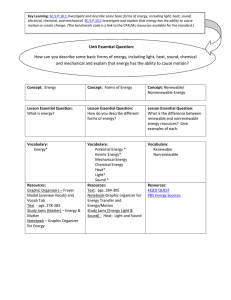
Energy Terms and Concepts
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. For example stored chemical energy in a battery can be converted to light in a flashlight. Or falling water can be used to turn a turbine, which motion can be used to make electricity ...
... Energy can be converted from one form to another. For example stored chemical energy in a battery can be converted to light in a flashlight. Or falling water can be used to turn a turbine, which motion can be used to make electricity ...
Energy Curriculum Map
... electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources available for the standard.) ...
... electrical, chemical, and mechanical SC.5.P.10.2 Investigate and explain that energy has the ability to cause motion or create change. (The benchmark code is a link to the CPALMs resources available for the standard.) ...
temperature
... • The amount of energy another in that system, in a system is always the and it can be same; no energy is ever transformed from one created, and no energy kind of energy to is ever destroyed. another kind of energy. ...
... • The amount of energy another in that system, in a system is always the and it can be same; no energy is ever transformed from one created, and no energy kind of energy to is ever destroyed. another kind of energy. ...
General
... Work is a transfer of (Energy) Energy of motion is what type of energy (Kinetic) Energy due to an object position or shape (Potential) 1 Newton meter is a (Joule) On the moon an object has the same mass as on earth, but a different (Weight) Energy stored in gasoline is what type of energy (Chemical) ...
... Work is a transfer of (Energy) Energy of motion is what type of energy (Kinetic) Energy due to an object position or shape (Potential) 1 Newton meter is a (Joule) On the moon an object has the same mass as on earth, but a different (Weight) Energy stored in gasoline is what type of energy (Chemical) ...
Potential and Kinetic energy
... C. __________________(KE) – energy of… Energy of motion 1. Depends on the ____________and _____________ of the moving object 2. Faster and more massive = D. Other forms of energy 1. Kinetic molecular energy energy of moving atoms and molecules 2. ________ energy energy released in chemical rea ...
... C. __________________(KE) – energy of… Energy of motion 1. Depends on the ____________and _____________ of the moving object 2. Faster and more massive = D. Other forms of energy 1. Kinetic molecular energy energy of moving atoms and molecules 2. ________ energy energy released in chemical rea ...
notes
... Catalysts are substances that change the rate of a chemical reaction with out being consumed in the reaction If the catalyst is a protein and is part of a biological reaction then it is an ENZYME Enzymes (catalysts) decrease the energy of activation required to start the reaction Heat and stirri ...
... Catalysts are substances that change the rate of a chemical reaction with out being consumed in the reaction If the catalyst is a protein and is part of a biological reaction then it is an ENZYME Enzymes (catalysts) decrease the energy of activation required to start the reaction Heat and stirri ...
Energy and Temperature
... Many chemical reactions either create or release energy when they occur. Forms of energy include: ...
... Many chemical reactions either create or release energy when they occur. Forms of energy include: ...
Lecture 4. - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Chemical Energy • Energy stored in structural units of chemicals Units = Joules • 1 Joule (J) = 1 kg m2 /s2 • 1 Calorie (cal) = 4.184 J ...
... Chemical Energy • Energy stored in structural units of chemicals Units = Joules • 1 Joule (J) = 1 kg m2 /s2 • 1 Calorie (cal) = 4.184 J ...
ENERGY power point
... nuclear power plants) or by combining atoms (known as fusion- happens in the sun and in nuclear bombs) Fusion Fission ...
... nuclear power plants) or by combining atoms (known as fusion- happens in the sun and in nuclear bombs) Fusion Fission ...
Work, Power and Energy
... cannot cause vertical displacements. The only means by which an external force can contribute to a potential energy change is if the force has a vertical component. Potential energy changes are the result of height changes and only a force with a vertical component can cause a height change. ...
... cannot cause vertical displacements. The only means by which an external force can contribute to a potential energy change is if the force has a vertical component. Potential energy changes are the result of height changes and only a force with a vertical component can cause a height change. ...
WORK (a) (b) Who is doing more work?
