Document
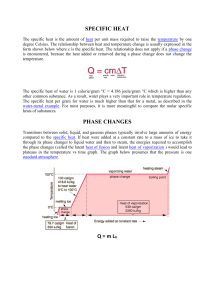
... • We define _________________ as the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 ...
... • We define _________________ as the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by 1 ...
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
... out in a sealed “bomb” such as this one. • The heat absorbed (or released) by the water is a very good approximation of the enthalpy change for the reaction. • qrxn = – Ccal × ∆T Thermochemistry © 2015 Pearson Education ...
... out in a sealed “bomb” such as this one. • The heat absorbed (or released) by the water is a very good approximation of the enthalpy change for the reaction. • qrxn = – Ccal × ∆T Thermochemistry © 2015 Pearson Education ...
Heat = (mass)
... the standard state is the state of a material at a defined set of conditions ◦ pure gas at exactly 1 atm pressure ◦ pure solid or liquid in its most stable form at exactly 1 atm pressure and temperature of interest usually 25°C ◦ substance in a solution with concentration 1 M the standard enthalpy ...
... the standard state is the state of a material at a defined set of conditions ◦ pure gas at exactly 1 atm pressure ◦ pure solid or liquid in its most stable form at exactly 1 atm pressure and temperature of interest usually 25°C ◦ substance in a solution with concentration 1 M the standard enthalpy ...
"heat of fusion". - IES Al
... The specific heat of water is 1 calorie/gram °C = 4.186 joule/gram °C which is higher than any other common substance. As a result, water plays a very important role in temperature regulation. The specific heat per gram for water is much higher than that for a metal, as described in the water-metal ...
... The specific heat of water is 1 calorie/gram °C = 4.186 joule/gram °C which is higher than any other common substance. As a result, water plays a very important role in temperature regulation. The specific heat per gram for water is much higher than that for a metal, as described in the water-metal ...
Chapter 4: Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
... Specific Heats and Changes in Internal Energy and Enthalpy for Ideal Gases Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must be determined. For real substances like water, the prope ...
... Specific Heats and Changes in Internal Energy and Enthalpy for Ideal Gases Before the first law of thermodynamics can be applied to systems, ways to calculate the change in internal energy of the substance enclosed by the system boundary must be determined. For real substances like water, the prope ...
H - Workforce3One
... calorimeter such as this one, one can indirectly measure the heat change for the system by measuring the heat change for the water in the calorimeter. Thermochemistry ...
... calorimeter such as this one, one can indirectly measure the heat change for the system by measuring the heat change for the water in the calorimeter. Thermochemistry ...
Chemical Energetics
... Heat and work are best thought of as processes by which energy is exchanged, rather than as energy itself. That is, heat “exists” only when it is flowing, work “exists” only when it is being done. When two bodies are placed in thermal contact and energy flows from the warmer body to the cooler one, ...
... Heat and work are best thought of as processes by which energy is exchanged, rather than as energy itself. That is, heat “exists” only when it is flowing, work “exists” only when it is being done. When two bodies are placed in thermal contact and energy flows from the warmer body to the cooler one, ...
Heat
... • H = Enthalpy: energy function that indicates how much energy is produced or absorbed in a reaction • ΔHp = energy that flows as heat • ΔH: the change in enthalpy • p: indicates process has occurred under constant pressure • The enthalpy change is the same as the heat of reaction • See Example 10.5 ...
... • H = Enthalpy: energy function that indicates how much energy is produced or absorbed in a reaction • ΔHp = energy that flows as heat • ΔH: the change in enthalpy • p: indicates process has occurred under constant pressure • The enthalpy change is the same as the heat of reaction • See Example 10.5 ...
Energy
... the standard state is the state of a material at a defined set of conditions ◦ pure gas at exactly 1 atm pressure ◦ pure solid or liquid in its most stable form at exactly 1 atm pressure and temperature of interest usually 25°C ◦ substance in a solution with concentration 1 M the standard enthalpy ...
... the standard state is the state of a material at a defined set of conditions ◦ pure gas at exactly 1 atm pressure ◦ pure solid or liquid in its most stable form at exactly 1 atm pressure and temperature of interest usually 25°C ◦ substance in a solution with concentration 1 M the standard enthalpy ...
