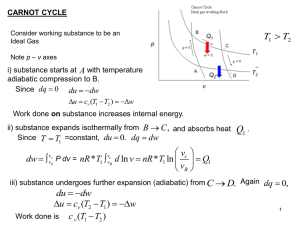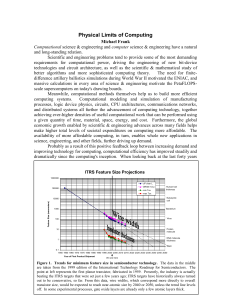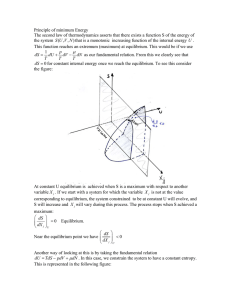
Example 1 First consider the case where there are no given
... energy Ei — note that Ei is a function of extensive thermodynamic co-ordinates such as S, V or number of particles etc. . We take the word ‘ensemble’ to be synonymous with the probability distribution. The macroscopic information which specifies the equilibrium state is the (expectation) values of ex ...
... energy Ei — note that Ei is a function of extensive thermodynamic co-ordinates such as S, V or number of particles etc. . We take the word ‘ensemble’ to be synonymous with the probability distribution. The macroscopic information which specifies the equilibrium state is the (expectation) values of ex ...
11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry
... The first law states that energy can’t be created or destroyed. In other words, when a system gains or losses energy from the surroundings, the total energy (i.e., the energy of the universe) will be constant. This is concept is expressed mathematically as: ∆E = q + w . The E (a.k.a. U) repr ...
... The first law states that energy can’t be created or destroyed. In other words, when a system gains or losses energy from the surroundings, the total energy (i.e., the energy of the universe) will be constant. This is concept is expressed mathematically as: ∆E = q + w . The E (a.k.a. U) repr ...
P - School of Chemical Sciences
... In all systems there is a tendency to evolve toward states whose properties are determined by intrinsic factors and not by previously applied external influences. Such simple states are, by definition, time-independent. They are called equilibrium states. Thermodynamics describes these simple static ...
... In all systems there is a tendency to evolve toward states whose properties are determined by intrinsic factors and not by previously applied external influences. Such simple states are, by definition, time-independent. They are called equilibrium states. Thermodynamics describes these simple static ...
2 The Laws of Black Hole Thermodynamics
... discussed in section 1.1, this is incomplete: there should be higher curvature corrections suppressed by the scale of new physics. In a general theory of gravity including curvature corrections, the formula for the entropy also receives corrections, S= ...
... discussed in section 1.1, this is incomplete: there should be higher curvature corrections suppressed by the scale of new physics. In a general theory of gravity including curvature corrections, the formula for the entropy also receives corrections, S= ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics, Preview of
... Clearly, from the ideal gas law, p2 = p1 /2. When the volume doubles isothermally, the pressure must be halved. We can figure out the entropy change by imagining an isothermal reversible expansion process between these two states ...
... Clearly, from the ideal gas law, p2 = p1 /2. When the volume doubles isothermally, the pressure must be halved. We can figure out the entropy change by imagining an isothermal reversible expansion process between these two states ...
Period 6a Activity Solutions: Entropy
... a) Does entropy naturally increase or decrease over time? Why? Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. Entropy naturally increases because systems, when left to themselves, become less ordered over time. b) Try to arrange the sets of photographs in chronological order. In which sets of pho ...
... a) Does entropy naturally increase or decrease over time? Why? Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. Entropy naturally increases because systems, when left to themselves, become less ordered over time. b) Try to arrange the sets of photographs in chronological order. In which sets of pho ...
EQATION OF STATE IN FORM WHICH RELATES MOL FRACTION
... Most people including specialists believe that a model was made that absolutely describes the thermodynamic system consisted of an ideal gas. Indeed the ideal gas state equation connects well all the parameters in an ideal gas system. But if we try to solve the following problem: A thermodynamic sys ...
... Most people including specialists believe that a model was made that absolutely describes the thermodynamic system consisted of an ideal gas. Indeed the ideal gas state equation connects well all the parameters in an ideal gas system. But if we try to solve the following problem: A thermodynamic sys ...
Thermochemistry
... Second Law of Thermodynamics One statement defining the second law is that a spontaneous natural processes tend to even out the energy gradients in a isolated system. Can be quantified based on the entropy of the system, S, such that S is at a maximum when energy is most uniform. Can also be vi ...
