energy
... (gravitational potential energy) and bounce height (kinetic energy). Students build on that knowledge as they investigate how the amount of energy transferred by a moving marble changes depending on the marble’s mass. 1. Recognize the different forms of energy and how energy can transform from one f ...
... (gravitational potential energy) and bounce height (kinetic energy). Students build on that knowledge as they investigate how the amount of energy transferred by a moving marble changes depending on the marble’s mass. 1. Recognize the different forms of energy and how energy can transform from one f ...
Lesson Plans 082415
... Monday, August 24, 2015 – Friday, August 28, 2015 Unit Overview The focus will be for students to recognize the properties and sources of different forms of energy including mechanical, electrical, chemical, radiant (solar), and thermal energy. By the end of the 6th grade students should demonstrate ...
... Monday, August 24, 2015 – Friday, August 28, 2015 Unit Overview The focus will be for students to recognize the properties and sources of different forms of energy including mechanical, electrical, chemical, radiant (solar), and thermal energy. By the end of the 6th grade students should demonstrate ...
Energy Education Teaching Ideas for Homeschool
... instead. But you don’t stretch gasoline to make it work, you burn it. You could release energy by burning rubber bands, but it is not practical to do so (it would take too many rubber bands and make too much of a mess!). The chemical makeup of gasoline (the arrangement of its molecules) makes it a g ...
... instead. But you don’t stretch gasoline to make it work, you burn it. You could release energy by burning rubber bands, but it is not practical to do so (it would take too many rubber bands and make too much of a mess!). The chemical makeup of gasoline (the arrangement of its molecules) makes it a g ...
Lesson 3: Energy Takes Many Forms
... Students may have already noticed that some of the forms described are stored forms of energy and some are moving forms of energy. Explain to students that scientists often categorize different forms of energy into two groups: potential energy and kinetic energy. Discuss the terms “potential” or “ki ...
... Students may have already noticed that some of the forms described are stored forms of energy and some are moving forms of energy. Explain to students that scientists often categorize different forms of energy into two groups: potential energy and kinetic energy. Discuss the terms “potential” or “ki ...
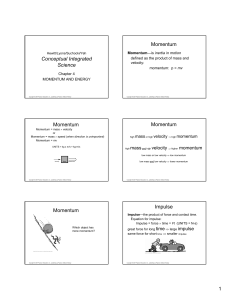
Conceptual Integrated Science Momentum Momentum Momentum
... Work falls into two categories: • work done against another force • work done to change the speed of an object ...
... Work falls into two categories: • work done against another force • work done to change the speed of an object ...
Chapter 3: Thermal Energy and Heat
... Gravitational Potential Energy The rock hanging above the ground has a form of stored energy called gravitational potential energy. This form of energy is due to the downward pull of Earth’s gravity. Gravitational potential energy depends on an object’s mass and its height above the ground. The hang ...
... Gravitational Potential Energy The rock hanging above the ground has a form of stored energy called gravitational potential energy. This form of energy is due to the downward pull of Earth’s gravity. Gravitational potential energy depends on an object’s mass and its height above the ground. The hang ...
Bronwyn Moroney B.Ed, P.G. Dip.Ed
... 1. Watch a video of a roller coaster or someone skate boarding. Discuss the movement and energy needs at different points of the ride, i.e. up versus going down. Why does a coaster go up on its own? What causes this? Would it be faster with more people in it or less? Why? Look at the way it is desig ...
... 1. Watch a video of a roller coaster or someone skate boarding. Discuss the movement and energy needs at different points of the ride, i.e. up versus going down. Why does a coaster go up on its own? What causes this? Would it be faster with more people in it or less? Why? Look at the way it is desig ...
Lesson 3: Energy Takes Many Forms
... Students may have already noticed that some of the forms described are stored forms of energy and some are moving forms of energy. Explain to students that scientists often categorize different forms of energy into two groups: potential energy and kinetic energy. Discuss the terms “potential” or “ki ...
... Students may have already noticed that some of the forms described are stored forms of energy and some are moving forms of energy. Explain to students that scientists often categorize different forms of energy into two groups: potential energy and kinetic energy. Discuss the terms “potential” or “ki ...
