
S-8-2-2_Vocabulary Matching Worksheet and KEY Vocabulary
... alternate forms of a gene that control the same characteristics traits that an organism is born with that are carried on their genes type of allele that is always expressed when it is present in an individual a molecule in the genes that passes characteristics from one generation to the next traits ...
... alternate forms of a gene that control the same characteristics traits that an organism is born with that are carried on their genes type of allele that is always expressed when it is present in an individual a molecule in the genes that passes characteristics from one generation to the next traits ...
Homologous Pairs- Pairs of chromosomes with the same genes on
... • Alleles on the same chromosome are often inherited together. • The closer the genes are to each other on a chromosome the more likely they are to be inherited together. • Alleles that are far apart can be separated by crossing over. ...
... • Alleles on the same chromosome are often inherited together. • The closer the genes are to each other on a chromosome the more likely they are to be inherited together. • Alleles that are far apart can be separated by crossing over. ...
Inheritance – Summary
... 4. One result of a chromosome mutation in humans is Down’s syndrome. Describe this condition and how it is caused. Down’s Syndrome _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
... 4. One result of a chromosome mutation in humans is Down’s syndrome. Describe this condition and how it is caused. Down’s Syndrome _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ ...
BIOINFORMATICS AND GENE DISCOVERY
... Neural Networks •interconnected assembly of simple processing elements (units or nodes) •nodes functionality is similar to that of the animal neuron •processing ability is stored in the inter-unit connection strengths (weights) •weights are obtained by a process of adaptation to, or learning from, ...
... Neural Networks •interconnected assembly of simple processing elements (units or nodes) •nodes functionality is similar to that of the animal neuron •processing ability is stored in the inter-unit connection strengths (weights) •weights are obtained by a process of adaptation to, or learning from, ...
Key Concepts -- Lecture 17 (BIOSYSTEMATICS 2) Spring 2009 IB
... intersterile or losing crossability before much morphological or ecological change has occurred. This difference between annuals and perennials may reflect higher overall rates of molecular evolution in annuals (recently demonstrated). In part, more rapid evolution of reproductive isolation in annua ...
... intersterile or losing crossability before much morphological or ecological change has occurred. This difference between annuals and perennials may reflect higher overall rates of molecular evolution in annuals (recently demonstrated). In part, more rapid evolution of reproductive isolation in annua ...
MENDEL AND MEIOSIS NOTES
... Occurs in the specialized body cells of each parent Male gametes – sperm – haploid (n) Female gametes – egg – haploid (n) Joining of sperm and egg – diploid (2n) number of chromosomes Zygote then undergoes mitosis to develop into ...
... Occurs in the specialized body cells of each parent Male gametes – sperm – haploid (n) Female gametes – egg – haploid (n) Joining of sperm and egg – diploid (2n) number of chromosomes Zygote then undergoes mitosis to develop into ...
Heredity – the passing of traits from parents to offspring
... DNA – cellular material with all the information about what traits a living thing may have Chromosome – thread like structures that organize DNA, each chromosome is a long DNA molecule (about 1.5 meters!) Gene – part of the DNA molecule that carries a specific trait (composed of 2 alleles) (ex. flow ...
... DNA – cellular material with all the information about what traits a living thing may have Chromosome – thread like structures that organize DNA, each chromosome is a long DNA molecule (about 1.5 meters!) Gene – part of the DNA molecule that carries a specific trait (composed of 2 alleles) (ex. flow ...
Mendelian Genetics
... chromosome tend to be inherited together. These genes do not follow the Mendelian pattern of independent assortment. The genes are inherited together on adjoining portions of the chromosome. This pattern is similar to the 3:1 ratio of monohybrid cross rather than the 9:3:3:1 ratio of a dihybrid cros ...
... chromosome tend to be inherited together. These genes do not follow the Mendelian pattern of independent assortment. The genes are inherited together on adjoining portions of the chromosome. This pattern is similar to the 3:1 ratio of monohybrid cross rather than the 9:3:3:1 ratio of a dihybrid cros ...
