Document
... determining the recombination frequency between a gene and an anonymous marker Anonymous markers such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be detected by molecular techniques. ...
... determining the recombination frequency between a gene and an anonymous marker Anonymous markers such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can be detected by molecular techniques. ...
Genetic disorder/testing PPT
... chromosomes. The chromosomes are organized by size, large to small. This arrangement helps scientists be able to identify genetic disorders caused by chromosome alterations. To be able to make a karyotype scientists take a picture of your chromosomes , cut them out and match them depending on size, ...
... chromosomes. The chromosomes are organized by size, large to small. This arrangement helps scientists be able to identify genetic disorders caused by chromosome alterations. To be able to make a karyotype scientists take a picture of your chromosomes , cut them out and match them depending on size, ...
Student Worksheet
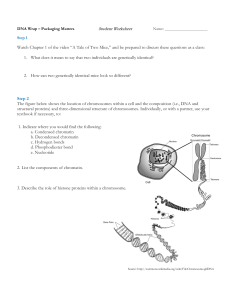
... Research suggests that the way DNA is “packaged” into chromatin plays an important role in genetic processes like DNA replication, recombination, repair, and transcription. This means that changes in gene expression (i.e., the yellow mouse versus the brown mouse in the video you saw) can occur witho ...
... Research suggests that the way DNA is “packaged” into chromatin plays an important role in genetic processes like DNA replication, recombination, repair, and transcription. This means that changes in gene expression (i.e., the yellow mouse versus the brown mouse in the video you saw) can occur witho ...
Part C: Genetics
... individuals on Earth are genetically identical. There are small differences in how we appear to each other. These differences are described as variation. Variation arises due to sexual reproduction. Each characteristic we possess is coded for by one or more genes. A gene is a section of DNA which co ...
... individuals on Earth are genetically identical. There are small differences in how we appear to each other. These differences are described as variation. Variation arises due to sexual reproduction. Each characteristic we possess is coded for by one or more genes. A gene is a section of DNA which co ...
What do Genes Look Like - Effingham County Schools
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
... Ex: German Shepard x German Shepard = German Shepard VII. _______________________________ – Desired genes are removed from one organism and added or recombined into another organism. This forms a transgenic organism with recombinant DNA A. This is used to make proteins not normally made by the cel ...
PPT - Michael J. Watts
... • Computationally expensive some problems require many days or weeks to run o often still faster than brute force, however o ...
... • Computationally expensive some problems require many days or weeks to run o often still faster than brute force, however o ...
Chapter 3 Genetics Study Guide
... 7. What do the inside squares of the Punnett Square represent? All the possible allele combinations 8. How are chromosomes related to heredity? Chromosomes are made of many genes strung together. Genes are the factors that control traits. 9. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? Genes are ca ...
... 7. What do the inside squares of the Punnett Square represent? All the possible allele combinations 8. How are chromosomes related to heredity? Chromosomes are made of many genes strung together. Genes are the factors that control traits. 9. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? Genes are ca ...
ion
... • The phenotypes of polygenic characteristics tend to show continuous variation. • Application: Polygenic traits such as human height may also be influenced by environmental factors. ...
... • The phenotypes of polygenic characteristics tend to show continuous variation. • Application: Polygenic traits such as human height may also be influenced by environmental factors. ...
File - Mrs. Lucier and Mrs. Magagna Life Science Class
... Fill in the blank with words found below. 1. ______________________ is a process in which defective genes are replaced ...
... Fill in the blank with words found below. 1. ______________________ is a process in which defective genes are replaced ...
Document
... Acts equally to increase or decrease frequencies. Eliminates or fixes new mutations. Happens because different individuals have different numbers of offspring by chance. The probability that an al lele will be fixed by drift is equal to its frequency. ...
... Acts equally to increase or decrease frequencies. Eliminates or fixes new mutations. Happens because different individuals have different numbers of offspring by chance. The probability that an al lele will be fixed by drift is equal to its frequency. ...
The human genome
... There are two kinds of distance metric for chromosome. Physical distances are measured in terms of number of base pairs (abbreviated as bp) Between two points. The units for physical distances are bp and kb (1000 bp). Genetic distances are defined as the expected numbers of crossovers between two p ...
... There are two kinds of distance metric for chromosome. Physical distances are measured in terms of number of base pairs (abbreviated as bp) Between two points. The units for physical distances are bp and kb (1000 bp). Genetic distances are defined as the expected numbers of crossovers between two p ...