... · Work is defined as the product of the net force acting on a body and the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work = force x parallel distance W= F x d · SI Units of work are joules (1 joule =1 Nm= 1 kgm 2 /s 2 ) ...
... · Work is defined as the product of the net force acting on a body and the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work = force x parallel distance W= F x d · SI Units of work are joules (1 joule =1 Nm= 1 kgm 2 /s 2 ) ...
Study Guide: Forces and Motion Motion and Speed The motion of an
... Objects that have potential energy do not use it until they move. That is why it is called “potential” energy. Potential means that something is capable of becoming active. Any object that can move to a lower place has the potential to do work on the way down – like a soccer ball rolling down a driv ...
... Objects that have potential energy do not use it until they move. That is why it is called “potential” energy. Potential means that something is capable of becoming active. Any object that can move to a lower place has the potential to do work on the way down – like a soccer ball rolling down a driv ...
Third Six Weeks SFA/Energy Transformation Review
... What is it called when one form of energy changes to another form of energy? Energy Transformation What energy transformation happens when you turn on a light? Electrical to Light What energy transformation occurs when wood is burned in a fireplace? Chemical to Thermal What energy transformation hap ...
... What is it called when one form of energy changes to another form of energy? Energy Transformation What energy transformation happens when you turn on a light? Electrical to Light What energy transformation occurs when wood is burned in a fireplace? Chemical to Thermal What energy transformation hap ...
Superconcepts
... 1. Energy is the ability to move an object against a force, to raise the temperature of an object, or the potential to do either. 2. Unless they involve the use or production of gases, chemical reactions involve potential energy and heat, but not kinetic energy. 3. Energy is conserved, but is transf ...
... 1. Energy is the ability to move an object against a force, to raise the temperature of an object, or the potential to do either. 2. Unless they involve the use or production of gases, chemical reactions involve potential energy and heat, but not kinetic energy. 3. Energy is conserved, but is transf ...
Forms of Energy and Energy Conservation
... The nucleus of an atom is the source of nuclear energy. When the nucleus splits (fission), nuclear energy is released in the form of heat energy and light energy. ...
... The nucleus of an atom is the source of nuclear energy. When the nucleus splits (fission), nuclear energy is released in the form of heat energy and light energy. ...
Energy - RidenourMHS
... Energy Types of energy Potential Energy Stored energy Stored in chemical bonds and the possibility of movement Kinetic Energy - Energy of motion - Part 2 of the Kinetic Theory!!! - Solids << liquids << gas ...
... Energy Types of energy Potential Energy Stored energy Stored in chemical bonds and the possibility of movement Kinetic Energy - Energy of motion - Part 2 of the Kinetic Theory!!! - Solids << liquids << gas ...
Faculty Mentor: Dr. Robert Ryan Project Supervisor: Dr. George
... The sample is first electrically loaded by applying a voltage across the top and bottom electrodes, then an axial compressive stress is applied to the specimen via a servo-hydraulic test frame (not shown in Figure 2) for mechanical characterization. The sample is isolated from the test frame via an ...
... The sample is first electrically loaded by applying a voltage across the top and bottom electrodes, then an axial compressive stress is applied to the specimen via a servo-hydraulic test frame (not shown in Figure 2) for mechanical characterization. The sample is isolated from the test frame via an ...
Science 9 Electrical Devices Energy is the ability to do The four most
... Chemical energy can also be converted into mechanical and energy (a CD player). Chemical energy can also be transformed into mechanical energy, with and light (dynamite). ...
... Chemical energy can also be converted into mechanical and energy (a CD player). Chemical energy can also be transformed into mechanical energy, with and light (dynamite). ...
energy - Denton ISD
... • Potential: stored energy and energy of position • Kinetic: motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules and substances. ...
... • Potential: stored energy and energy of position • Kinetic: motion of waves, electrons, atoms, molecules and substances. ...
ENERGY
... • Rapid variation of electric and magnetic field • Examples: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays, etc ...
... • Rapid variation of electric and magnetic field • Examples: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays, etc ...
Types of Energy
... • Examples: biomass (wood), fossil fuels (oil), batteries, living organisms-plants/animals ...
... • Examples: biomass (wood), fossil fuels (oil), batteries, living organisms-plants/animals ...