Pre-notes across the bottom of home screen: Energy makes all
... Pre-notes across the bottom of home screen: Energy makes all movement and change possible. It exists in many forms. Your body gives off heat energy. Land and the oceans are warmed by solar energy. Electrical energy flows through wires. This app explores several forms of energy with videos and fun fa ...
... Pre-notes across the bottom of home screen: Energy makes all movement and change possible. It exists in many forms. Your body gives off heat energy. Land and the oceans are warmed by solar energy. Electrical energy flows through wires. This app explores several forms of energy with videos and fun fa ...
S1 Topic 10 Energy
... This set of ELA materials focuses on Energy Changes and covers Section 4.2, Unit 4 of the CDC Science syllabus. The activities include three tasks (A, B and C) and can be completed within an 80-min lesson. Task A helps students to review what they have learned in Part I; it includes a vocabulary exe ...
... This set of ELA materials focuses on Energy Changes and covers Section 4.2, Unit 4 of the CDC Science syllabus. The activities include three tasks (A, B and C) and can be completed within an 80-min lesson. Task A helps students to review what they have learned in Part I; it includes a vocabulary exe ...
8.21 The Physics of Energy
... • Units: All these different forms must have the same units of mass × length2 / time2 ) • Review a little 8.01 & 8.02 and see what’s to come ...
... • Units: All these different forms must have the same units of mass × length2 / time2 ) • Review a little 8.01 & 8.02 and see what’s to come ...
Ch04_Clicker_Questions - Saint Leo University Faculty
... from rest from the top of a one-story building. When hitting the ground below, compared with the 1-kg ball, the 10-kg ball has a) less momentum and KE. b) the same momentum and KE. c) 10 times as much momentum and 10 times as much KE. d) 10 times as much momentum and 100 times as much KE. ...
... from rest from the top of a one-story building. When hitting the ground below, compared with the 1-kg ball, the 10-kg ball has a) less momentum and KE. b) the same momentum and KE. c) 10 times as much momentum and 10 times as much KE. d) 10 times as much momentum and 100 times as much KE. ...
Energy HD APP Student - Moore Public Schools
... Energy makes all movement and change possible. It exists in many forms. Your body gives off heat energy. Land and the oceans are warmed by solar energy. Electrical energy flows through wires. This app explores several forms of energy with videos and fun facts. We will explore the major types of ener ...
... Energy makes all movement and change possible. It exists in many forms. Your body gives off heat energy. Land and the oceans are warmed by solar energy. Electrical energy flows through wires. This app explores several forms of energy with videos and fun facts. We will explore the major types of ener ...
6.9C Energy Transformations
... electrons (-). If the charges are not moving, we call it static electricity (potential energy). Examples of static electrical energy are the charge a person picks up when walking across carpet, charges in a cloud just before a lightning discharge, and the charge stored in a capacitor in an electrica ...
... electrons (-). If the charges are not moving, we call it static electricity (potential energy). Examples of static electrical energy are the charge a person picks up when walking across carpet, charges in a cloud just before a lightning discharge, and the charge stored in a capacitor in an electrica ...
Energy - Schoolwires.net
... source into electric energy. • One source of energy comes from burning fuels, such as coal. • Nuclear power plants use the nuclear energy in uranium and hydroelectric power plants convert the kinetic energy in falling water into electric energy. ...
... source into electric energy. • One source of energy comes from burning fuels, such as coal. • Nuclear power plants use the nuclear energy in uranium and hydroelectric power plants convert the kinetic energy in falling water into electric energy. ...
Energy - Schoolwires.net
... source into electric energy. • One source of energy comes from burning fuels, such as coal. • Nuclear power plants use the nuclear energy in uranium and hydroelectric power plants convert the kinetic energy in falling water into electric energy. ...
... source into electric energy. • One source of energy comes from burning fuels, such as coal. • Nuclear power plants use the nuclear energy in uranium and hydroelectric power plants convert the kinetic energy in falling water into electric energy. ...
Energy powerpoint
... its advantages and disadvantages. • One disadvantage is the amount of uranium in Earth’s crust is nonrenewable. • Another is that the waste produced by nuclear power plants is radioactive and can be dangerous to living things. ...