Human genome and meiosis
... chromosomes (with 1669 genes)iii, and contains genes involved in such vital systems as blood clotting, eyesight, and bone formation. You cannot survive without at least one X chromosome. Healthy human females are XX. The Y chromosome is one of the smallest chromosomes (with only 426 genes)iv and is ...
... chromosomes (with 1669 genes)iii, and contains genes involved in such vital systems as blood clotting, eyesight, and bone formation. You cannot survive without at least one X chromosome. Healthy human females are XX. The Y chromosome is one of the smallest chromosomes (with only 426 genes)iv and is ...
Chapter 14 Study Guide 1. What is a karyotype and how many
... What is colorblindness and how is it inherited? What is a Barr body? How does it relate to X chromosomes What is nondisjunction? What does it involve? What are conditions involving errors in the X chromosome? What is DNA fingerprinting and how does it work? What is the Human Genome project? How was ...
... What is colorblindness and how is it inherited? What is a Barr body? How does it relate to X chromosomes What is nondisjunction? What does it involve? What are conditions involving errors in the X chromosome? What is DNA fingerprinting and how does it work? What is the Human Genome project? How was ...
Snímek 1
... How a supernumerary B chromosome survives over time? transmission higher than Mendelian kept in populations drive (pre-meiotic, meiotic, post-meiotic) = preferential maintenance of Bs post-meiotic drive common in plants during gametophyte maturation (examples: rye, maize) ...
... How a supernumerary B chromosome survives over time? transmission higher than Mendelian kept in populations drive (pre-meiotic, meiotic, post-meiotic) = preferential maintenance of Bs post-meiotic drive common in plants during gametophyte maturation (examples: rye, maize) ...
Genetics Review
... 3. Radiation (nuclear and solar) Many common place items are capable of causing mutations: microwave, fruit from the store, radar, cellular phones…. ...
... 3. Radiation (nuclear and solar) Many common place items are capable of causing mutations: microwave, fruit from the store, radar, cellular phones…. ...
NAME ______ AVERILL PARK HS THE LIVING ENVIRONMENT
... 8. Record the letters (genes) you have obtained for your baby Reebop in Table 1: Genotype & Phenotype Data. For example, if you have one chromosome with the letter A and another with the letter a, the genotype is Aa. 9. Use the Decoding Key (Table 2) to decide what characteristics (phenotype) your b ...
... 8. Record the letters (genes) you have obtained for your baby Reebop in Table 1: Genotype & Phenotype Data. For example, if you have one chromosome with the letter A and another with the letter a, the genotype is Aa. 9. Use the Decoding Key (Table 2) to decide what characteristics (phenotype) your b ...
2016‐12‐15 1
... during mitosis and is dispersed as chromatin during mitosis. What are chromosome homologs? One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the female (maternal chromosome) and one comes from the male (paternal chromosome). Homologous chromosomes are very similar but not identical. Each carries t ...
... during mitosis and is dispersed as chromatin during mitosis. What are chromosome homologs? One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the female (maternal chromosome) and one comes from the male (paternal chromosome). Homologous chromosomes are very similar but not identical. Each carries t ...
HL#1 Meiosis - hutchhighIBbiology
... (alternate forms of a gene). The allele pairs separate in Meiosis I, when a diploid cell divides into two haploid cells, before the formation of gametes. So, for example each sperm or egg will get just one big R, or one little r, or one big T, or one little t. ...
... (alternate forms of a gene). The allele pairs separate in Meiosis I, when a diploid cell divides into two haploid cells, before the formation of gametes. So, for example each sperm or egg will get just one big R, or one little r, or one big T, or one little t. ...
Cross-dressing or Crossing-over: Sex Testing of Women Athletes
... • Purpose of meiosis: in animals, produce gametes with just half the parents’ genetic material. Gametes are ______ (haploid/diploid). • Mechanism: Only one of each pair of homologous chromosomes gets into each gamete. • The happy ending: Gametes from the two parents get to fuse, restoring the origin ...
