energy - staff.harrisonburg.k12.va
... 2. Potential energy - energy that is stored in an object Examples: holding a ball before you drop it, a book on the edge of a table, a roller coaster at the top *As potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases. ...
... 2. Potential energy - energy that is stored in an object Examples: holding a ball before you drop it, a book on the edge of a table, a roller coaster at the top *As potential energy decreases, kinetic energy increases. ...
Law of the Conservation of Energy
... chemical. Potential energy is stored energy that can be harnessed for a later action like falling or rolling. Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving cars and bikes have kinetic energy. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy; it is stored in food, batteries and gasoline. All of these ...
... chemical. Potential energy is stored energy that can be harnessed for a later action like falling or rolling. Kinetic energy is the energy of movement. Moving cars and bikes have kinetic energy. Chemical energy is a form of potential energy; it is stored in food, batteries and gasoline. All of these ...
Answers
... 2. In every energy transformation there are two outcomes: 1. ___work_________ is done and 2._heat_______ is given off. 3. In a battery ___chemical_______________ energy is changed to electrical energy. 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In ...
... 2. In every energy transformation there are two outcomes: 1. ___work_________ is done and 2._heat_______ is given off. 3. In a battery ___chemical_______________ energy is changed to electrical energy. 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? solids_______ 5. In ...
Transparancies for Energy & Momentum Section
... – Elastic: momentum and kinetic energy conserved Initial k.e.: ½m1 v02 = ½ m1v12+ ½ m2v22 : final k.e. – Inelastic: momentum is conserved, kinetic energy is not • Kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy ...
... – Elastic: momentum and kinetic energy conserved Initial k.e.: ½m1 v02 = ½ m1v12+ ½ m2v22 : final k.e. – Inelastic: momentum is conserved, kinetic energy is not • Kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy Notes
... • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to walk, run, kick, etc. ...
... • Kinetic to potential – skateboarding to the top of the ramp and doing a stall • Potential to kinetic – standing on a diving board then jumping off • Light energy to chemical – photosynthesis in plants • Chemical to kinetic – eating breakfast and using that energy to walk, run, kick, etc. ...
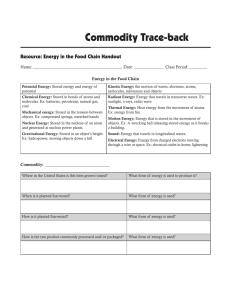
Energy in the Food Chain Handout
... Thermal Energy: Heat energy from the movement of atoms. Ex: energy from fire Motion Energy: Energy that is stored in the movement of objects. Ex: A wrecking ball releasing stored energy as it breaks a building. Sound: Energy that travels in longitudinal waves. Electrical Energy: Energy from charged ...
... Thermal Energy: Heat energy from the movement of atoms. Ex: energy from fire Motion Energy: Energy that is stored in the movement of objects. Ex: A wrecking ball releasing stored energy as it breaks a building. Sound: Energy that travels in longitudinal waves. Electrical Energy: Energy from charged ...
Energy Test Review Answer Key
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
Energy Test Review Answer Key Lowery
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
... Radiant (Light or Electromagnetic) – energy that travels in electromagnetic waves Electrical – movement of electrons ...
Vocabulary for Energy Unit
... Dependent variable - the thing in the experiment that changes because of what you did. Elastic Potential energyElectrical energy –energy in the form of a moving charged particle, i.e. Electricity is the movement of negatively charged particle Energy is an ability to bring about a change (we can see ...
... Dependent variable - the thing in the experiment that changes because of what you did. Elastic Potential energyElectrical energy –energy in the form of a moving charged particle, i.e. Electricity is the movement of negatively charged particle Energy is an ability to bring about a change (we can see ...
The BIG Idea— Energy is the ability to do work or make something
... because the electricity sends the digital information of a song up the wire to the headphone piece, which causes the air to vibrate. Energy Conversion [C]: The ipod has light energy. The electrical energy converts to light energy because it lights up the display screen on the ipod. ...
... because the electricity sends the digital information of a song up the wire to the headphone piece, which causes the air to vibrate. Energy Conversion [C]: The ipod has light energy. The electrical energy converts to light energy because it lights up the display screen on the ipod. ...
Energy Notes with Answers energy_notes_with_answers
... Energy Notes Energy: The work that energy allows us to do can be divided into 5 main tasks. 1.) Produce ...
