
Webquest
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
... Please tour the following website based on the DNA content you have been learning recently. They will show you visually some of what is going on and help you to understand exactly what it happening. You will have to answer some questions based on what you see. 1. First go to the page: http://learn.g ...
8.1 INTRO to Genetics Practice Monohybrid Crosses
... Punnett squares are used to predict the probability of traits being passed from parents to offspring ...
... Punnett squares are used to predict the probability of traits being passed from parents to offspring ...
Biology 11 The Fit Bird Gets the Worm! Name: Chap 14 ANSWER
... environment and most likely to survive and pass on their genes c. What does this suggest about the presence of this allele (trait) in future populations. Is it likely to become more or less common? Explain how you know. The allele (beak type) that caught the most food is most likely to become a trai ...
... environment and most likely to survive and pass on their genes c. What does this suggest about the presence of this allele (trait) in future populations. Is it likely to become more or less common? Explain how you know. The allele (beak type) that caught the most food is most likely to become a trai ...
No Slide Title
... Spontaneous vs. induced – Human deleterious mutations are spontaneous, or environmentally induced – Mutation induction in mice (and other model organisms) is a tool of functional genomics ...
... Spontaneous vs. induced – Human deleterious mutations are spontaneous, or environmentally induced – Mutation induction in mice (and other model organisms) is a tool of functional genomics ...
Genetic Engineering
... Genetics or genetic engineering began as a science in the early 1900's with the scientific experimentations of the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel. American geneticists later developed techniques of isolating and altering genes to produce insulin and interferon in the early 1970's. The Food and Drug Adm ...
... Genetics or genetic engineering began as a science in the early 1900's with the scientific experimentations of the Austrian monk Gregor Mendel. American geneticists later developed techniques of isolating and altering genes to produce insulin and interferon in the early 1970's. The Food and Drug Adm ...
Document
... (1) Specialized cell: over-represented hemoglobin in blood cells. (2) Different stages of life cycle: hemoglobins before and after birth, caterpillar and butterfly. ...
... (1) Specialized cell: over-represented hemoglobin in blood cells. (2) Different stages of life cycle: hemoglobins before and after birth, caterpillar and butterfly. ...
Genetic Notes review page (blanks filled in except for
... called regeneration)______. ((There is one we do not learn about in 7th grade called: Parthenogenesis -Though most of the organisms that use asexual reproduction are invertebrates, several species of vertebrate animals do make use of it. Some, like copperhead snakes, Amazonian frogs, Komodo dragons ...
... called regeneration)______. ((There is one we do not learn about in 7th grade called: Parthenogenesis -Though most of the organisms that use asexual reproduction are invertebrates, several species of vertebrate animals do make use of it. Some, like copperhead snakes, Amazonian frogs, Komodo dragons ...
Chapter 12 Individual Genetic Variation and Gene Regulation
... • Gametes are produced with chromosome numbers varying from the 1N haploid number to the 2N diploid number • Most of these gametes fail to produce viable offspring when they combine at fertilization, but sometimes those gametes that carry the 2N diploid number find and fertilize other like 2N diploi ...
... • Gametes are produced with chromosome numbers varying from the 1N haploid number to the 2N diploid number • Most of these gametes fail to produce viable offspring when they combine at fertilization, but sometimes those gametes that carry the 2N diploid number find and fertilize other like 2N diploi ...