Chemical Thermodynamics John Murrell Introduction
... Energy. We can convert energy from one form to another but it cannot change in a closed system (this ignores mass to energy conversion which occurs in nuclear reactions). The second law is concerned with spontaneous change and results from the important observation that heat always flows from hotter ...
... Energy. We can convert energy from one form to another but it cannot change in a closed system (this ignores mass to energy conversion which occurs in nuclear reactions). The second law is concerned with spontaneous change and results from the important observation that heat always flows from hotter ...
g - Cloudfront.net
... When energy is transferred from one object to another, it appears as work and/or as heat. For our work we must define a system to study; everything else then becomes the surroundings. The system is composed of particles with their own internal energies (E or U). Therefore the system has an internal ...
... When energy is transferred from one object to another, it appears as work and/or as heat. For our work we must define a system to study; everything else then becomes the surroundings. The system is composed of particles with their own internal energies (E or U). Therefore the system has an internal ...
Lecture 3: Fluid Dynamics and Balance Equations for Reacting Flows
... Another important form of the energy equation is that in terms of the temperature. With ...
... Another important form of the energy equation is that in terms of the temperature. With ...
Fluid Dynamics and Balance Equations for Reacting Flows
... Another important form of the energy equation is that in terms of the temperature. With and ...
... Another important form of the energy equation is that in terms of the temperature. With and ...
Thermodynamics states that `the change in internal energy (∆ ) of a
... electrochemical cell. The energy of a system is defined as its capacity to do work. During an exothermic reaction energy is released to the surroundings and hence the energy of the system is decreased i.e. following the combustion of propane the products have less capacity to do work. It is crucial ...
... electrochemical cell. The energy of a system is defined as its capacity to do work. During an exothermic reaction energy is released to the surroundings and hence the energy of the system is decreased i.e. following the combustion of propane the products have less capacity to do work. It is crucial ...
Chapter 6 - Saint Leo University Faculty
... 1) Hess’s Law states that the overall enthalpy change for a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the reaction. H is NOT dependent upon the pathway taken, since H is a state function. 2) Characteristics of H changes A) If a reaction is reversed, the sign ...
... 1) Hess’s Law states that the overall enthalpy change for a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the reaction. H is NOT dependent upon the pathway taken, since H is a state function. 2) Characteristics of H changes A) If a reaction is reversed, the sign ...
Heat Capacity. Enthalpy. Magnetic Systems.
... system (via translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedom). And remember that, roughly speaking, temperature is a measure of energy per degree of freedom. If no work is done, all the heat does is add/remove energy to/from the system. The equipartition idea is that this energy gets div ...
... system (via translational, rotational and vibrational degrees of freedom). And remember that, roughly speaking, temperature is a measure of energy per degree of freedom. If no work is done, all the heat does is add/remove energy to/from the system. The equipartition idea is that this energy gets div ...
Chapter 9: Thermochemistry VanKoppen
... differ. Energy change is independent of the pathway, whereas work and heat are both dependent on the pathway. A property that is independent of the pathway is called a state function. Energy is a state function. Work and heat are not state functions. ...
... differ. Energy change is independent of the pathway, whereas work and heat are both dependent on the pathway. A property that is independent of the pathway is called a state function. Energy is a state function. Work and heat are not state functions. ...
Assignment 05 A
... 1- Calculate the kinetic energy of a 7.3-kg steel ball traveling at 18.0 m/s. a) 66 J b) 4.8 x 103 J c) 1.2 x 103 J d) 2.4 x 103 J (The kinetic energy is equal to one-half the product of the mass (in kg) and the velocity (in m/s)2.) 2- According to the first law of thermodynamics, a) the amount of w ...
... 1- Calculate the kinetic energy of a 7.3-kg steel ball traveling at 18.0 m/s. a) 66 J b) 4.8 x 103 J c) 1.2 x 103 J d) 2.4 x 103 J (The kinetic energy is equal to one-half the product of the mass (in kg) and the velocity (in m/s)2.) 2- According to the first law of thermodynamics, a) the amount of w ...
Chapter 9
... Hess's law : If two or more chemical equations are added to give another chemical equation, the corresponding enthalpies of reaction must be added. (Enthalpy is a state function. The calculated ∆H for a reaction is independent of how many steps were taken to get from reactants to products. It can be ...
... Hess's law : If two or more chemical equations are added to give another chemical equation, the corresponding enthalpies of reaction must be added. (Enthalpy is a state function. The calculated ∆H for a reaction is independent of how many steps were taken to get from reactants to products. It can be ...
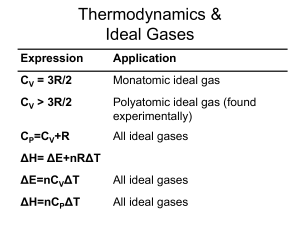
ΔE=nC V ΔT
... The change in enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of a compound from the elements. All substances are at their standard states. gas P = 1 atm solution 1 M @ 1 atm solid pure solid liquid pure liquid T ...
... The change in enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of a compound from the elements. All substances are at their standard states. gas P = 1 atm solution 1 M @ 1 atm solid pure solid liquid pure liquid T ...
