SoftMatter
... Soft matter is held together by the two weakest types of bonding, the hydrogen bond and the van der Waals bond. It does not exhibit the crystalline order that is characteristic of most hard matter. Nevertheless, some order remains in soft matter. It is driven by the organization of hydrophobic and h ...
... Soft matter is held together by the two weakest types of bonding, the hydrogen bond and the van der Waals bond. It does not exhibit the crystalline order that is characteristic of most hard matter. Nevertheless, some order remains in soft matter. It is driven by the organization of hydrophobic and h ...
Episode 23 0 Proetin: Structure and Function
... 3. What are the building blocks used to form proteins? How many are found in nature? amino acids - 20 amino acids are found in most living systems 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in diffe ...
... 3. What are the building blocks used to form proteins? How many are found in nature? amino acids - 20 amino acids are found in most living systems 4. The video estimates that 100 billion proteins may exist. How can so many proteins form from just a few molecules? When amino acids are joined in diffe ...
Problem Set 1
... ii) The carbonyl and amide groups of the protein backbone are hydrophilic and form hydrogen bonds with water; they can also hydrogen bond to each other. The free energy of formation of a hydrogen bond between the atoms of the peptide group in the interior of a protein is : a) more favorable than it ...
... ii) The carbonyl and amide groups of the protein backbone are hydrophilic and form hydrogen bonds with water; they can also hydrogen bond to each other. The free energy of formation of a hydrogen bond between the atoms of the peptide group in the interior of a protein is : a) more favorable than it ...
Amino Acids and Proteins
... helix or pleated sheet Hydrogen bonds hold in structure on place (configuration) Secondary structure coils/ folds into complex 3D shape (v. precise) Held together by bonds between side chains Proteins of greater than one polypeptide have quaternary structures either GLOBULAR or FIBROUS ...
... helix or pleated sheet Hydrogen bonds hold in structure on place (configuration) Secondary structure coils/ folds into complex 3D shape (v. precise) Held together by bonds between side chains Proteins of greater than one polypeptide have quaternary structures either GLOBULAR or FIBROUS ...
Aromatic Amino Acids
... absorbance of ultraviolet light (ca. 280 nm) by proteins. Tyrosine is the only one of the aromatic amino acids with an ionizable side chain. Tyrosine is one of three hydroxyl containing amino acids. ...
... absorbance of ultraviolet light (ca. 280 nm) by proteins. Tyrosine is the only one of the aromatic amino acids with an ionizable side chain. Tyrosine is one of three hydroxyl containing amino acids. ...
Biochemistry H Silent Tea Party Name_______________ 1. What is
... a polysaccharide found in plants to store energy long term 41. What is glycogen? a polysaccharide found in animals to store energy long term 42. What is cellulose? a polysaccharide found in plants to provide structural support(cell wall) 43. What is chitin? a polysaccharide found in animals like ins ...
... a polysaccharide found in plants to store energy long term 41. What is glycogen? a polysaccharide found in animals to store energy long term 42. What is cellulose? a polysaccharide found in plants to provide structural support(cell wall) 43. What is chitin? a polysaccharide found in animals like ins ...
Estimation of the protein secondary structure in aqueous solutions
... The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large number of types ...
... The secondary structure of proteins is very important for their proper functioning. The investigation of the secondary structure gives us an insight into the mechanisms of protein functioning in the living cell. IR absorption spectroscopy provides the opportunity to identify a large number of types ...
View video content as a PDF
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
... The Final 3-Dimensional Shape of the Protein Once the secondary structures of a protein have been folded, the model must be given the correct overall shape. When doing this it is very useful to refer back to the online visualization environment. This display can be edited to match what the final phy ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... order of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to the ...
... order of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to the ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to the ...
... of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to the ...
protein structure - MBBS Students Club
... of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to the ...
... of amino acids is that: • The N-terminal end (i.e. the end bearing the residue with the free α-amino group) is to the left (and the number 1 amino acid) and the Cterminal end (i.e. the end with the residue containing a free α-carboxyl group) is to the ...
Proteins
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
... 6. Label the type of bond used to make proteins. 7. Draw arrows to identify these bonds in your model 8. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus 9. Put SQUARES around the R groups 10. Use your amino acid chart to identify & label the type of R group (non-polar, polar, charge basic, charged acidic, etc) ...
C h e m g u id e –... PROTEINS: STRUCTURE
... should draw the structure of the peptide link fully displayed in both cases. b) Suppose you had a short polypeptide with the structure Gly.Lys.Pro.Val.Val.Ala where the abbreviations show the amino acid residues – for example, Gly comes from glycine, and Ala from alanine. The two ends are referred t ...