... Second Law of Thermodynamics One statement defining the second law is that a spontaneous natural processes tend to even out the energy gradients in a isolated system. Can be quantified based on the entropy of the system, S, such that S is at a maximum when energy is most uniform. Can also be vi ...
Entropy, Carnot Engine and Thermoelectric Effect
... Isolated System : It is the system that is both thermally and mechanically isolated from the surroundings. Thermal Equilibrium : Two systems placed in contact with each other are said to be in thermal equilibrium if no net transfer of heat takes place between them. Mechanical Equilibrium : Two mecha ...
... Isolated System : It is the system that is both thermally and mechanically isolated from the surroundings. Thermal Equilibrium : Two systems placed in contact with each other are said to be in thermal equilibrium if no net transfer of heat takes place between them. Mechanical Equilibrium : Two mecha ...
PPT
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
... We need to generalize the definition of entropy since real systems are typically spontaneous and irreversible, moving from a state of non-equilibrium to a state of equilibrium. Second law can be formulated as 4 postulates: 1. There exists a STATE VARIABLE for any substance called the ENTROPY. 2. Ent ...
Principle of minimum Energy The second law of thermodynamics
... will try to minimize its free energy F. Any isothermal process that increases the internal never occur spontaneously. Irreversible isothermal process happens spontaneously until dF = 0 (F reaches a minimum) Using the Enthalpy: Joule Thompson Effect In laboratory processes we are mostly using a const ...
... will try to minimize its free energy F. Any isothermal process that increases the internal never occur spontaneously. Irreversible isothermal process happens spontaneously until dF = 0 (F reaches a minimum) Using the Enthalpy: Joule Thompson Effect In laboratory processes we are mostly using a const ...
Physics Qualifying Examination – Part I 7-Minute Questions September 12, 2015
... How much mass, M (r), is enclosed within a radius r ? How does the average density within R compare to ρ0 ? For which values of ρ0 and R would you expect a black hole to be implied? (Hint: Escape speed?) Given that Newtonian gravity is fully described by the Poisson equation ∇ 2 Φ = 4π G ρ (x), form ...
... How much mass, M (r), is enclosed within a radius r ? How does the average density within R compare to ρ0 ? For which values of ρ0 and R would you expect a black hole to be implied? (Hint: Escape speed?) Given that Newtonian gravity is fully described by the Poisson equation ∇ 2 Φ = 4π G ρ (x), form ...
BEZOUT IDENTITIES WITH INEQUALITY CONSTRAINTS
... Pascal's law : (päskälz') [key] [for Blaise Pascal], states that pressure applied to a confined fluid at any point is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid in all directions and acts upon every part of the confining vessel at right angles to its interior surfaces and equally upon equal areas ...
... Pascal's law : (päskälz') [key] [for Blaise Pascal], states that pressure applied to a confined fluid at any point is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid in all directions and acts upon every part of the confining vessel at right angles to its interior surfaces and equally upon equal areas ...
Lecture_3 - Department of Mathematics
... Pascal's law : (päskälz') [key] [for Blaise Pascal], states that pressure applied to a confined fluid at any point is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid in all directions and acts upon every part of the confining vessel at right angles to its interior surfaces and equally upon equal areas ...
... Pascal's law : (päskälz') [key] [for Blaise Pascal], states that pressure applied to a confined fluid at any point is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid in all directions and acts upon every part of the confining vessel at right angles to its interior surfaces and equally upon equal areas ...
H-theorem

In classical statistical mechanics, the H-theorem, introduced by Ludwig Boltzmann in 1872, describes the tendency to increase in the quantity H (defined below) in a nearly-ideal gas of molecules. As this quantity H was meant to represent the entropy of thermodynamics, the H-theorem was an early demonstration of the power of statistical mechanics as it claimed to derive the second law of thermodynamics—a statement about fundamentally irreversible processes—from reversible microscopic mechanics.The H-theorem is a natural consequence of the kinetic equation derived by Boltzmann that has come to be known as Boltzmann's equation. The H-theorem has led to considerable discussion about its actual implications, with major themes being: What is entropy? In what sense does Boltzmann's quantity H correspond to the thermodynamic entropy? Are the assumptions (such as the Stosszahlansatz described below) behind Boltzmann's equation too strong? When are these assumptions violated?↑