CHAPTER I
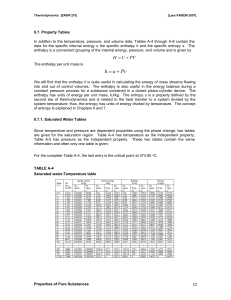
... It is noted that the value of any extensive property per unit mass in the saturation region is calculated from an equation having a form similar to that of the above equation. Let Y be any extensive property and let y be the corresponding intensive property, Y/m, then ...
... It is noted that the value of any extensive property per unit mass in the saturation region is calculated from an equation having a form similar to that of the above equation. Let Y be any extensive property and let y be the corresponding intensive property, Y/m, then ...
lecture1 - Unaab.edu.ng
... (f) Intensive Properties. Are those whose values are independent of the size of system taken i.e the properties will be the same whether small or great amount of the system is considered. E.g temperature, pressure, density, refractive index ,etc. (g) Extensive properties: are those whose values depe ...
... (f) Intensive Properties. Are those whose values are independent of the size of system taken i.e the properties will be the same whether small or great amount of the system is considered. E.g temperature, pressure, density, refractive index ,etc. (g) Extensive properties: are those whose values depe ...
Thermodynamics - Deland High School
... o ∆H = n∆Hfus = (3.06 mol)(6.01 kJ/mol) = 18.39 kJ o Step 3: Heat the liquid from 00 C to 1000 C o ∆H = mCp∆T = (55 grams)(4.184 J/g0C)(1000) = 23,012 J o Step 4: Undergo the phase change from a liquid to gas. o ∆H = n∆Hvap = (3.06 mol)(40.7 kJ/mol) = 124.54 kJ o Step 5: Heat the steam from 1000 C t ...
... o ∆H = n∆Hfus = (3.06 mol)(6.01 kJ/mol) = 18.39 kJ o Step 3: Heat the liquid from 00 C to 1000 C o ∆H = mCp∆T = (55 grams)(4.184 J/g0C)(1000) = 23,012 J o Step 4: Undergo the phase change from a liquid to gas. o ∆H = n∆Hvap = (3.06 mol)(40.7 kJ/mol) = 124.54 kJ o Step 5: Heat the steam from 1000 C t ...
Thermochemistry
... absolute heat contents of hydrogen, oxygen or water. But if we have defined the H of any free element (hydrogen and oxygen) to be zero then ∆H = H (2 moles of water) We see that the ∆H that we measure for this experiment is equal to the heat content of 2 moles of water. This ∆H is thus a measure of ...
... absolute heat contents of hydrogen, oxygen or water. But if we have defined the H of any free element (hydrogen and oxygen) to be zero then ∆H = H (2 moles of water) We see that the ∆H that we measure for this experiment is equal to the heat content of 2 moles of water. This ∆H is thus a measure of ...
In Chapter 2, we will concentrate on the concepts associated with
... convert to work, we just multiply the force by the change in distance, x. This gives Pressure x Area x Distance. But the Area times the distance traveled is just the volume change, so we can say that the work is just the negative of the Pressure times the change in volume. ...
... convert to work, we just multiply the force by the change in distance, x. This gives Pressure x Area x Distance. But the Area times the distance traveled is just the volume change, so we can say that the work is just the negative of the Pressure times the change in volume. ...
GRE-thermo
... in a volume V at a temperature such that the particles obey classical Boltzmann statistics. If the temperature is lowered to the point at which quantum effects become important, the pressure of the gas may differ depending on whether the particles are fermions or bosons. Let PF be the pressure exert ...
... in a volume V at a temperature such that the particles obey classical Boltzmann statistics. If the temperature is lowered to the point at which quantum effects become important, the pressure of the gas may differ depending on whether the particles are fermions or bosons. Let PF be the pressure exert ...
Notes - PowerPoint
... Constant Pressure Calorimetry • By carrying out a reaction in aqueous solution in a simple calorimeter such as this one, one can indirectly measure the heat change for the system by measuring the heat change for the water in the calorimeter. • Because the specific heat for water is well known (4.18 ...
