• Thermodynamics, what is it? • System, Surrounding and Boundary
... • is developed based on empirical observations • describes macroscopic quantities, such as heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs free energy, etc. • does not contain any information about the state or even existence of molecules! • assumes that the world is made up of a continuum Qua ...
... • is developed based on empirical observations • describes macroscopic quantities, such as heat, work, internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs free energy, etc. • does not contain any information about the state or even existence of molecules! • assumes that the world is made up of a continuum Qua ...
What is Thermodynamics?
... Therefore, the deep impression which classical thermodynamics made on me. It is the only physical theory of universal content, which I am convinced, that within the framework of applicability of its basic concepts will never be overthrown. Albert Einstein, quoted in M.J. Klein, Thermodynamics in Ein ...
... Therefore, the deep impression which classical thermodynamics made on me. It is the only physical theory of universal content, which I am convinced, that within the framework of applicability of its basic concepts will never be overthrown. Albert Einstein, quoted in M.J. Klein, Thermodynamics in Ein ...
Lecture 12
... If we decide to assign a value zero to entropies of elements in their perfect crystalline form at T = 0, then all perfect crystalline compounds have entropy = 0 at T = 0 Third Law of Thermodynamics If the entropy of every element in its most stable state at T = 0 is taken as zero, then every substan ...
... If we decide to assign a value zero to entropies of elements in their perfect crystalline form at T = 0, then all perfect crystalline compounds have entropy = 0 at T = 0 Third Law of Thermodynamics If the entropy of every element in its most stable state at T = 0 is taken as zero, then every substan ...
Second Law of thermodynamics
... • Ideal- the process is reversible, that is, is done so slow that can be considered a series of equilibrium states, so the whole process can be done in reverse with no change in the magnitude of work done or heat exchanged. • Real- the process is done more quickly so there is heat lost because of fr ...
... • Ideal- the process is reversible, that is, is done so slow that can be considered a series of equilibrium states, so the whole process can be done in reverse with no change in the magnitude of work done or heat exchanged. • Real- the process is done more quickly so there is heat lost because of fr ...
What is thermodynamics?
... In order to design materials with optimum performance in various applications, we need to know how properties change in response to their environment o These responses determine how we can synthesize/fabricate materials, build devices from materials, and how the devices will operate in a given appli ...
... In order to design materials with optimum performance in various applications, we need to know how properties change in response to their environment o These responses determine how we can synthesize/fabricate materials, build devices from materials, and how the devices will operate in a given appli ...
Midterm Exam Problem 10 Example of using van der Waals
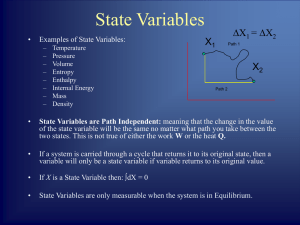
... uniquely on the state of a system makes it useful. Like internal energy U, S is a property that is not obvious, but needs to be calculated from other properties of the system. If volume V were such a nonobvious property, how could we discover it? Consider as the system an ideal gas in a cylinder con ...
... uniquely on the state of a system makes it useful. Like internal energy U, S is a property that is not obvious, but needs to be calculated from other properties of the system. If volume V were such a nonobvious property, how could we discover it? Consider as the system an ideal gas in a cylinder con ...
66 In Thermodynamics, the total energy E of our system (as
... applicable in quasi-static processes. In this process, the transfer of heat or work is infinitesimally slow, that the system is always in equilibrium, i.e. a temperature is defined. Reversible means that the process can be reversed without changing the (entropy of the) environment. • We can understa ...
... applicable in quasi-static processes. In this process, the transfer of heat or work is infinitesimally slow, that the system is always in equilibrium, i.e. a temperature is defined. Reversible means that the process can be reversed without changing the (entropy of the) environment. • We can understa ...
Black Hole Entropy in String Theory.
... entropy formula is modified. If there is a Killing horizon, then one can associate an entropy, Wald ...
... entropy formula is modified. If there is a Killing horizon, then one can associate an entropy, Wald ...
BCJ0205-15 Thermal phenomena (3-1-4)
... Important thermodynamic quantities from the atomic/molecular view-point. ...