... • Purpose of meiosis: in animals, produce gametes with just half the parents’ genetic material. Gametes are ______ (haploid/diploid). • Mechanism: Only one of each pair of homologous chromosomes gets into each gamete. • The happy ending: Gametes from the two parents get to fuse, restoring the origin ...
chapt16_lecture_edited [Compatibility Mode]
... At meiosis, one member of each chromosome pair segregates into one daughter nucleus and its homologue segregates into the other daughter nucleus. Each of the resulting haploid cells contains only one set of chromosomes. During the formation of haploid cells, the members of different chromosome pairs ...
... At meiosis, one member of each chromosome pair segregates into one daughter nucleus and its homologue segregates into the other daughter nucleus. Each of the resulting haploid cells contains only one set of chromosomes. During the formation of haploid cells, the members of different chromosome pairs ...
FISH
... Is a chromosomal condition that is associated with severe mental retardation and certain physical abnormalities. The critical region has been reported to include 13q14-13q32 with variable expression, gene interactions, or interchromosomal effects. ...
... Is a chromosomal condition that is associated with severe mental retardation and certain physical abnormalities. The critical region has been reported to include 13q14-13q32 with variable expression, gene interactions, or interchromosomal effects. ...
3U Exam Review june 2015
... 5. What is the difference between analogous and homologous traits and provide an example of each 6. What is the difference between convergent and divergent evolution? Provide an example of both. 7. What is the difference between Stabilizing Selection, Directional Selection and Disruptive Selection. ...
... 5. What is the difference between analogous and homologous traits and provide an example of each 6. What is the difference between convergent and divergent evolution? Provide an example of both. 7. What is the difference between Stabilizing Selection, Directional Selection and Disruptive Selection. ...
quiz_-_chapter_5
... 7. Four genetic concepts help to explain the wide variety of phenotypes: incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles and polygenic traits. Choose two of these concepts and explain them. ...
... 7. Four genetic concepts help to explain the wide variety of phenotypes: incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles and polygenic traits. Choose two of these concepts and explain them. ...
Finding a cancer-causing gene
... feature is often determined by a ``gene”, which can take several forms, called its alleles. Each individual inherits an allele from the father and an allele from the mother; one of these two alleles is then randomly passed on to each offspring. When studying the transmission of a disease, the geneti ...
... feature is often determined by a ``gene”, which can take several forms, called its alleles. Each individual inherits an allele from the father and an allele from the mother; one of these two alleles is then randomly passed on to each offspring. When studying the transmission of a disease, the geneti ...
X and Y Chromosomes
... Or, to put it more precisely, the heterozygous offspring of those two individuals can produce gametes with neither mutation. ...
... Or, to put it more precisely, the heterozygous offspring of those two individuals can produce gametes with neither mutation. ...
CB - Human Genome WS 2pp
... DNA Fingerprinting No two people have exactly the same genetic code, except for identical twins. DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their genetic code. Using DNA fingerprinting, DNA from blood and other materials left at a crime scene can be compared to a suspect ...
... DNA Fingerprinting No two people have exactly the same genetic code, except for identical twins. DNA fingerprinting is a technique used to identify individuals based on their genetic code. Using DNA fingerprinting, DNA from blood and other materials left at a crime scene can be compared to a suspect ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide: Mendel and Heredity Section 1 – Origins of
... does NOT clot properly; a serious injury may cause them to bleed to death. 7. Human males inherit the recessive allele for colorblindness and hemophilia from their __________________, who gives them their X sex chromosome. Females don’t usually inherit these diseases because they inherit two X sex c ...
... does NOT clot properly; a serious injury may cause them to bleed to death. 7. Human males inherit the recessive allele for colorblindness and hemophilia from their __________________, who gives them their X sex chromosome. Females don’t usually inherit these diseases because they inherit two X sex c ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)










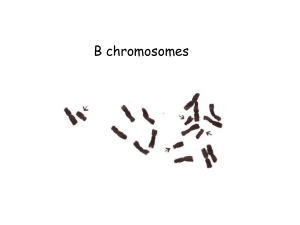





![chapt16_lecture_edited [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000263591_1-cfed90f240fe045be4528c9a104d2a9a-300x300.png)