... Constant Pressure Calorimetry • By carrying out a reaction in aqueous solution in a simple calorimeter such as this one, one can indirectly measure the heat change for the system by measuring the heat change for the water in the calorimeter. • Because the specific heat for water is well known (4.18 ...
Ch 6 Thermochemistry
... - Internal Energy (U) is the combined kinetic and potential energies of particles (molecules) within a system. Ex 6.1 Ek = (1/2)mv2 = (1/2)(0.143 kg)(33.5 m/s)2 = 80.2 kg·m2/s2 = 80.2 Joules Law of Conservation of Energy - Energy may be converted between forms, but total quantity of energy is consta ...
... - Internal Energy (U) is the combined kinetic and potential energies of particles (molecules) within a system. Ex 6.1 Ek = (1/2)mv2 = (1/2)(0.143 kg)(33.5 m/s)2 = 80.2 kg·m2/s2 = 80.2 Joules Law of Conservation of Energy - Energy may be converted between forms, but total quantity of energy is consta ...
Chapter 6 - ETSU.edu
... (there is a decrease in internal energy that is the energy leaves the system) and the positive means the system expands. • 1 L-atm = 101.325 J ...
... (there is a decrease in internal energy that is the energy leaves the system) and the positive means the system expands. • 1 L-atm = 101.325 J ...
PowerPoint - Dr. Samples` Chemistry Classes
... • So the heat capacity, the amount of a substance and the T for a rxn can let us calculate the H for a rxn, Hrxn • What kind of substances have high heat capacities? • Water has one of the highest heat capacities, much higher than most common substances. It’s specific heat capacity is 4.184 J/g•° ...
... • So the heat capacity, the amount of a substance and the T for a rxn can let us calculate the H for a rxn, Hrxn • What kind of substances have high heat capacities? • Water has one of the highest heat capacities, much higher than most common substances. It’s specific heat capacity is 4.184 J/g•° ...
Chapter-9-Handouts
... mL of 0.500 M HCl (0.0500 mol HCl) was mixed with 75.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH (0.0375 mol NaOH) in a constant-pressure calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. The initial temperature of the HCl and NaOH solution was the same, 22.50°C, and the final temperature of the mixed solution was 25.86°C. Calcula ...
... mL of 0.500 M HCl (0.0500 mol HCl) was mixed with 75.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH (0.0375 mol NaOH) in a constant-pressure calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. The initial temperature of the HCl and NaOH solution was the same, 22.50°C, and the final temperature of the mixed solution was 25.86°C. Calcula ...
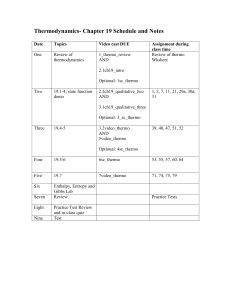
Schedule and sample problems
... Bond enthalpy is the enthalpy change, H, for the breaking of a particular bond in one mole of a gaseous substance. Use bond enthalpies from p.330 in your text to estimate the enthalpy of reaction for the combustion of gaseous ethane, producing carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. p. 332. ...
... Bond enthalpy is the enthalpy change, H, for the breaking of a particular bond in one mole of a gaseous substance. Use bond enthalpies from p.330 in your text to estimate the enthalpy of reaction for the combustion of gaseous ethane, producing carbon dioxide gas and water vapor. p. 332. ...
Free Energy of Pure Substances
... Heat Capacity at Constant Volume and Constant Pressure. The heat quantity (per mole) that is required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 K is called the heat capacity. However, it is also called specific heat (per unit mass) or molar heat in physics. There are two kinds of heat capacity: ...
... Heat Capacity at Constant Volume and Constant Pressure. The heat quantity (per mole) that is required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 K is called the heat capacity. However, it is also called specific heat (per unit mass) or molar heat in physics. There are two kinds of heat capacity: ...
Thermochemistry
... insulated container of water. The mass of the water is 132 g and its temperature before adding the iron is 20.0˚C. What will be the final temperature of the system? Heat lost by Fe = heat gained by water ...
