Lecture Outline
... 1. Tracking even a single gene through several generation may produce results that are different than expected. 2. Camptodactyly (immobile, bent fingers) can express itself on one hand only, both hands, or neither due the possibility that a gene product is missing in one of the several steps along t ...
... 1. Tracking even a single gene through several generation may produce results that are different than expected. 2. Camptodactyly (immobile, bent fingers) can express itself on one hand only, both hands, or neither due the possibility that a gene product is missing in one of the several steps along t ...
BioSc 231 Exam 4 2008
... (2 pts) Occasionally, DNA polymerase makes a mistake and incorporates an incorrect base into a newly synthesized DNA strand. The cell has mechanisms to repair these errors. However, the repair enzymes need to know which DNA strand has the correct base. In other words, it needs to know which is the o ...
... (2 pts) Occasionally, DNA polymerase makes a mistake and incorporates an incorrect base into a newly synthesized DNA strand. The cell has mechanisms to repair these errors. However, the repair enzymes need to know which DNA strand has the correct base. In other words, it needs to know which is the o ...
natural selection - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Ch. 17
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
CST Review Sheet 2 DNA and RNA 1. The unit to the right which
... A Cells divide only once during meiosis. B Meiosis does not occur in reproductive cells. C The cells produced at the end of meiosis are genetically identical to the parent cell. D The cells produced at the end of meiosis contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. 7. Which of the foll ...
... A Cells divide only once during meiosis. B Meiosis does not occur in reproductive cells. C The cells produced at the end of meiosis are genetically identical to the parent cell. D The cells produced at the end of meiosis contain half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. 7. Which of the foll ...
Week 8, Class 2
... have a variable base of A or G. • Substitution – loss of an ancestral allele through fixation of a new allele in a population. The sequence has changed and can be observed as a difference in comparison with other species. ...
... have a variable base of A or G. • Substitution – loss of an ancestral allele through fixation of a new allele in a population. The sequence has changed and can be observed as a difference in comparison with other species. ...
docx Probes and fingerprint matching Card sort or vocab
... This technique is used to determine the order of bases in our target DNA. ...
... This technique is used to determine the order of bases in our target DNA. ...
Biodiversity, Ancestry, & Rates of Evolution Notes
... of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. ...
... of biodiversity, ancestry, and the rates of evolution. ...
Biology EOCT Review
... Law of Segregation – the two different forms of an allele randomly separate during meiosis – during fertilization new combos of the alleles come together Laws of Independent Assortment – genes for different traits sort out separately from one another during meiosis ...
... Law of Segregation – the two different forms of an allele randomly separate during meiosis – during fertilization new combos of the alleles come together Laws of Independent Assortment – genes for different traits sort out separately from one another during meiosis ...
1 Molecular Genetics
... DNA (not protein) is the genetic material. - RNA (not protein) is genetic material of some viruses, - but no known prokaryotes or eukaryotes use RNA as their genetic material. ...
... DNA (not protein) is the genetic material. - RNA (not protein) is genetic material of some viruses, - but no known prokaryotes or eukaryotes use RNA as their genetic material. ...
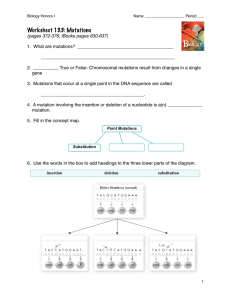
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
Molecular Genetics of Viruses
... • Conjugation- DNA exchange between bacteria – Donor bacterium produces a tube or pilus that connects to a recipient bacterium. – Exchange of chromosomal or plasmid DNA. – F plasmids- genes for production of pili. – R plasmid- provides bacteria with resistance against antibiotics ...
... • Conjugation- DNA exchange between bacteria – Donor bacterium produces a tube or pilus that connects to a recipient bacterium. – Exchange of chromosomal or plasmid DNA. – F plasmids- genes for production of pili. – R plasmid- provides bacteria with resistance against antibiotics ...
Photosynthesis - Cathedral High School
... the HEXA gene on chromosome 15 This causes a stop codon in the wrong location Deficient hexosaminidase (hex A). ...
... the HEXA gene on chromosome 15 This causes a stop codon in the wrong location Deficient hexosaminidase (hex A). ...
Fundamentals of human genetic
... Genetics terms you need to know: • Inheritance – is the way of passing of hereditary information which depends on the forms of reproduction During asexual reproduction the main traits are inherited through spores or vegetative cells, that's why the maternal and daughter cells are very similar. Duri ...
... Genetics terms you need to know: • Inheritance – is the way of passing of hereditary information which depends on the forms of reproduction During asexual reproduction the main traits are inherited through spores or vegetative cells, that's why the maternal and daughter cells are very similar. Duri ...
Modern Genetics
... clinically normal but have one mutation of a particular gene) both must pass the mutation to a child in order for that child to be affected. This inheritance pattern is distinctive in that the parents and other relatives of the person with the disease appear to be completely normal, while 25% of ...
... clinically normal but have one mutation of a particular gene) both must pass the mutation to a child in order for that child to be affected. This inheritance pattern is distinctive in that the parents and other relatives of the person with the disease appear to be completely normal, while 25% of ...
Richard A. Spinello, Sarah Cabral Presentation
... biological material isolated from its natural environment: Bulgaria, Canada, Australia, ...
... biological material isolated from its natural environment: Bulgaria, Canada, Australia, ...
Mendelian Genetics
... Your Mom gives you the gene for having a Unibrow (recessive) and your father gives you the gene for having two eye brows (dominant) Dad ...
... Your Mom gives you the gene for having a Unibrow (recessive) and your father gives you the gene for having two eye brows (dominant) Dad ...
Macroevolution or - the evolution of species The Biological Species
... but cannot produce viable offspring. The reason is usually traceable to incompatible chromosomes that don’t match up in meiosis. An example: horses and donkeys mate, the offspring (mules) are viable, but sterile ...
... but cannot produce viable offspring. The reason is usually traceable to incompatible chromosomes that don’t match up in meiosis. An example: horses and donkeys mate, the offspring (mules) are viable, but sterile ...
Bacteria cells reproduce differently from other single celled
... phase of the Human Genome Project. What have they accomplished through this project? a. They used a single cell from one organism to create an identical organism. b. They created a single pedigree for every genetic disorder. c. They created DNA synthetically in a laboratory. d. They identified the s ...
... phase of the Human Genome Project. What have they accomplished through this project? a. They used a single cell from one organism to create an identical organism. b. They created a single pedigree for every genetic disorder. c. They created DNA synthetically in a laboratory. d. They identified the s ...