Insight into Blindness
... Define the term mutation and identify ways in which mutations may affect an organism Identify the causes of mutations Differentiate between somatic and gametic mutations and identify the potential effect of each of these. Describe the effect of gene mutations; identify types of gene mutations ...
... Define the term mutation and identify ways in which mutations may affect an organism Identify the causes of mutations Differentiate between somatic and gametic mutations and identify the potential effect of each of these. Describe the effect of gene mutations; identify types of gene mutations ...
This examination paper consists of 4 pages
... Can hold large pieces of chromosomal DNA Are rodent cell lines Are produced by irradiation with UV light Have been used in mapping the yeast genome ...
... Can hold large pieces of chromosomal DNA Are rodent cell lines Are produced by irradiation with UV light Have been used in mapping the yeast genome ...
Evolution - VCC Library - Vancouver Community College
... When a single species evolves to produce several new species with different characteristics, it is termed adaptive radiation or divergent evolution. Structures that are similar in the new species (because of their shared ancestry) are called homologous. Often, organisms with similar characteristics ...
... When a single species evolves to produce several new species with different characteristics, it is termed adaptive radiation or divergent evolution. Structures that are similar in the new species (because of their shared ancestry) are called homologous. Often, organisms with similar characteristics ...
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
... Inbreeding: crossing two organisms that are very similar to retain desirable characteristics. ...
... Inbreeding: crossing two organisms that are very similar to retain desirable characteristics. ...
today
... enable yeast to speed DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and malt degradation, presumably representing yeast's recent interaction with humans. ...
... enable yeast to speed DNA synthesis, protein synthesis, and malt degradation, presumably representing yeast's recent interaction with humans. ...
genetics - Maria Regina
... reduced cost and longer shelf life Faster growing plants and animals Food with more desirable traits, such as potatoes that absorb less fat when ...
... reduced cost and longer shelf life Faster growing plants and animals Food with more desirable traits, such as potatoes that absorb less fat when ...
Document
... acid that the codon codes 2. Does not cause alteration on the amino acid that the codon codes 3. Alters codon in the way that it becomes stop-codon for protein synthesis ...
... acid that the codon codes 2. Does not cause alteration on the amino acid that the codon codes 3. Alters codon in the way that it becomes stop-codon for protein synthesis ...
Chapter 6: Genetic diseases
... A normal human being has 46 of these chromosomes in each cell (excepting reproductive cells) Of these 46 chromosomes, 44 are ‘autosomal’ 2 chromosomes are ‘sex chromosomes’ ...
... A normal human being has 46 of these chromosomes in each cell (excepting reproductive cells) Of these 46 chromosomes, 44 are ‘autosomal’ 2 chromosomes are ‘sex chromosomes’ ...
how mutations affect gene function
... • Inversion: 180˚ rotation of piece of DNA • Reciprocal translocation: parts of nonhomologous chromosomes change places • Chromosomal rearrangements: affect many genes at one time ...
... • Inversion: 180˚ rotation of piece of DNA • Reciprocal translocation: parts of nonhomologous chromosomes change places • Chromosomal rearrangements: affect many genes at one time ...
Module 3 Nature vs. Nurture - Jackson Liberty Psychology
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – complex molecule that contains genetic information that makes up chromosomes Cell -> Nucleus -> Chromosomes -> DNA -> Genes ...
... DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – complex molecule that contains genetic information that makes up chromosomes Cell -> Nucleus -> Chromosomes -> DNA -> Genes ...
Radiation and Gene Damage
... energy waves. Often the repair of the DNA strand by enzymes or other chemicals is not adequate enough to put the DNA molecule back together in its proper sequence. When replication occurs, the new strands of DNA carry the new altered sequence of genes. As each generation of cells is produced the mut ...
... energy waves. Often the repair of the DNA strand by enzymes or other chemicals is not adequate enough to put the DNA molecule back together in its proper sequence. When replication occurs, the new strands of DNA carry the new altered sequence of genes. As each generation of cells is produced the mut ...
Unit 4: Genetic Engineering and Gene Expression
... 1. What is the purpose of genetic engineering/synthetic biology? To change the genetic makeup of cells so that they express new traits 2. What is the very important relationship between DNA and proteins? DNA holds the information that codes for proteins, the workers of the cell. 3. Does a cell alway ...
... 1. What is the purpose of genetic engineering/synthetic biology? To change the genetic makeup of cells so that they express new traits 2. What is the very important relationship between DNA and proteins? DNA holds the information that codes for proteins, the workers of the cell. 3. Does a cell alway ...