... Important thermodynamic quantities from the atomic/molecular view-point. ...
thus
... value of U/n), which for fixed value of V and n, U will increase. Also as T increases the value of β decreases and the shape of the exponential distribution changes will be as shown in figure (4.3). As the macrostate of the system is fixed by fixing the values of U, V, and n, then T as a dependent ...
... value of U/n), which for fixed value of V and n, U will increase. Also as T increases the value of β decreases and the shape of the exponential distribution changes will be as shown in figure (4.3). As the macrostate of the system is fixed by fixing the values of U, V, and n, then T as a dependent ...
Entropy Analysis of Pressure Driven Flow in a Curved Duct
... that the inertial effect is very small and the wall wave length is comparatively large with duct width. The velocity and temperature fields are obtained analytically by solving momentum and energy equations. The entropy generation number is calculated by utilizing velocity and temperature profiles. ...
... that the inertial effect is very small and the wall wave length is comparatively large with duct width. The velocity and temperature fields are obtained analytically by solving momentum and energy equations. The entropy generation number is calculated by utilizing velocity and temperature profiles. ...
Thermodynamic Laws/Definition of Entropy Carnot Cycle
... cP > cV because the volume expands at constant pressure and the system does work which means it stores less energy. Note that for non P V T systems analogous heat capacities can be defined. In a magnetic system, P → H and V → M and we can define cH and cM . A statistical approach can be used to obta ...
... cP > cV because the volume expands at constant pressure and the system does work which means it stores less energy. Note that for non P V T systems analogous heat capacities can be defined. In a magnetic system, P → H and V → M and we can define cH and cM . A statistical approach can be used to obta ...
here
... If A and B are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium means that two bodies are in states such that if they are connected, then their condition will not change. ...
... If A and B are each in thermal equilibrium with a third body C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium means that two bodies are in states such that if they are connected, then their condition will not change. ...
Chemical Thermodynamic
... Q3. Define intensive properties? Ans3. Those properties which depend only on the nature of the substance and not on the amount of the substance taken are called Intensive properties. Q4. Why heat changes reported are usually enthalpy changes and not internal energy changes? Ans4. This is because mos ...
... Q3. Define intensive properties? Ans3. Those properties which depend only on the nature of the substance and not on the amount of the substance taken are called Intensive properties. Q4. Why heat changes reported are usually enthalpy changes and not internal energy changes? Ans4. This is because mos ...
Construction of microcanonical entropy on
... To prove that all primitives must be of the form in Eq. (14) we consider the adiabatic manifolds, namely, the L-dimensional manifolds in the space (E,λ) identified by the condition that " = const, i.e., d" = ωδQ = 0. Note that the density of states is a strictly positive function ω = ∂"/∂E > 0. This ...
... To prove that all primitives must be of the form in Eq. (14) we consider the adiabatic manifolds, namely, the L-dimensional manifolds in the space (E,λ) identified by the condition that " = const, i.e., d" = ωδQ = 0. Note that the density of states is a strictly positive function ω = ∂"/∂E > 0. This ...
derivation of some new distributions in statistical mechanics using
... mechanics. The central idea of these distributions is to predict the distribution of the microstates, which are the particle of the system, on the basis of the knowledge of some macroscopic data. The latter information is specified in the form of some simple moment constraints. One distribution diff ...
... mechanics. The central idea of these distributions is to predict the distribution of the microstates, which are the particle of the system, on the basis of the knowledge of some macroscopic data. The latter information is specified in the form of some simple moment constraints. One distribution diff ...
Entropy in thermodynamics and information theory
There are close parallels between the mathematical expressions for the thermodynamic entropy, usually denoted by S, of a physical system in the statistical thermodynamics established by Ludwig Boltzmann and J. Willard Gibbs in the 1870s, and the information-theoretic entropy, usually expressed as H, of Claude Shannon and Ralph Hartley developed in the 1940s. Shannon, although not initially aware of this similarity, commented on it upon publicizing information theory in A Mathematical Theory of Communication.This article explores what links there are between the two concepts, and how far they can be regarded as connected.