* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sci_ch9_Lesson_3_notes
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
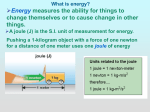
Lesson 3 Energy Energy is the ability to perform work or to change an object. Work is the measurement of the energy used to perform a task. Work = force x distance. The unit of measure for work and energy is joules (J). Potential Energy: Energy does not always involve motion. Potential energy is energy that is stored in the position or the structure of an object. Types of potential energy: -Chemical potential energy is energy in the links between atoms and molecules. Examples: food, matches - Elastic potential energy is the energy stored by something that can stretch or compress. Examples: stretched rubber band, slingshot, spring, bow - Gravitational potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position above Earth’s surface. Examples: boulder on a hill, pencil on the edge of your desk Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy of a moving object. Examples: roller coaster moving along the track, ball rolling across the ground. Types of kinetic energy include electricity, light, sound, heat, and motion. The amount of kinetic energy an object has depends on the object’s velocity (speed/direction). The faster an object moves, the greater the kinetic energy the object has. Potential energy can easily change to kinetic energy. Like when you use a bow to shoot an arrow. Law of conservation of energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes from one form to another.