Thermochemistry
... 6.2 Enthalpy and Calorimetry In chemistry most of our concern will be with electrical work and that due to expanding gases. Of these, we will concentrate on the latter. • Ex. Consider an imaginary system with a cylinder and a weightless piston. 1 mol of water at 100ºC will be converted from liquid t ...
... 6.2 Enthalpy and Calorimetry In chemistry most of our concern will be with electrical work and that due to expanding gases. Of these, we will concentrate on the latter. • Ex. Consider an imaginary system with a cylinder and a weightless piston. 1 mol of water at 100ºC will be converted from liquid t ...
Title - ALevelChemistryRossett
... If ∆Gθ for a reaction is negative (or zero) then the reaction is feasible; if it is positive then the reaction is not feasible. Note 1: If ∆H is positive (endothermic) then, providing T∆S is __________ positive then the reaction will be feasible. Note 2: The term T∆S is temperature dependent meaning ...
... If ∆Gθ for a reaction is negative (or zero) then the reaction is feasible; if it is positive then the reaction is not feasible. Note 1: If ∆H is positive (endothermic) then, providing T∆S is __________ positive then the reaction will be feasible. Note 2: The term T∆S is temperature dependent meaning ...
Chapter 2. The First Law
... (b) The measurement of an enthalpy change 1. Isobaric calorimeter : monitors the temperature change at constant pressure 2. Adiabatic flame calorimeter 3. When a process involves only solids or liquids, the values of ΔH and ΔU are almost identical because pVm is so small. 4. Differential scannin ...
... (b) The measurement of an enthalpy change 1. Isobaric calorimeter : monitors the temperature change at constant pressure 2. Adiabatic flame calorimeter 3. When a process involves only solids or liquids, the values of ΔH and ΔU are almost identical because pVm is so small. 4. Differential scannin ...
thermochemistry -1 - Dr. Gupta`s Professional Page
... potential energies of all particles. Etotal = Ek + Ep + U • Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. ...
... potential energies of all particles. Etotal = Ek + Ep + U • Energy cannot be created nor destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. ...
Calorimetry - NC State University
... a Diatomic Molecule For a diatomic molecule there is contribution from rotations as well as translations. This means that as heat is added to the system the rotational levels can be populated in addition to an increase in molecular speed. The kinetic theory of gases considers only the speed. An appr ...
... a Diatomic Molecule For a diatomic molecule there is contribution from rotations as well as translations. This means that as heat is added to the system the rotational levels can be populated in addition to an increase in molecular speed. The kinetic theory of gases considers only the speed. An appr ...
Energy
... Intensive Property: does not depend on the amount of substance o Density o Melting Point o Boiling Point o Specific heat ...
... Intensive Property: does not depend on the amount of substance o Density o Melting Point o Boiling Point o Specific heat ...
Chapter 1
... If a compound is formed from its constituent elements, then the enthalpy change for the reaction is called the enthalpy of formation, ∆Hf. Standard state (standard conditions) refer to the substance at: • 1 atm and 25 °C (298 K). Standard enthalpy, ∆H˚, is the enthalpy measured when everything is in ...
... If a compound is formed from its constituent elements, then the enthalpy change for the reaction is called the enthalpy of formation, ∆Hf. Standard state (standard conditions) refer to the substance at: • 1 atm and 25 °C (298 K). Standard enthalpy, ∆H˚, is the enthalpy measured when everything is in ...
11 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry
... The value of ∆G may be obtained by the formula below if ∆H, T, and ∆S is known: ∆G = ∆H - T∆S . When using this formula the temperature must be in Kelvin, and the units of energy for ∆H and ∆S must be the same. The relationship between ∆H, T, and ∆S as they relates to spontaneity is shown in ...
... The value of ∆G may be obtained by the formula below if ∆H, T, and ∆S is known: ∆G = ∆H - T∆S . When using this formula the temperature must be in Kelvin, and the units of energy for ∆H and ∆S must be the same. The relationship between ∆H, T, and ∆S as they relates to spontaneity is shown in ...
Notes
... positive H corresponds to an endothermic process. Hsolution , sometimes called heat of solution or molar enthalpy of dissolution, refers to the Hrxn for the physical process of dissolving one mole of a substance in water. ...
... positive H corresponds to an endothermic process. Hsolution , sometimes called heat of solution or molar enthalpy of dissolution, refers to the Hrxn for the physical process of dissolving one mole of a substance in water. ...
c - Iust personal webpages
... – If a process occurs in stages or steps (even hypothetically), the enthalpy change for the overall process is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. ½N2(g) + ½O2(g) → NO(g) ...
... – If a process occurs in stages or steps (even hypothetically), the enthalpy change for the overall process is the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. ½N2(g) + ½O2(g) → NO(g) ...
Verdana 30 pt - Liceo Statale Aprosio
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...
... which we can describe the behavior with relatively simple and accurate laws, based on measures of volume, pressure and temperature, said state quantities; these, we add the internal energy U of an ideal gas, which is all kinetic and depends only on the temperature. ...