amino acids
... – polymer = polypeptide • protein can be two or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together via covalent and hydrogen bonds ...
... – polymer = polypeptide • protein can be two or more polypeptide chains folded & bonded together via covalent and hydrogen bonds ...
Problem 2
... The web site also located a single -hairpin and several -bulges. I had no idea what a -bulge is, so I picked one and made a picture. ...
... The web site also located a single -hairpin and several -bulges. I had no idea what a -bulge is, so I picked one and made a picture. ...
Prof. Kamakaka`s Lecture 3 Notes
... • The backbone is more extended with the y dihedral (N–Ca—C–N) in the range ( 90° < y < 180°) • The planarity of the peptide bond and tetrahedral geometry of the a-carbon create a pleated sheetlike structure • Sheet-like arrangement of backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds between the more dis ...
... • The backbone is more extended with the y dihedral (N–Ca—C–N) in the range ( 90° < y < 180°) • The planarity of the peptide bond and tetrahedral geometry of the a-carbon create a pleated sheetlike structure • Sheet-like arrangement of backbone is held together by hydrogen bonds between the more dis ...
A Novel Scoring Function for Predicting the Conformation of Pairs of
... Many pairs of helices in transmembrane (TM) proteins are tightly packed. We present a scoring function and a computational methodology for predicting the tertiary fold of a pair of α-helices, such that its chances of being tightly packed are maximized. Since the number of TM protein structures solve ...
... Many pairs of helices in transmembrane (TM) proteins are tightly packed. We present a scoring function and a computational methodology for predicting the tertiary fold of a pair of α-helices, such that its chances of being tightly packed are maximized. Since the number of TM protein structures solve ...
Lecture 7-protein design lecture (Mike).cdx
... -in principle, lowering pH should destabilize helix by protonating carboxylate groups to discourage salt bridge formation -however, the helix was highly helical at pH 2 -in general, salt bridges do not have large effects on helix stability but do frequently have important roles in assuring the corre ...
... -in principle, lowering pH should destabilize helix by protonating carboxylate groups to discourage salt bridge formation -however, the helix was highly helical at pH 2 -in general, salt bridges do not have large effects on helix stability but do frequently have important roles in assuring the corre ...
Amino acids and Protein Structure
... favorable entropy of too many conformations opposes folding ...
... favorable entropy of too many conformations opposes folding ...
BB 450/500 Lecture 5 Highlights
... 1. Another type of fibrous protein is collagen, the most abundant protein in your body. It contains three intertwined helices comprised of abundant repeating units of glycine, proline, and hydroxylproline 2. Hydroxylation of proline is a post-translational modification (occurs after the protein is m ...
... 1. Another type of fibrous protein is collagen, the most abundant protein in your body. It contains three intertwined helices comprised of abundant repeating units of glycine, proline, and hydroxylproline 2. Hydroxylation of proline is a post-translational modification (occurs after the protein is m ...
ppt
... lack of symmetry. The arrangement seems to be almost totally lacking in the kind of regularities which one instinctively anticipates, and it is more complicated than has been predicted by any theory of protein structure.’ – John Kendrick, 1958 ...
... lack of symmetry. The arrangement seems to be almost totally lacking in the kind of regularities which one instinctively anticipates, and it is more complicated than has been predicted by any theory of protein structure.’ – John Kendrick, 1958 ...
Document
... Each polypeptide is twisted, folded, & coiled into a unique shape. Denaturation - an unfavorable change in temperature, pH, or some other quality of the environment can cause a protein to unravel and lose its normal shape ...
... Each polypeptide is twisted, folded, & coiled into a unique shape. Denaturation - an unfavorable change in temperature, pH, or some other quality of the environment can cause a protein to unravel and lose its normal shape ...
Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
... serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 different locations along the length of the molecule that specifically direct the production of ...
... serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 different locations along the length of the molecule that specifically direct the production of ...
Word Doc - Biochemistry
... number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears to be the lower limit for a functional domain size. Protein sizes range from this lower limit to several hundred residues in multi-functional proteins. Very large aggregates can be formed ...
... number of residues is necessary to perform a particular biochemical function, and around 40-50 residues appears to be the lower limit for a functional domain size. Protein sizes range from this lower limit to several hundred residues in multi-functional proteins. Very large aggregates can be formed ...
The Amino Acid Song
... The Amino Acid Song (to the tune of Old McDonald) Tracey Tripp, Nell Ditch, Julie Milam and Frances Jenkins Amino acids are the building blocks of protein And there are 20 of them. Nine of them we call essential Our body cannot make them. They are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, ...
... The Amino Acid Song (to the tune of Old McDonald) Tracey Tripp, Nell Ditch, Julie Milam and Frances Jenkins Amino acids are the building blocks of protein And there are 20 of them. Nine of them we call essential Our body cannot make them. They are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, ...
The_Structure_of_Protein_Activity
... aspartic acid unit, calculate the approximate number of amino acid molecules that are needed to produce on molecule of haemoglobin. 3. How does the hydrogen bonding explain: a) The solubility of many proteins in water. b) The precise 3D structure of those enzymes which are proteins. c) The eleastici ...
