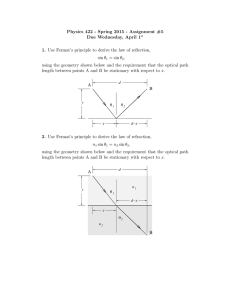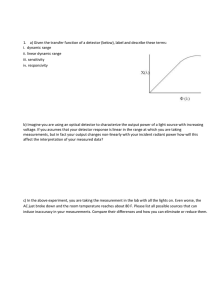
a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and
... Please use your drawing to illustrate how PMT and APD work and compare the mechanisms which enable them to achieve signal amplification. Also, explain why is it hard to make a detector that has high detectivity while also preserves a high detection speed? ...
... Please use your drawing to illustrate how PMT and APD work and compare the mechanisms which enable them to achieve signal amplification. Also, explain why is it hard to make a detector that has high detectivity while also preserves a high detection speed? ...
肖连团 - 山西大学
... • By focusing the excitation light near to the extinction crosssection of a molecule, it is possible to explore resonance fluorescence over nine orders of magnitude of excitation intensity and to separate its coherent and incoherent parts. • Under weak excitation, the detection of a single molecule ...
... • By focusing the excitation light near to the extinction crosssection of a molecule, it is possible to explore resonance fluorescence over nine orders of magnitude of excitation intensity and to separate its coherent and incoherent parts. • Under weak excitation, the detection of a single molecule ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... Breaking the diffraction limit. The field of superresolution microscopy, so-called optical nanoscopy, has been recognized recently with the award of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to the inventors of stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED) [1] and single molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) ...
... Breaking the diffraction limit. The field of superresolution microscopy, so-called optical nanoscopy, has been recognized recently with the award of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to the inventors of stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED) [1] and single molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) ...
RESOLVING POWER AND MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION
... neutrons. The power of imaging is due to the fact that structurizing a 2-D area becomes possible in one exposure, at the same time the control of the imaging parameters allows selecting the image size, e.g. by demagnifying. However, the resolution achievable by the optical system limits the imaging ...
... neutrons. The power of imaging is due to the fact that structurizing a 2-D area becomes possible in one exposure, at the same time the control of the imaging parameters allows selecting the image size, e.g. by demagnifying. However, the resolution achievable by the optical system limits the imaging ...
How does a confocal microscope work
... order to speed up the scanning. This uses a high-frequency sound wave in a special crystal to create a diffraction grating, which deflects the laser light (actually, the first diffraction peak is used, with the zeroth-order peak being thrown away). By varying the frequency of the sound wave, the AOD ...
... order to speed up the scanning. This uses a high-frequency sound wave in a special crystal to create a diffraction grating, which deflects the laser light (actually, the first diffraction peak is used, with the zeroth-order peak being thrown away). By varying the frequency of the sound wave, the AOD ...
Microscopy Overview
... source is usually used. In critical illumination, the source is focused on to the object by a condenser lens. The disadvantage of this approach is that variations in emission of the source are imaged directly into the image. Cheaper microscopes avoid this problem by using a diffuser. Better microsco ...
... source is usually used. In critical illumination, the source is focused on to the object by a condenser lens. The disadvantage of this approach is that variations in emission of the source are imaged directly into the image. Cheaper microscopes avoid this problem by using a diffuser. Better microsco ...
Microscope
... objective by the condenser. The method used to ensure that this cone of light is at maximum volume is called Kohler illumination. Setting Up the Microscope for Kohler Illumination a. Begin the alignment at low illumination. b. Use a 10X eyepiece and the 10X objective c. Place an easily visible test ...
... objective by the condenser. The method used to ensure that this cone of light is at maximum volume is called Kohler illumination. Setting Up the Microscope for Kohler Illumination a. Begin the alignment at low illumination. b. Use a 10X eyepiece and the 10X objective c. Place an easily visible test ...
Biology 3235: Resolution and magnification of a light microscopes
... objective (NA = 1.3), you could resolve details as small as 0.23 µm using green light. Note that shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue light (λ = 480 nm) than with red light (λ = 650 nm). The NA of dry lenses is limited by the ref ...
... objective (NA = 1.3), you could resolve details as small as 0.23 µm using green light. Note that shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue light (λ = 480 nm) than with red light (λ = 650 nm). The NA of dry lenses is limited by the ref ...
Light microscopy
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
... 5. By noting the length of an unknown structure in graticule divisions you can then convert this into absolute units of length, e.g. µm. 6. Each objective lens needs to be calibrated in the same way. Once calibrated objects can be measured in EPUs. EPUs are converted into absolute measurement using ...
A short introduction to light and electron microscopy
... In wide field microscopy the whole sample is illuminated with light. Different modes of illumination can be employed. In transmission microscopy white light is transmitted through stained histological samples. Unstained samples can be analyzed using optical contrast methods (phase contrast, differen ...
... In wide field microscopy the whole sample is illuminated with light. Different modes of illumination can be employed. In transmission microscopy white light is transmitted through stained histological samples. Unstained samples can be analyzed using optical contrast methods (phase contrast, differen ...
Optics in Confocal Microscopy
... infinite radius. The rays passing from a single point through a planar boundary into a medium of different refractive index are bent at the interface in such a way that , when traced back, they no longer intersect in a single point. It is possible to correct for this by incorporating special spheric ...
... infinite radius. The rays passing from a single point through a planar boundary into a medium of different refractive index are bent at the interface in such a way that , when traced back, they no longer intersect in a single point. It is possible to correct for this by incorporating special spheric ...