A4.3.1HowDoChromosomesCarryInformation
... 6. Where are centromeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its centromere is located. 7. Where are telomeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its telomeres are located. 8. From the variation window, select one of the chro ...
... 6. Where are centromeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its centromere is located. 7. Where are telomeres located on chromosomes? Make a sketch of a chromosome and indicate where its telomeres are located. 8. From the variation window, select one of the chro ...
Chapter 15: Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... -Females that are heterozygous for a certain X chromosome trait can express both traits ...
... -Females that are heterozygous for a certain X chromosome trait can express both traits ...
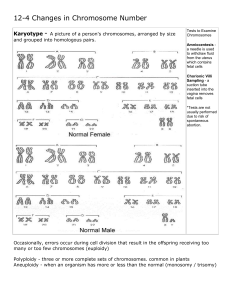
Looking at karyotypes
... Klinefelter’s syndrome produces a sterile male with female features and small testes. 6. Explain why a person with Klinefelter’s syndrome is male, not female, even though they have two X chromosomes. 7. Half of all miscarriages are due to chromosome abnormalities. This means that parts of chromosome ...
... Klinefelter’s syndrome produces a sterile male with female features and small testes. 6. Explain why a person with Klinefelter’s syndrome is male, not female, even though they have two X chromosomes. 7. Half of all miscarriages are due to chromosome abnormalities. This means that parts of chromosome ...
DNA Glossary - FutureLearn
... over 3 billion base pairs Twenty-two of the 23 pairs of chromosomes look the same and carry the same genes at the same loci. These are called Homologous chromosomes. The exception is the pair of sex chromosomes where the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X ch ...
... over 3 billion base pairs Twenty-two of the 23 pairs of chromosomes look the same and carry the same genes at the same loci. These are called Homologous chromosomes. The exception is the pair of sex chromosomes where the male gender- determining Y chromosome is a different size and shape to the X ch ...
Advanced Genetics: Karyotypes and Pedigrees
... • A karyotype is a picture of all chromosomes in a cell, for one organism • Karyotypes can show: • changes in chromosomes • deletion of part or loss of a chromosome • extra chromosomes ...
... • A karyotype is a picture of all chromosomes in a cell, for one organism • Karyotypes can show: • changes in chromosomes • deletion of part or loss of a chromosome • extra chromosomes ...
Genes & Chromosomes
... section of DNA between chromosomes. Recombinants: Individual organism with a new combination of genes due to crossing-over. ...
... section of DNA between chromosomes. Recombinants: Individual organism with a new combination of genes due to crossing-over. ...
Karyotypes and Mutations
... • When does crossing over occur? When does independent assortment occur? • Describe the cells that result at the end of meiosis ...
... • When does crossing over occur? When does independent assortment occur? • Describe the cells that result at the end of meiosis ...
14-2 Human Chromosomes – Reading Guide
... 1. Genes make up only a small part of chromosomes; only about _________% of chromosome’s DNA functions as genes. 2. The first two human chromosomes whose sequences were determined were chromosome ______ & ______. 3. Chromosome 21 contains about _______ genes, including one associated with amyotropic ...
... 1. Genes make up only a small part of chromosomes; only about _________% of chromosome’s DNA functions as genes. 2. The first two human chromosomes whose sequences were determined were chromosome ______ & ______. 3. Chromosome 21 contains about _______ genes, including one associated with amyotropic ...
Genetic Birth Defects
... chromosome 18 are copied instead of two. It’s named after of John H.Edwards who first described it in 1960. ...
... chromosome 18 are copied instead of two. It’s named after of John H.Edwards who first described it in 1960. ...
Document
... Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together. You have 23 pairs of chromosome. Each chromosome has 200 – 3000 genes. Therefore, you have between 20,000 – 25,000 genes. Each gene controls a trait. About Chromosome 1 Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs. It represents ab ...
... Chromosomes are made up of many genes joined together. You have 23 pairs of chromosome. Each chromosome has 200 – 3000 genes. Therefore, you have between 20,000 – 25,000 genes. Each gene controls a trait. About Chromosome 1 Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs. It represents ab ...
Changes in Chromosome Number
... suction tube inserted into the vagina removes fetal cells *Tests are not usually performed due to risk of spontaneous abortion. ...
... suction tube inserted into the vagina removes fetal cells *Tests are not usually performed due to risk of spontaneous abortion. ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Autosomes are homologous Sex chromosomes are not Female carries XX Male carries XY Y chromosome only carries 330 genes X chromosome carries 2,062 genes Males and females express the same levels of certain genes found on the X chromosome Dosage compensation In females one X chromosome is randomly sel ...
... Autosomes are homologous Sex chromosomes are not Female carries XX Male carries XY Y chromosome only carries 330 genes X chromosome carries 2,062 genes Males and females express the same levels of certain genes found on the X chromosome Dosage compensation In females one X chromosome is randomly sel ...
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
Genetics - the science of heredity and variation
... parents and offspring; sum of qualities genetically derived from one’s parents Allele - one of a pair of genes that occupy the same location on homologous chromosomes and affect the same trait in animals Diploid - refers to paired chromosomes in body cells Gametes - male or female reproductive cells ...
... parents and offspring; sum of qualities genetically derived from one’s parents Allele - one of a pair of genes that occupy the same location on homologous chromosomes and affect the same trait in animals Diploid - refers to paired chromosomes in body cells Gametes - male or female reproductive cells ...
Y chromosome

The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or absence of Y that determines the male or female sex of offspring produced in sexual reproduction. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development. The DNA in the human Y chromosome is composed of about 59 million base pairs. The Y chromosome is passed only from father to son. With a 30% difference between humans and chimpanzees, the Y chromosome is one of the fastest evolving parts of the human genome. To date, over 200 Y-linked genes have been identified. All Y-linked genes are expressed and (apart from duplicated genes) hemizygous (present on only one chromosome) except in the cases of aneuploidy such as XYY syndrome or XXYY syndrome. (See Y linkage.)