Pauli Exclusion Principle
... The electron configuration of an atom gives the distribution of electrons among atomic orbitals in the atom. Two general methods are used to show electron configurations. The subshell notation uses numbers to designate the principal shells and the letters s, p, d, and f to identify the subshells. A ...
... The electron configuration of an atom gives the distribution of electrons among atomic orbitals in the atom. Two general methods are used to show electron configurations. The subshell notation uses numbers to designate the principal shells and the letters s, p, d, and f to identify the subshells. A ...
Che-30042 Lecture 1 - Rob Jackson`s Website
... • For Be, the ordering of the orbitals will not be affected, but in the case of K and Ca, the energy of the 4s orbital will be found to be lower than 3d at the end of the calculation, explaining the orbital occupancies. • A problem with the SCF method is that it does not treat electron correlation ( ...
... • For Be, the ordering of the orbitals will not be affected, but in the case of K and Ca, the energy of the 4s orbital will be found to be lower than 3d at the end of the calculation, explaining the orbital occupancies. • A problem with the SCF method is that it does not treat electron correlation ( ...
Quantum Numbers - Evan`s Chemistry Corner
... o For ℓ =1 there is one node, so p orbitals have two lobes o For ℓ =2 there are two nodes, so d orbitals have four lobes o For ℓ =3 there are three nodes, so most f orbitals have eight lobes ...
... o For ℓ =1 there is one node, so p orbitals have two lobes o For ℓ =2 there are two nodes, so d orbitals have four lobes o For ℓ =3 there are three nodes, so most f orbitals have eight lobes ...
No Slide Title
... He deals the cards to find the answers the sacred geometry of chance the hidden law of a probable outcome the numbers lead a dance Sting: Shape of my heart ...
... He deals the cards to find the answers the sacred geometry of chance the hidden law of a probable outcome the numbers lead a dance Sting: Shape of my heart ...
mp2b-16 honors
... What was different about Planck's description of light compared to the previous theory of light? C. Know how to use the two equations of light - know the metric system! E=hx C=x D. What are the frequency, wavelength, and amplitude of a light wave? Be able to diagram. What happens when each is cha ...
... What was different about Planck's description of light compared to the previous theory of light? C. Know how to use the two equations of light - know the metric system! E=hx C=x D. What are the frequency, wavelength, and amplitude of a light wave? Be able to diagram. What happens when each is cha ...
PART 1 Identical particles, fermions and bosons. Pauli exclusion
... So, we end up with usual Schrodinger equation. In this case the number of variational parameters = ∞, Ψ∗ (x) at each point x. The variational method does not bring anything new. ...
... So, we end up with usual Schrodinger equation. In this case the number of variational parameters = ∞, Ψ∗ (x) at each point x. The variational method does not bring anything new. ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms
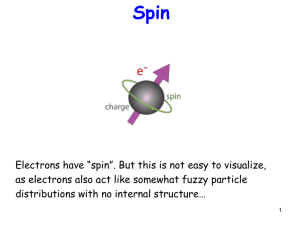
... • The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy. • This led to a fourth quantum number, the spin quantum number, ms. • The spin quantum number has only 2 allowed values: +1/2 and ...
... • The “spin” of an electron describes its magnetic field, which affects its energy. • This led to a fourth quantum number, the spin quantum number, ms. • The spin quantum number has only 2 allowed values: +1/2 and ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... Quantum Mechanical Model • As the energy of an electron increases, so does the quantum number (n) • Each principle energy level is also split up into one or more sublevels • Chart on Pg. 145 [http://www.chemistry.mcmaster.ca/esam/Chapter_4/fig4-2.jpg] ...
... Quantum Mechanical Model • As the energy of an electron increases, so does the quantum number (n) • Each principle energy level is also split up into one or more sublevels • Chart on Pg. 145 [http://www.chemistry.mcmaster.ca/esam/Chapter_4/fig4-2.jpg] ...
Guidelines for Abstract
... 1. Introduction After more than a decade of the formulation of multi-configuration time-dependent HartreeFock (MCTDHF) method to treat electronic dynamics in atoms and molecules induced by the interaction with intense ultrafast laser pulses from first principles [1], the theoretical efforts exerted ...
... 1. Introduction After more than a decade of the formulation of multi-configuration time-dependent HartreeFock (MCTDHF) method to treat electronic dynamics in atoms and molecules induced by the interaction with intense ultrafast laser pulses from first principles [1], the theoretical efforts exerted ...
Slide1
... Spin is like angular momentum Recall m can have (2l+1) values between –l and l. For spin, since only 2 ...
... Spin is like angular momentum Recall m can have (2l+1) values between –l and l. For spin, since only 2 ...
Chapt. 5: Quantum Theory of the Hydrogen Atom
... -This is the equation we just derived, but with nf fixed at a value of 2 -So, the Bohr model also accurately predicts the frequencies of the Balmer Series emission lines -BUT, it also predicts other emission lines (for nf = 1, 3, 4, etc.) ...
... -This is the equation we just derived, but with nf fixed at a value of 2 -So, the Bohr model also accurately predicts the frequencies of the Balmer Series emission lines -BUT, it also predicts other emission lines (for nf = 1, 3, 4, etc.) ...