... Energy Notes Energy: The work that energy allows us to do can be divided into 5 main tasks. 1.) Produce ...
Energy Transformations
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
... 4 - Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 - Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 - Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identify examples of kinetic and potential energy. ...
Mechanical Energy - Miss Burnett`s 6th grade Classroom
... 2) How do you think this graph might change in 10 years? _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ ...
... 2) How do you think this graph might change in 10 years? _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ ...
In every transformation, some energy is always transferred into
... What is meant by energy of position? What force affects potential energy due to position? What is meant by stored chemical energy? Give an example of potential energy due to position and potential energy due to chemical composition. How is the compression of an object considered potential ...
... What is meant by energy of position? What force affects potential energy due to position? What is meant by stored chemical energy? Give an example of potential energy due to position and potential energy due to chemical composition. How is the compression of an object considered potential ...
Page 1 of 3 FOSS California Matter and Energy Module Glossary
... Gram (g): The basic unit of mass in the metric system. Heat: A form of energy. Light: A form of energy. Light source: Anything that makes light, such as the Sun, a lightbulb, or a flame. Liquid: Matter that flows and takes the shape of the container it is in. Liter (L): The basic unit of fluid volu ...
... Gram (g): The basic unit of mass in the metric system. Heat: A form of energy. Light: A form of energy. Light source: Anything that makes light, such as the Sun, a lightbulb, or a flame. Liquid: Matter that flows and takes the shape of the container it is in. Liter (L): The basic unit of fluid volu ...
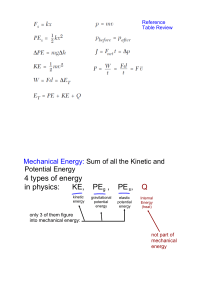
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
... Mechanical Energy: Sum of all the Kinetic and Potential Energy ...
File - Ms. Conger*6th Grade Science
... • http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/en ergy_electricity_forces/energy_transfer_stora ge/activity/ • Reviews conduction, convection, and radiation as well. ...
... • http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks3/science/en ergy_electricity_forces/energy_transfer_stora ge/activity/ • Reviews conduction, convection, and radiation as well. ...
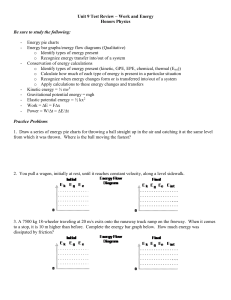
Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
... Energy bar graphs/energy flow diagrams (Qualitative) o Identify types of energy present o Recognize energy transfer into/out of a system Conservation of energy calculations o Identify types of energy present (kinetic, GPE, EPE, chemical, thermal (Eint)) o Calculate how much of each type of energy is ...
Potential Energy - Hays High School
... when 1.0 J of work is done or 1.0 J of energy is transferred in a time of 1.0 s. ...
... when 1.0 J of work is done or 1.0 J of energy is transferred in a time of 1.0 s. ...
Review
... 15. A moving car has kinetic energy. If it speeds up until it is going 3 times the original speed, how much kinetic energy does it have compared to the original? ...
... 15. A moving car has kinetic energy. If it speeds up until it is going 3 times the original speed, how much kinetic energy does it have compared to the original? ...
Energy and Power - Reeths
... • Example 1- A bike on top of a hill waiting to get the energy out by going down the hill. • Example 2- Sleeping before awakening to alarm ...
... • Example 1- A bike on top of a hill waiting to get the energy out by going down the hill. • Example 2- Sleeping before awakening to alarm ...
Chapter 12: Work and Energy
... 1. List the 6 types of simple machines. 2. Identify which simple machine the following represent: (a) a drill bit (b) a skateboard ramp (c) a boat oar 3. Describe how a lever can increase the force without changing the amount of work being done. 4. Explain why pulleys are in the lever family. 5. Com ...
... 1. List the 6 types of simple machines. 2. Identify which simple machine the following represent: (a) a drill bit (b) a skateboard ramp (c) a boat oar 3. Describe how a lever can increase the force without changing the amount of work being done. 4. Explain why pulleys are in the lever family. 5. Com ...
Chemical Energy
... least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your ...
... least kinetic energy? When would it have the greatest and the least potential energy? If the potential energy at Y was 30,000 j and the Kinetic energy was 40,000 j, what is the mechanical energy of the cart? What do you think the potential and kinetic energy at points w and x would be based on your ...