Energy review 2016 - Mayfield City Schools
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
Energy Review Name: Fill in: 1. The energy associated with the
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
... 1. The energy associated with the motion and position of an object. is known as ___________________________ It is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. 2. _________________________ is a quantity that is related to the ability of an object to change or cause change. 3. _____________________ ...
Energy Conservation Notes Filled-in
... What does conservation mean? To save or protect Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created nor destroyed it can only change forms What is an engineer? A person who designs energy transformations. Trace back the energy involved with consuming an apple. ...
... What does conservation mean? To save or protect Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created nor destroyed it can only change forms What is an engineer? A person who designs energy transformations. Trace back the energy involved with consuming an apple. ...
Post Test
... 18. The ability to do work is called _________. 19. __________ energy is energy of position. 20. _________ energy is the most concentrated form of energy. ...
... 18. The ability to do work is called _________. 19. __________ energy is energy of position. 20. _________ energy is the most concentrated form of energy. ...
Forms of Energy Research Energy Form Description Examples and
... As you have studied potential and kinetic energy, you have realized that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Instead, energy transfers from one form to another. You are already familiar with mechanical energy, (the energy of motion), but what about when objects are not in motion? What are the oth ...
... As you have studied potential and kinetic energy, you have realized that energy cannot be created or destroyed. Instead, energy transfers from one form to another. You are already familiar with mechanical energy, (the energy of motion), but what about when objects are not in motion? What are the oth ...
CURRICULUM MAPPING EXAMPLES Grade : 9 Physical Science
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
Curriculum Mapping Samples
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
... Students will investigate forces and the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (I,,R, M) Objects change their motion only when a net force is applied. Laws of motion are used to describe the effects of forces on the motions of objects. (SC-H-1.4.1) (I, R, M) Gravity is a universal force that ...
Example
... We can measure the energy by burning it in calorimeter, since the (heat) energy given out in the burning process is nearly is the same when it is digested and absorb inside body, so the energy can be easily measure. The set up of the calorimeter have known amount of water. Then the food is light up ...
... We can measure the energy by burning it in calorimeter, since the (heat) energy given out in the burning process is nearly is the same when it is digested and absorb inside body, so the energy can be easily measure. The set up of the calorimeter have known amount of water. Then the food is light up ...
x F F=kx
... “In my exercise physiology class we learned about the Running Anaerobic Sprint Test that is used to evaluate power output for runners. I figured the mass of an athlete to be around 72.6kg The formula used is Power=(bodymass*distance^2)/time^3. But then I thought about the Kinetic energy equation whi ...
... “In my exercise physiology class we learned about the Running Anaerobic Sprint Test that is used to evaluate power output for runners. I figured the mass of an athlete to be around 72.6kg The formula used is Power=(bodymass*distance^2)/time^3. But then I thought about the Kinetic energy equation whi ...
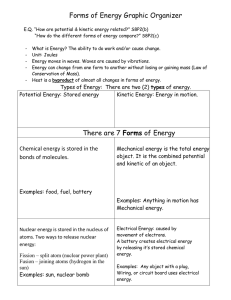
Forms of Energy
... E.Q. “How are potential & kinetic energy related?” S8P2(b) “How do the different forms of energy compare?” S8P2(c) ...
... E.Q. “How are potential & kinetic energy related?” S8P2(b) “How do the different forms of energy compare?” S8P2(c) ...
Sci_ch9_Lesson_3_notes
... hill, pencil on the edge of your desk Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. Examples: roller coaster moving along the track, ball rolling across the ground. Types of kinetic energy include electricity, light, sound, heat, and motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object ...
... hill, pencil on the edge of your desk Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. Examples: roller coaster moving along the track, ball rolling across the ground. Types of kinetic energy include electricity, light, sound, heat, and motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object ...