Energy and the First Law of Thermodynamics
... – Some examples of state functions include energy (and many other thermodynamic terms), pressure, volume, altitude, distance, etc. • An energy change in a system can occur by many pathways (different combinations of heat and work), but no matter what the combination, DE is always the same — the amou ...
... – Some examples of state functions include energy (and many other thermodynamic terms), pressure, volume, altitude, distance, etc. • An energy change in a system can occur by many pathways (different combinations of heat and work), but no matter what the combination, DE is always the same — the amou ...
In Praise of Entropy Gary D. Patterson Professor of Chemistry
... adiabatic irreversible process. If the science of Thermodynamics had ended its development in the 19th century, perhaps theologians would not have chosen to slander the entropy. However, attempts to understand the macroscopic laws of Thermodynamics in terms of the microscopic behavior of the consti ...
... adiabatic irreversible process. If the science of Thermodynamics had ended its development in the 19th century, perhaps theologians would not have chosen to slander the entropy. However, attempts to understand the macroscopic laws of Thermodynamics in terms of the microscopic behavior of the consti ...
27 Oct. 2010 - PHA Science
... 1.435 grams of naphthalene (C10H8) was burned in a constant-volume bomb calorimeter. The temperature of the water rose from 20.28oC to 25.95oC. If the heat capacity of the bomb plus water was 10.17 kJ/oC, calculate the heat of combustion of naphthalene on a molar basis (find the molar heat of combus ...
... 1.435 grams of naphthalene (C10H8) was burned in a constant-volume bomb calorimeter. The temperature of the water rose from 20.28oC to 25.95oC. If the heat capacity of the bomb plus water was 10.17 kJ/oC, calculate the heat of combustion of naphthalene on a molar basis (find the molar heat of combus ...
Chapter 11 Notes - Mr-Durands
... (Note the capital C) This unit is general used to measure the energy content in ...
... (Note the capital C) This unit is general used to measure the energy content in ...
Water - HSC Chemistry 9
... Since water is in a liquid form at the reference temperature of 25 °C for pressures higher than 0.032 bar, the Cp functions for steam follow the saturated steam curve below the boiling point. This means that the pressure is not kept constant below this point and thus the pressure value in the specie ...
... Since water is in a liquid form at the reference temperature of 25 °C for pressures higher than 0.032 bar, the Cp functions for steam follow the saturated steam curve below the boiling point. This means that the pressure is not kept constant below this point and thus the pressure value in the specie ...
thermodynamics type 1
... The essence of first law is that all physical and chemical processes take place in such a manner that the total energy of the universe remain constant. However, it is observed that all processes have a natural direction ,i.e. a direction in which they take place spontaneously. First law fails to ans ...
... The essence of first law is that all physical and chemical processes take place in such a manner that the total energy of the universe remain constant. However, it is observed that all processes have a natural direction ,i.e. a direction in which they take place spontaneously. First law fails to ans ...
Thermochemistry, thermodynamics Thermochemistry
... Changes in Internal Energy Most chemical reactions and physical changes occur at constant (usually atmospheric) pressure. In constant-pressure processes the equation ∆E = q + w becomes ∆E = qp − p∆V The quantity of heat transferred into or out of a system as it undergoes a chemical or physical chang ...
... Changes in Internal Energy Most chemical reactions and physical changes occur at constant (usually atmospheric) pressure. In constant-pressure processes the equation ∆E = q + w becomes ∆E = qp − p∆V The quantity of heat transferred into or out of a system as it undergoes a chemical or physical chang ...
Chapter 13 Energy, Heat, and Chemical Change
... statistical drive toward maximum entropy). 7. The internal energy of our ideal gas is given by E =inRT -- i (1.00 ...
... statistical drive toward maximum entropy). 7. The internal energy of our ideal gas is given by E =inRT -- i (1.00 ...
Mt. SAC
... h mass iit will ill take k twice i as muchh heat h energy to raise the temperature the same amount. ...
... h mass iit will ill take k twice i as muchh heat h energy to raise the temperature the same amount. ...
From the first law of thermodynamics
... State Functions State function: depends only on the initial and final states of system, not on how the internal energy is used. ...
... State Functions State function: depends only on the initial and final states of system, not on how the internal energy is used. ...