... its advantages and disadvantages. • One disadvantage is the amount of uranium in Earth’s crust is nonrenewable. • Another is that the waste produced by nuclear power plants is radioactive and can be dangerous to living things. ...
Energy - Pflugerville ISD
... energy to do the work of cooling. A machine called a compressor does the work of compressing a refrigerant. A refrigerant is a gas that can easily change state to become liquid. Chapter 5 Section 3 ...
... energy to do the work of cooling. A machine called a compressor does the work of compressing a refrigerant. A refrigerant is a gas that can easily change state to become liquid. Chapter 5 Section 3 ...
Energy - Glencoe
... Recall that in the SI system of units, time is measured in seconds and distance is measured in meters. In the SI system of units, energy is measured using a unit called the joule (J). A student with a mass of 50 kg walking at a speed of 2 m/s has 100 J of kinetic energy. The same student sitting on ...
... Recall that in the SI system of units, time is measured in seconds and distance is measured in meters. In the SI system of units, energy is measured using a unit called the joule (J). A student with a mass of 50 kg walking at a speed of 2 m/s has 100 J of kinetic energy. The same student sitting on ...
Using Content-Aligned Assessment to Probe Middle
... energy. These five key ideas focus on the nature of four different forms or manifestations of energy. Ideas dealing with energy transformations, transfer, and conservation are dealt with in a separate topic. Those results will be reported at another time. Each student received four or five assessmen ...
... energy. These five key ideas focus on the nature of four different forms or manifestations of energy. Ideas dealing with energy transformations, transfer, and conservation are dealt with in a separate topic. Those results will be reported at another time. Each student received four or five assessmen ...
Chapter 6 Resource: Energy
... Because of your height on the mountain, you have potential energy. As you ski down the side of the mountain, your speed and kinetic energy increase, but as you lose height, your potential energy decreases. Where does your potential energy go? Where does your kinetic energy come from? ...
... Because of your height on the mountain, you have potential energy. As you ski down the side of the mountain, your speed and kinetic energy increase, but as you lose height, your potential energy decreases. Where does your potential energy go? Where does your kinetic energy come from? ...
Chapter 15 Energy
... • It is nonpolluting and available in this area due to naturally occurring hot springs • most places are not near a volcano or hot springs • Def: biomass energy is the energy stored in living things • Biomass can be converted directly to thermal energy • Agricultural waste such as turning corn into ...
... • It is nonpolluting and available in this area due to naturally occurring hot springs • most places are not near a volcano or hot springs • Def: biomass energy is the energy stored in living things • Biomass can be converted directly to thermal energy • Agricultural waste such as turning corn into ...
Section 1 What Is Energy?
... • Potential energy is the energy an object has because of its position. • Elastic potential energy can be stored in objects like bowstrings, springs, and rubber bands. The energy put into stretching becomes elastic potential energy. • Gravitational Potential Energy The amount of gravitational potent ...
... • Potential energy is the energy an object has because of its position. • Elastic potential energy can be stored in objects like bowstrings, springs, and rubber bands. The energy put into stretching becomes elastic potential energy. • Gravitational Potential Energy The amount of gravitational potent ...
Energy
... Roller coasters work because of the energy that is built into the system. Initially, the cars are pulled mechanically up the tallest hill, giving them a great deal of potential energy. From that point, the conversion between potential and kinetic energy powers the cars throughout the entire ride. ...
... Roller coasters work because of the energy that is built into the system. Initially, the cars are pulled mechanically up the tallest hill, giving them a great deal of potential energy. From that point, the conversion between potential and kinetic energy powers the cars throughout the entire ride. ...
Regenerative brake

A regenerative brake is an energy recovery mechanism which slows a vehicle or object by converting its kinetic energy into a form which can be either used immediately or stored until needed. This contrasts with conventional braking systems, where the excess kinetic energy is converted to heat by friction in the brakes and therefore wasted. In addition to improving the overall efficiency of the vehicle, regeneration can also greatly extend the life of the braking system as its parts do not wear as quickly.