* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ΔE=nC V ΔT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
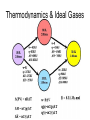
Thermodynamics & Ideal Gases Expression Application CV = 3R/2 Monatomic ideal gas CV > 3R/2 Polyatomic ideal gas (found experimentally) CP=CV+R All ideal gases ΔH= ΔE+nRΔT ΔE=nCVΔT All ideal gases ΔH=nCPΔT All ideal gases Thermodynamics & Ideal Gases Thermodynamics Calorimetry Molar heat capacity, heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of the substance 1 Kelvin. Specific heat capacity, heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of the substance 1 Kelvin. Or: Specific Heat = Molar Heat/Molar Mass Thermodynamics ΔE = q + w; Δ H = qp therefore Δ E = qP + w = Δ H + w How much work would 0.0100 grams of nitrogen triiodide do when it decomposed at STP? 2NI3(s) N2(g) + 3I2(g) Thermodynamics & Calorimetry Suppose we drop a 100.0 gram piece of iron at 200 oC into a large coffee cup calorimeter containing 250 grams of water at 25 oC. What will the final temperature be inside the cup? The specific heats of iron and water are 0.45 and 4.18 J-K-1-g-1. If the density of the water changes from 0.993 to 0.985 g/ml will your answer change? What are q, w, ΔE & Δ H for the process? Thermodynamics & Hess’s Law For any reaction, Δ H is the same when going from a particular set of reactants to a particular set of products. The path followed is irrelevant. E.g. (all gases except graphite) CO + 1/2O2 Δ H2 C + O2 Δ H3 Δ H1 CO2 Δ H1 = Δ H2 + Δ H3 = (-110.5kJ)+(-283.0kJ) Thermodynamics Standard Enthalpies of Formation. ΔHfo: The change in enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of a compound from the elements. All substances are at their standard states. gas P = 1 atm solution 1 M @ 1 atm solid pure solid liquid pure liquid T usually 25 oC ΔHfo of any element in its SS is zero