Chapter 5 – Work and Energy Study Guide
... 2. Work is only done by forces (or components of forces) that are parallel to the displacement 3. No work is done by forces (or components of forces) that are perpendicular to the displacement 4. Work = force X displacement 5. W = F dcos θ 6. Wnet = Fnet d cos 7. Units of work: N m = J 8. PRA ...
... 2. Work is only done by forces (or components of forces) that are parallel to the displacement 3. No work is done by forces (or components of forces) that are perpendicular to the displacement 4. Work = force X displacement 5. W = F dcos θ 6. Wnet = Fnet d cos 7. Units of work: N m = J 8. PRA ...
File
... • A screw is simply an inclined plane that is wrapped around a cylinder or a cone. The main purpose is to raise a load over the threads, which is the spiral part of the screw, by applying a small force. ...
... • A screw is simply an inclined plane that is wrapped around a cylinder or a cone. The main purpose is to raise a load over the threads, which is the spiral part of the screw, by applying a small force. ...
Forms of Energy
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
... Energy is found in different forms including light, heat, chemical, and motion. There are many forms of energy, but they can all be put into two categories: potential and kinetic. ...
Heat and Energy
... Use caloric values to calculate the kilocalories (Cal) in a food. Given a temperature, calculate a corresponding temperature on another scale. Use specific heat to calculate heat loss or gain, temperature change, or mass of a sample. Identify the physical state of a substance as a solid, liquid, or ...
... Use caloric values to calculate the kilocalories (Cal) in a food. Given a temperature, calculate a corresponding temperature on another scale. Use specific heat to calculate heat loss or gain, temperature change, or mass of a sample. Identify the physical state of a substance as a solid, liquid, or ...
HW5 - Problem 3
... used to model atoms or, more generically, as a parallel particle simulator at the atomic, meso, or continuum scale. Uses material “Potentials” to predict probability of interaction. TRIM requires much less computational power than LAMMPS as it uses simplified physics and collision approximations. SP ...
... used to model atoms or, more generically, as a parallel particle simulator at the atomic, meso, or continuum scale. Uses material “Potentials” to predict probability of interaction. TRIM requires much less computational power than LAMMPS as it uses simplified physics and collision approximations. SP ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... We will also study the types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. Again, we will look at real life scenarios and calculate the amount of kinetic, gravitational potential energy or elas ...
... We will also study the types of energy involved in doing work (potential and kinetic, as well as other forms) and how work is done to transform that energy from one form to another. Again, we will look at real life scenarios and calculate the amount of kinetic, gravitational potential energy or elas ...
Ideas about Work and Energy
... moving. Potential Energy (gravitational) = mgh. This is the energy an object has because it has height and the potential to fall. ...
... moving. Potential Energy (gravitational) = mgh. This is the energy an object has because it has height and the potential to fall. ...
Chapter 6: Energy and Technology
... bioenergy: energy from organic matter. Biochemicals, biofuels, and biopower are three ways bioenergy is used. biomass: the sum of all organic matter in an area. chemical energy: a reaction between two substances when mixed. For example, when petroleum and oxygen are mixed, they will burn rapidly, if ...
... bioenergy: energy from organic matter. Biochemicals, biofuels, and biopower are three ways bioenergy is used. biomass: the sum of all organic matter in an area. chemical energy: a reaction between two substances when mixed. For example, when petroleum and oxygen are mixed, they will burn rapidly, if ...
Energy Unit Class Notes
... Energy Unit Class Notes Energy – the ability to do work (joules) - kinetic and potential Types of Energy 1. Mechanical – the energy of movement or position (KE + PE) - sound is an example of mechanical energy 2. Thermal (heat) energy – total energy of the moving molecules within a substance Temperat ...
... Energy Unit Class Notes Energy – the ability to do work (joules) - kinetic and potential Types of Energy 1. Mechanical – the energy of movement or position (KE + PE) - sound is an example of mechanical energy 2. Thermal (heat) energy – total energy of the moving molecules within a substance Temperat ...