Thermodynamic Basis
... • S298: by integrating Cp/T from 0 to 298 K and using 3rd law of thermodynamics (the entropy of any homogeneous substance in complete internal equilibrium may be taken as zero at 0 K) • H298: from first principles calculations, but generally unknown ※ H298 becomes a reference value for GT ※ Introduc ...
... • S298: by integrating Cp/T from 0 to 298 K and using 3rd law of thermodynamics (the entropy of any homogeneous substance in complete internal equilibrium may be taken as zero at 0 K) • H298: from first principles calculations, but generally unknown ※ H298 becomes a reference value for GT ※ Introduc ...
5 Statistical Fluid Dynamics
... unreasonable result. However, we can understand this calamity, and use the understanding to repair (2.14). To understand why (2.14) predicts negative Yi, suppose that the initial conditions {Yi(0)} correspond to a sharp peak in the wavenumber spectrum at t=0 (Figure 5.1). At small t>0, we expect the ...
... unreasonable result. However, we can understand this calamity, and use the understanding to repair (2.14). To understand why (2.14) predicts negative Yi, suppose that the initial conditions {Yi(0)} correspond to a sharp peak in the wavenumber spectrum at t=0 (Figure 5.1). At small t>0, we expect the ...
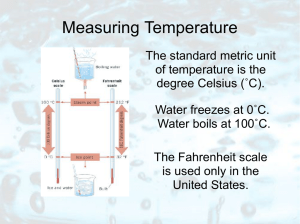
Measuring Temperature
... Our sense of how hot or cold something feels cannot be trusted. Try this! Put one hand in hot water and the other in cold. Then put them both into the same container of warm water. Conflicting messages will be sent to your brain. ...
... Our sense of how hot or cold something feels cannot be trusted. Try this! Put one hand in hot water and the other in cold. Then put them both into the same container of warm water. Conflicting messages will be sent to your brain. ...
unit ii chemical thermodynamics
... completely into work by a cyclic process without transferring a part of heat to cold body. • II law in terms of entropy: A spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in entropy of the universe. • Other statements: • All spontaneous process are irreversible • It is not possible to const ...
... completely into work by a cyclic process without transferring a part of heat to cold body. • II law in terms of entropy: A spontaneous process is always accompanied by an increase in entropy of the universe. • Other statements: • All spontaneous process are irreversible • It is not possible to const ...
Entanglement Entropies in the Ground States of Helium
... than the results of the recent calculations [16]. The only accurate value reported in the literature is that for the helium atom [18] which compares well with our result. The vN entropy for other values of Z was calculated only in Ref. [23], where the convergence of correlated Gaussian basis sets ha ...
... than the results of the recent calculations [16]. The only accurate value reported in the literature is that for the helium atom [18] which compares well with our result. The vN entropy for other values of Z was calculated only in Ref. [23], where the convergence of correlated Gaussian basis sets ha ...
Carnot - UniMAP Portal
... environment, its boundary is a thermal insulator. • But if a system has an entropy which has not yet reached its maximum equilibrium value, the entropy will increase even though the system is thermally insulated. ...
... environment, its boundary is a thermal insulator. • But if a system has an entropy which has not yet reached its maximum equilibrium value, the entropy will increase even though the system is thermally insulated. ...
Thermodynamics
... Positive when system gains heat Negative when system loses heat W = net work done by ...
... Positive when system gains heat Negative when system loses heat W = net work done by ...
Announcements
... ◆ time’s arrow always points from order to disorder l What about the Earth? Entropy can be seen to decrease the increase in entropy is equal to the amount of heat ◆ not a closed system added to the system divided ◆ energy input from the Sun ...
... ◆ time’s arrow always points from order to disorder l What about the Earth? Entropy can be seen to decrease the increase in entropy is equal to the amount of heat ◆ not a closed system added to the system divided ◆ energy input from the Sun ...
The Concentration Dependence of the
... concentration-independent entropy terms. Often, the concentration-independent determinants of ∆S are more familiar to biochemistry students. For example, most students know that the local (system) entropy decreases when differences in translational or rotational freedom cause products to be more con ...
... concentration-independent entropy terms. Often, the concentration-independent determinants of ∆S are more familiar to biochemistry students. For example, most students know that the local (system) entropy decreases when differences in translational or rotational freedom cause products to be more con ...
An equal area law for holographic entanglement entropy of the AdS
... on the temperature-entropy plane have an unstable portion when the charge is smaller than a critical value. Moreover, at critical charge, the unstable portion squeezes to an inflection point. It was subsequently pointed out in [14] that the same qualitative behavior can be observed if we study the i ...
... on the temperature-entropy plane have an unstable portion when the charge is smaller than a critical value. Moreover, at critical charge, the unstable portion squeezes to an inflection point. It was subsequently pointed out in [14] that the same qualitative behavior can be observed if we study the i ...
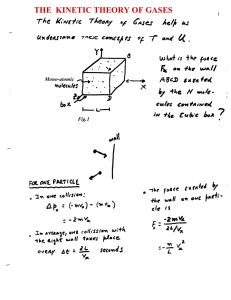
The kinetic theory of the gases
... Question: Is expression (9) still valid when considering diatomic molecules? First, let’s put expression (9) again in terms of the average kinetic energy per molecule, PV = (2/3) U = (2/3) N < ½ m v2 > (mono-atomic gas) Notice that, during its derivation we were invoking the collision of mono-atomic ...
... Question: Is expression (9) still valid when considering diatomic molecules? First, let’s put expression (9) again in terms of the average kinetic energy per molecule, PV = (2/3) U = (2/3) N < ½ m v2 > (mono-atomic gas) Notice that, during its derivation we were invoking the collision of mono-atomic ...
Review of fundamental principles ? Thermodynamics : Part I
... work giving a thermal efficiency of 100 percent. Only a part of heat transfer at high temperature in a cyclic process can be converted into work, the remaining part has to be rejected to surroundings at lower temperature. If it were possible to obtain work continuously by heat transfer with a single ...
... work giving a thermal efficiency of 100 percent. Only a part of heat transfer at high temperature in a cyclic process can be converted into work, the remaining part has to be rejected to surroundings at lower temperature. If it were possible to obtain work continuously by heat transfer with a single ...
Thermodynamics: Heat and Work
... • If a gas expands rapidly its temperature, pressure, and internal energy decrease. • If this happens in a closed environment, no heat can be transferred to or from the environment, such a process is called an adiabatic process from a Greek word meaning ...
... • If a gas expands rapidly its temperature, pressure, and internal energy decrease. • If this happens in a closed environment, no heat can be transferred to or from the environment, such a process is called an adiabatic process from a Greek word meaning ...
H-theorem

In classical statistical mechanics, the H-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to increase in the quantity H (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. As this quantity H was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the H-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics.The H-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The H-theorem has led to considerable discussion about its actual implications, with major themes being: What is entropy? In what sense does Boltzmann's quantity H correspond to the thermodynamic entropy? Are the assumptions (such as the Stosszahlansatz described below) behind Boltzmann's equation too strong? When are these assumptions violated?↑