... aspartic acid unit, calculate the approximate number of amino acid molecules that are needed to produce on molecule of haemoglobin. 3. How does the hydrogen bonding explain: a) The solubility of many proteins in water. b) The precise 3D structure of those enzymes which are proteins. c) The eleastici ...
Past Exam Question
... Proteins Revision L.O: To recall info on proteins To identify and correct any misconceptions ...
... Proteins Revision L.O: To recall info on proteins To identify and correct any misconceptions ...
Lecture 1
... hydrogen bonds with Ala residues located in an ahelix? A. Residues in a neighbouring a-helix. ...
... hydrogen bonds with Ala residues located in an ahelix? A. Residues in a neighbouring a-helix. ...
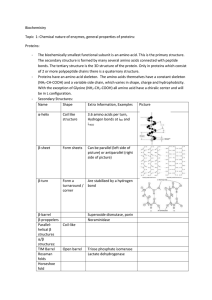
Biochemistry Topic 1: Chemical nature of enzymes, general
... The tertiary structure will be a 3 dimensional structure which will be the most stable structure (ΔGF < ΔGD). The 3D structure depends on the primary structure and if there has ben an error during translation or transcribtion or there has been a DNA mutatuin the most stable 3d structure might not be ...
... The tertiary structure will be a 3 dimensional structure which will be the most stable structure (ΔGF < ΔGD). The 3D structure depends on the primary structure and if there has ben an error during translation or transcribtion or there has been a DNA mutatuin the most stable 3d structure might not be ...
Lecture 3
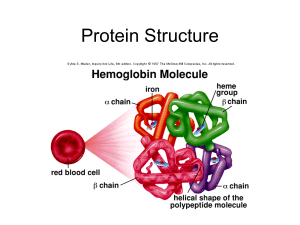
... Conjugated – in addition to the polypeptide chain these proteins contain other non-amino acid components known as prosthetic groups (e.g. metal ions, cofactors, lipids, carbohydrates) Example: Hemoglobin – Heme Each polypeptide chain which is a polymer of amino acids linked by peptide bonds can be c ...
... Conjugated – in addition to the polypeptide chain these proteins contain other non-amino acid components known as prosthetic groups (e.g. metal ions, cofactors, lipids, carbohydrates) Example: Hemoglobin – Heme Each polypeptide chain which is a polymer of amino acids linked by peptide bonds can be c ...
7.5 Proteins notes
... The primary structure of a polypeptide has group projecting from the backbone. These groups can attract each other and through hydrogen bonding cause a folding of the amino acid chain. There are three noted forms of secondary structure: 1. Alpha Helix: Formed from Hydrogen Bonds There are 3.6 amino ...
... The primary structure of a polypeptide has group projecting from the backbone. These groups can attract each other and through hydrogen bonding cause a folding of the amino acid chain. There are three noted forms of secondary structure: 1. Alpha Helix: Formed from Hydrogen Bonds There are 3.6 amino ...
Quiz-2
... 4. What is the difference between the cross-linking of keratin in hair and that of collagens fibrils in connective tissue? 5. The helical structure in collagen is very compact. What is the structural explanation for this phenomenon? 6. What were the two physical criterion used by Ramchandran to pred ...
... 4. What is the difference between the cross-linking of keratin in hair and that of collagens fibrils in connective tissue? 5. The helical structure in collagen is very compact. What is the structural explanation for this phenomenon? 6. What were the two physical criterion used by Ramchandran to pred ...
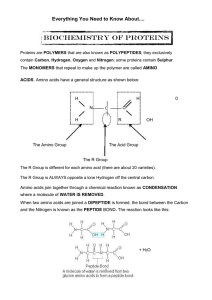
AS Biology - Everything Protein
... where a molecule of WATER IS REMOVED. When two amino acids are joined a DIPEPTIDE is formed, the bond between the Carbon and the Nitrogen is known as the PEPTIDE BOND. The reaction looks like this: ...
... where a molecule of WATER IS REMOVED. When two amino acids are joined a DIPEPTIDE is formed, the bond between the Carbon and the Nitrogen is known as the PEPTIDE BOND. The reaction looks like this: ...
Proteins - Boardworks
... Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. They have a wide range of biological roles, including: ...
... Proteins are a diverse group of large and complex polymer molecules, made up of long chains of amino acids. They have a wide range of biological roles, including: ...
Biochemistry 3020 1. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only ______
... Some examples are 4-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, Selenocysteine, and Pyrrolysin. Uncommon amino acids in proteins (other than selenocysteine/ pyrrolysin) usually result from chemical modifications of standard amino acid R groups after a protein has been synthesized (post translational). Selenocy ...
... Some examples are 4-hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine, Selenocysteine, and Pyrrolysin. Uncommon amino acids in proteins (other than selenocysteine/ pyrrolysin) usually result from chemical modifications of standard amino acid R groups after a protein has been synthesized (post translational). Selenocy ...
Supplementary Material
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...
... The secondary structure definitions of amino acids were generated with DSSP [1] considering only three groups: helical (H), extended (E) and coil (C). Based on this 7 types of protein interfaces can be defined taking into consideration the amount of each of the three basic secondary structural eleme ...