... insulated container of water. The mass of the water is 132 g and its temperature before adding the iron is 20.0˚C. What will be the final temperature of the system? Heat lost by Fe = heat gained by water ...
Chapter Six Outline
... transferred out of the system whereas a positive sign indicates energy is transferred into the system. E. Conservation of Energy and Chemical Reactions The law of conservation of energy can be written as ∆Esystem = qsystem + wsystem where q represents the quantity of energy transferred by heating ...
... transferred out of the system whereas a positive sign indicates energy is transferred into the system. E. Conservation of Energy and Chemical Reactions The law of conservation of energy can be written as ∆Esystem = qsystem + wsystem where q represents the quantity of energy transferred by heating ...
Unit 4 - Thermo Chemistry Learning Objectives
... You will be able to explain how to measure the enthalpy of a chemical reaction using a calorimeter and Hess's Law. Hess's Law - in a chemical reaction, the enthalpy change from reactants to products can be calculated by the sum of a series of steps ∆Hreaction = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3 ... * Reversing a reac ...
... You will be able to explain how to measure the enthalpy of a chemical reaction using a calorimeter and Hess's Law. Hess's Law - in a chemical reaction, the enthalpy change from reactants to products can be calculated by the sum of a series of steps ∆Hreaction = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3 ... * Reversing a reac ...
Learning Objectives
... You will be able to explain how to measure the enthalpy of a chemical reaction using a calorimeter and Hess's Law. Hess's Law - in a chemical reaction, the enthalpy change from reactants to products can be calculated by the sum of a series of steps ∆Hreaction = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3 ... * Reversing a reac ...
... You will be able to explain how to measure the enthalpy of a chemical reaction using a calorimeter and Hess's Law. Hess's Law - in a chemical reaction, the enthalpy change from reactants to products can be calculated by the sum of a series of steps ∆Hreaction = ∆H1 + ∆H2 + ∆H3 ... * Reversing a reac ...
Chapter 5 Outline 1213 full
... • The equation tells us that 483.6 kJ of energy are released to the surroundings when water is formed. • H noted at the end of the balanced equation depends on the number of moles of reactants and products associated with the H value. • These equations are called thermochemical equations. ...
... • The equation tells us that 483.6 kJ of energy are released to the surroundings when water is formed. • H noted at the end of the balanced equation depends on the number of moles of reactants and products associated with the H value. • These equations are called thermochemical equations. ...
2.1 A thermodynamics system and the control volume Chapter 2
... Can be described by certain observable, macroscopic properties, such as temperature, pressure, density, etc. 機械工程系 陳俊勳老師 ...
... Can be described by certain observable, macroscopic properties, such as temperature, pressure, density, etc. 機械工程系 陳俊勳老師 ...
Thermochemistry
... (usually) and is the amt of substance ∆T [=] C° and is the change in temperature ∆T also equal Tf - Ti where Tf and Ti represent the final and initial temperatures Note: Q will be positive if the temp is increasing (∆T +) and negative if the temp is decreasing (∆T -). Cp is the amount of heat needed ...
... (usually) and is the amt of substance ∆T [=] C° and is the change in temperature ∆T also equal Tf - Ti where Tf and Ti represent the final and initial temperatures Note: Q will be positive if the temp is increasing (∆T +) and negative if the temp is decreasing (∆T -). Cp is the amount of heat needed ...
12-1 Chemical Reactions That Involve Heat
... 3. Fats are able to supply twice the energy as carbohydrates. Give a possible explanation for this. 4. What error is introduced by including only the raise in temperature of water in the calorimeter as the heat of a reaction? 12-5 What is Heat? The Caloric Theory- scientists like Lavoisier of the 17 ...
... 3. Fats are able to supply twice the energy as carbohydrates. Give a possible explanation for this. 4. What error is introduced by including only the raise in temperature of water in the calorimeter as the heat of a reaction? 12-5 What is Heat? The Caloric Theory- scientists like Lavoisier of the 17 ...