Chemistry CPA Activity Sheet Week of November 18, 2013 Unit
... Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light. Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model. Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. Explain how the Heisenberg unce ...
... Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light. Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect and the line-emission spectrum of hydrogen to the development of the atomic model. Discuss Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom. Explain how the Heisenberg unce ...
Chapter 3
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
... finding an electron at various locations around the nucleus of. An atomic orbitals is represented pictorially as a region of space in which there is a high probably of finding an electron. ...
Chapter 6
... •As the number of electrons increases, though, so does the repulsion between them. •Therefore, in many-electron atoms, orbitals on the same energy level are no longer degenerate. ...
... •As the number of electrons increases, though, so does the repulsion between them. •Therefore, in many-electron atoms, orbitals on the same energy level are no longer degenerate. ...
Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... (R is ozen labeled as RH for reasons that will be obvious later.) ...
... (R is ozen labeled as RH for reasons that will be obvious later.) ...
BCIT Fall 2012 Chem 3615 Exam #2
... Section II: Short answer calculations do not need to be shown (16 points total). ...
... Section II: Short answer calculations do not need to be shown (16 points total). ...
Questions
... We have seen that the spectrum of hydrogen has an “accidental” degeneracy – states with the same principle quantum number n, but different angular momentum quantum number l are degenerate. This was an artifact of the pure 1/r Coulomb potential associated . In a multielectron atom things are, of cour ...
... We have seen that the spectrum of hydrogen has an “accidental” degeneracy – states with the same principle quantum number n, but different angular momentum quantum number l are degenerate. This was an artifact of the pure 1/r Coulomb potential associated . In a multielectron atom things are, of cour ...
Computational Quantum Chemistry of Chemical Kinetic Modeling
... for generating the Hartree-Fock operator F orbitals generated by this estimate of the Hartree-Fock operator is then used to repeat the calculations and so on until the orbital no longer changes (within a certain tolerance) on further interactions. These orbitals are said to be self-consistent with t ...
... for generating the Hartree-Fock operator F orbitals generated by this estimate of the Hartree-Fock operator is then used to repeat the calculations and so on until the orbital no longer changes (within a certain tolerance) on further interactions. These orbitals are said to be self-consistent with t ...
The Quantum Model of the Atom
... -the # of orbital shapes possible is equal to n -values are zero and positive integers less than or equal to n-1 (0 = s, 1 = p, 2 = d, 3 = f) -s orbitals are spherical; p orbitals are dumbbell shaped; d and f orbitals are more complex -value of n = # of sublevels. Ex: nth main energy level is n subl ...
... -the # of orbital shapes possible is equal to n -values are zero and positive integers less than or equal to n-1 (0 = s, 1 = p, 2 = d, 3 = f) -s orbitals are spherical; p orbitals are dumbbell shaped; d and f orbitals are more complex -value of n = # of sublevels. Ex: nth main energy level is n subl ...
Light Control using Organometallic Chromophores Johan Henriksson Link¨
... absorption and processes following [20]. The problem with this part of the device is that it will saturate, and, therefore, only be able to block a first, or a first few pulses, and not against continuous lasers or consecutive pulses. However, this initial, self-activating, part buys time necessary ...
... absorption and processes following [20]. The problem with this part of the device is that it will saturate, and, therefore, only be able to block a first, or a first few pulses, and not against continuous lasers or consecutive pulses. However, this initial, self-activating, part buys time necessary ...
Chapter 7, Quantum Nos.
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
ID_72_paper
... integro-differential closed-shell Hartree-Fock equations to a set of algebraic equations, known as Roothaan equations [2]. In order to fulfil the antisymmetic principle, the wave function for N-electron system is taken in the form of Slater determinant [7] and using the Born-Oppenheimer approximatio ...
... integro-differential closed-shell Hartree-Fock equations to a set of algebraic equations, known as Roothaan equations [2]. In order to fulfil the antisymmetic principle, the wave function for N-electron system is taken in the form of Slater determinant [7] and using the Born-Oppenheimer approximatio ...
Chp7,Quantum_Num
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
... For the H atom the orbital energy depends only on n, so all orbitals with the same value of n have the same energy. This is not true, however, for any other atom! The H atom orbitals may be used to approximate the orbitals for multi-electron atoms. But since these atoms have more than one electron, ...
Modern Model of the Atom
... 1. AUFBAU PRINCIPLE - electrons enter orbitals of the lowest energy levels first 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic orbital may hold at most two electrons. Each must have an opposite spin. 3. HUND’S RULE - when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy one electron enters each orbital until al ...
... 1. AUFBAU PRINCIPLE - electrons enter orbitals of the lowest energy levels first 2. PAULI EXCLUSION PRINCIPLE - an atomic orbital may hold at most two electrons. Each must have an opposite spin. 3. HUND’S RULE - when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy one electron enters each orbital until al ...
Quantum Numbers “Where are the Electrons?”
... An orbital is a three-dimensional region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron. Quantum numbers are used to describe atomic orbitals and the electrons in them. There are 4 quantum numbers: o The principal quantum number (n), indicates the main energy level occupied b ...
... An orbital is a three-dimensional region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron. Quantum numbers are used to describe atomic orbitals and the electrons in them. There are 4 quantum numbers: o The principal quantum number (n), indicates the main energy level occupied b ...