Energy Transformation Demos
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy using a generator o Electromagnetic Energy Energy from Sun created by fusion…form ...
... o Electrical Energy (energy of moving electrons) Mechanical energy is usually converted to electrical energy using a generator o Electromagnetic Energy Energy from Sun created by fusion…form ...
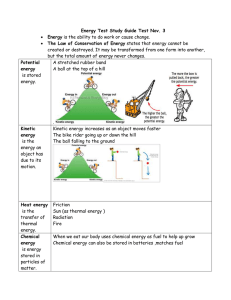
Energy Test Study Guide
... Sun (as thermal energy ) Radiation Fire When we eat our body uses chemical energy as fuel to help up grow Chemical energy can also be stored in batteries ,matches fuel ...
... Sun (as thermal energy ) Radiation Fire When we eat our body uses chemical energy as fuel to help up grow Chemical energy can also be stored in batteries ,matches fuel ...
Energy Assesment 1
... Q2. Energy cannot be destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Give 3 examples. ...
... Q2. Energy cannot be destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another. Give 3 examples. ...
energy-powerpoint
... • Work is a change in a position caused by a force. – Moving a pencil, opening a door, and carrying a backpack are examples of work. – What are some agricultural examples of ...
... • Work is a change in a position caused by a force. – Moving a pencil, opening a door, and carrying a backpack are examples of work. – What are some agricultural examples of ...
I hypothesize a correlation between irradiation of the
... I use the Arrival Time Difference Thunderstorm data to obtain an estimate of the measured energy stored in the ground (ignoring the invisible discharges), due to the electrostatic forces: the density of the lightning in Europe is 0.1 − 4 flashes for km2 for year, so that the mean energy release is ( ...
... I use the Arrival Time Difference Thunderstorm data to obtain an estimate of the measured energy stored in the ground (ignoring the invisible discharges), due to the electrostatic forces: the density of the lightning in Europe is 0.1 − 4 flashes for km2 for year, so that the mean energy release is ( ...
Energy - ability of an object to do work
... Energy - ability of an object to do work Potential energy – ability of an object to have energy Kinetic energy – the actual movement of an object Mechanical – when potential and kinetic energy are put to an object Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a ...
... Energy - ability of an object to do work Potential energy – ability of an object to have energy Kinetic energy – the actual movement of an object Mechanical – when potential and kinetic energy are put to an object Electric energy – form of moving energy that has a flow of electric charges Circuit- a ...
Additional Energy Terms
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
... Name and describe different types of energy. • Potential: chemical, gravitational, elastic, nuclear, magnetic • Kinetic: motion, heat, electric, light, sound What can happen to energy? • Transfer or transformation. Always conserved. Heat energy: movement/vibration of molecules. Measured by temperatu ...
File
... 4. A 12-kg sled is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. At what speed will the sled have twice as much kinetic energy? 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give three examples of objects with elastic potential energy. 7. A 3-kilogram cat is resting on top of a bookshelf th ...
... 4. A 12-kg sled is moving at a speed of 5 m/s. At what speed will the sled have twice as much kinetic energy? 5. An object’s gravitational potential energy is directly related to… 6. Give three examples of objects with elastic potential energy. 7. A 3-kilogram cat is resting on top of a bookshelf th ...
Energy Study Guide Key
... 2. Explain the transfer of energy. Give 3 examples. When one form of energy changes into another form of energy; gasoline in a lawn mower – chemical to mechanical; coal-power plants – chemical to electrical; light bulb – electrical to heat and light; toaster – electrical to heat; power drill – elect ...
... 2. Explain the transfer of energy. Give 3 examples. When one form of energy changes into another form of energy; gasoline in a lawn mower – chemical to mechanical; coal-power plants – chemical to electrical; light bulb – electrical to heat and light; toaster – electrical to heat; power drill – elect ...
The Down-Low On Energy
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
... There are many ways to measure energy but one of the main constant units of measure is the: • BTU: British Thermal Unit • 1 BTU is the amount of energy it takes to heat 1 pound of water 1 degrees F. ...
Unit 2 - Glenbard #87
... motion and interactions of matter and radiation with that system. situations in all places?) The single quantity called energy is due to the fact that a system’s total energy is conserved, eve ...
... motion and interactions of matter and radiation with that system. situations in all places?) The single quantity called energy is due to the fact that a system’s total energy is conserved, eve ...
Energy Conversion Quiz Answer Key
... 10. Give an example of energy changing from one form to another. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Energy changes from chemical energy to mechanical energy when you digest food and use the energy it releases to move your body. ...
... 10. Give an example of energy changing from one form to another. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Energy changes from chemical energy to mechanical energy when you digest food and use the energy it releases to move your body. ...
Energy - Office Mix
... Calculate Kinetic Energy Distinguish between kinetic energy and Potential energy • Classify different types of potential Energy • Calculate Potential energy associated with an object ...
... Calculate Kinetic Energy Distinguish between kinetic energy and Potential energy • Classify different types of potential Energy • Calculate Potential energy associated with an object ...
Energy and energy resources
... Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually be silent) Light- the ...
... Electrical- when the electrons in a wire ( or other substance) move back and forth. Sound- is the movement and vibrations of particles in the air, usually caused by movement. ( needs particles to work, there is no sound in space, so a space ship blowing up would actually be silent) Light- the ...
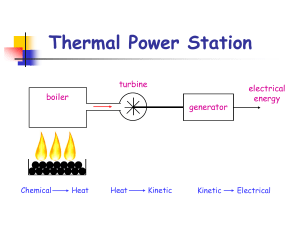
Thermal Power Station
... More neutrons are also released which can go on to split more Uranium nuclei. Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to absorb some of these new neutrons preventing too much energy being released in a short time. ...
... More neutrons are also released which can go on to split more Uranium nuclei. Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to absorb some of these new neutrons preventing too much energy being released in a short time. ...
short
... Solar Radiation Received at Earth’s Surface: average is about 150 watts per square meter ...
... Solar Radiation Received at Earth’s Surface: average is about 150 watts per square meter ...
2-ch50182-energy
... Energy is always conserved but … … can be transformed from one form to another Energy, E (unit: 1 joule = 1 J or N m) Power, P = dE / dt (unit: 1 watt = 1 J s-1 or 1 W) (where time, t / s) 1 J is about the energy required to raise 100 g (e. g., a mobile phone) vertically 1 m against Earth’s gravity ...
... Energy is always conserved but … … can be transformed from one form to another Energy, E (unit: 1 joule = 1 J or N m) Power, P = dE / dt (unit: 1 watt = 1 J s-1 or 1 W) (where time, t / s) 1 J is about the energy required to raise 100 g (e. g., a mobile phone) vertically 1 m against Earth’s gravity ...
Resource Page Work, Power, and Energy
... SC.4.P.10.4 - Describe how moving water and air are sources of energy and can be used to move things. SC.5.P.10.1 - Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. SC.5.P.10.2 - Investigate and explain that energy has the abili ...
... SC.4.P.10.4 - Describe how moving water and air are sources of energy and can be used to move things. SC.5.P.10.1 - Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. SC.5.P.10.2 - Investigate and explain that energy has the abili ...
What Is Energy Power Point
... • No matter how you do the work (with or without simple machines), the amount of work done is the same. • No matter how you transfer energy (with or without simple machines), the amount of energy transferred is the same. ...
... • No matter how you do the work (with or without simple machines), the amount of work done is the same. • No matter how you transfer energy (with or without simple machines), the amount of energy transferred is the same. ...