... should draw the structure of the peptide link fully displayed in both cases. b) Suppose you had a short polypeptide with the structure Gly.Lys.Pro.Val.Val.Ala where the abbreviations show the amino acid residues – for example, Gly comes from glycine, and Ala from alanine. The two ends are referred t ...
Organic Chemistry Notes
... m. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon bonded covalently to four other partners. n. Three of those partners are common to all amino acids: a carboxyl group (COOH), an amino group (-NH2) and a hydrogen atom. o. The fourth spot is called the side group and varies between amino acids; the side ...
... m. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon bonded covalently to four other partners. n. Three of those partners are common to all amino acids: a carboxyl group (COOH), an amino group (-NH2) and a hydrogen atom. o. The fourth spot is called the side group and varies between amino acids; the side ...
Branched Chain Amino Acid
... • Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and there are three specific essential amino acids that make up as much as 33 percent of skeletal muscle. • These amino acids are known as the branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and they include, valine, leucine and isoleucine. • Valine is necessar ...
... • Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and there are three specific essential amino acids that make up as much as 33 percent of skeletal muscle. • These amino acids are known as the branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) and they include, valine, leucine and isoleucine. • Valine is necessar ...
2013 version with answers.
... high temperature clearing step. a) Neither Harry nor John has a 3D structure of the protein. And they can both at best make a very poor homology model that at best gives them ideas about which residues are in the core, in the active site, or at the surface. So their plans to stabilize their proteins ...
... high temperature clearing step. a) Neither Harry nor John has a 3D structure of the protein. And they can both at best make a very poor homology model that at best gives them ideas about which residues are in the core, in the active site, or at the surface. So their plans to stabilize their proteins ...
structure_property
... of the helix axis. This is because proline cannot form a regular alphahelix due to steric hindrance arising from its cyclic side chain, which also blocks the main chain N atom and chemically prevents it forming a hydrogen bond. Janet Thornton has shown that proline causes two H-bonds in the helix to ...
... of the helix axis. This is because proline cannot form a regular alphahelix due to steric hindrance arising from its cyclic side chain, which also blocks the main chain N atom and chemically prevents it forming a hydrogen bond. Janet Thornton has shown that proline causes two H-bonds in the helix to ...
File
... AA #2 loses a hydrogen from its amine (NH2) group The Carbon atom in the carboxyl group of AA#1 is now free to make ONE bond with the Nitrogen of the amine group in AA#2 This bond is called a PEPTIDE Bond ...
... AA #2 loses a hydrogen from its amine (NH2) group The Carbon atom in the carboxyl group of AA#1 is now free to make ONE bond with the Nitrogen of the amine group in AA#2 This bond is called a PEPTIDE Bond ...
Proteins & Nucleic Acids - St. Mary Catholic Secondary School
... Tertiary shape is held together by R-group bonding within the chain and R-group interactions with the environment. Tertiary structure is also aided by prosthetic groups that are inorganic compounds that act as a central point for bonding within the protein. Quaternary structure occurs when a few ter ...
... Tertiary shape is held together by R-group bonding within the chain and R-group interactions with the environment. Tertiary structure is also aided by prosthetic groups that are inorganic compounds that act as a central point for bonding within the protein. Quaternary structure occurs when a few ter ...
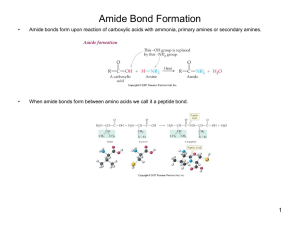
Amide Bond Formation
... – Gene expression is due to proteins – Almost all enzymes are proteins – Many hormones are proteins or peptides – Proteins form structural tissue – Storage and transportation of many molecules is possible due to proteins (think back to passive transport of hydrophilic molecules in and out of cells) ...
... – Gene expression is due to proteins – Almost all enzymes are proteins – Many hormones are proteins or peptides – Proteins form structural tissue – Storage and transportation of many molecules is possible due to proteins (think back to passive transport of hydrophilic molecules in and out of cells) ...
Fundamentals of protein structure
... (2)Hydrophobic bonds (between the non-polar side chain of a.a.) (3)Electrostatic bonds (salt bonds)(Formed between oppositely charged group in the side chains of amino acids)e.g. epsilon-amino group of lysine and carboxyl group of aspartate, interact electrostatically to stabilize the protein struct ...
... (2)Hydrophobic bonds (between the non-polar side chain of a.a.) (3)Electrostatic bonds (salt bonds)(Formed between oppositely charged group in the side chains of amino acids)e.g. epsilon-amino group of lysine and carboxyl group of aspartate, interact electrostatically to stabilize the protein struct ...