Many-electron wave functions
... orbitals, so we can assume the orbitals are orthonormal without any loss of generality. This development also shows that given any set of N orbitals from which the Slater wave function has been constructed, we can take N linear combinations of the orbitals to obtain new orbitals that give the same S ...
... orbitals, so we can assume the orbitals are orthonormal without any loss of generality. This development also shows that given any set of N orbitals from which the Slater wave function has been constructed, we can take N linear combinations of the orbitals to obtain new orbitals that give the same S ...
Exam and Study Notes
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
... o The Aufbau Principle (electrons start from the lowest energy) “The building up principle” The Aufbau Principle states that the to fill the 3d subshell, the 4s subshell must have 2 electrons in the subshell first o Pauli Exclusion Principle(Opposite spins) No two electron can have the same sp ...
Quantum Chemistry and Spectroscopy
... not very accurate). The reactants will have a certain lowest energy geometry, the transition state will have an other geometry and the products will again have some geometry. If these geometries can be found the Reactant, Transition state and Product energies can be computed. Unfortunately the relev ...
... not very accurate). The reactants will have a certain lowest energy geometry, the transition state will have an other geometry and the products will again have some geometry. If these geometries can be found the Reactant, Transition state and Product energies can be computed. Unfortunately the relev ...
Chemistry I Midterm Exam
... Put the correct sign (“<” or “>”) for the comparison of orbital energies below for a manyelectron atom ...
... Put the correct sign (“<” or “>”) for the comparison of orbital energies below for a manyelectron atom ...
Atomic Variational Calculations: Hydrogen to Boron
... The purpose of this tutorial is to calculate the ground-state energies of simple multi-electron atoms and ions using the variational method. In the interest of mathematical and computational simplicity the single parameter, orthonormal hydrogenic wave functions shown below will be used. The method w ...
... The purpose of this tutorial is to calculate the ground-state energies of simple multi-electron atoms and ions using the variational method. In the interest of mathematical and computational simplicity the single parameter, orthonormal hydrogenic wave functions shown below will be used. The method w ...
4.quantumorbitals
... Quantum Theory The electron is like a cloud of negative energy or a wave. Orbitals are areas in 3D space where the electrons most probably are. The energy of the electron is in its vibrational modes- like notes on a guitar string. Photons are produced when high energy modes change to lower energy mo ...
... Quantum Theory The electron is like a cloud of negative energy or a wave. Orbitals are areas in 3D space where the electrons most probably are. The energy of the electron is in its vibrational modes- like notes on a guitar string. Photons are produced when high energy modes change to lower energy mo ...
Chap 8.
... quantum-mechanical problem which cannot be solved exactly. Nevertheless, as we will show, approximation methods applied to helium can give accurate solutions in perfect agreement with experimental results. In this sense, it can be concluded that quantum mechanics is correct for atoms more complicate ...
... quantum-mechanical problem which cannot be solved exactly. Nevertheless, as we will show, approximation methods applied to helium can give accurate solutions in perfect agreement with experimental results. In this sense, it can be concluded that quantum mechanics is correct for atoms more complicate ...
2 - IS MU
... We start from the mean field approximation. This is an educated way, similar to (almost identical with) the HARTREE APPROXIMATION we know for many electron systems. Most of the interactions is indeed absorbed into the mean field and what remains are explicit quantum correlation corrections ...
... We start from the mean field approximation. This is an educated way, similar to (almost identical with) the HARTREE APPROXIMATION we know for many electron systems. Most of the interactions is indeed absorbed into the mean field and what remains are explicit quantum correlation corrections ...
chapt-5-review
... energies of multi-electron orbitals for a many-electron atom, the energy depends on both the principal quantum number and the angular momentum quantum number i.e., each subshell represents a different energy in a multi-electron system ...
... energies of multi-electron orbitals for a many-electron atom, the energy depends on both the principal quantum number and the angular momentum quantum number i.e., each subshell represents a different energy in a multi-electron system ...
Electrons in the Atom
... 3. What is the energy released when a hydrogen electron moves from n=6 to n=2? 4. What is the difference between ground state and excited state? How do electrons move between these two states? 5. What does it mean for an atom to become an ion? How does the charge relate to the change in electrons? ...
... 3. What is the energy released when a hydrogen electron moves from n=6 to n=2? 4. What is the difference between ground state and excited state? How do electrons move between these two states? 5. What does it mean for an atom to become an ion? How does the charge relate to the change in electrons? ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... We now minimize E () with respect to by differentiating with respect to and setting the result equal to zero. We solve the equation: ...
... We now minimize E () with respect to by differentiating with respect to and setting the result equal to zero. We solve the equation: ...
Chapter 7 Lect. 2
... 2. 2p orbitals (n = 2, l = 1) have 2 lobes with a node at the nucleus 3. There are three different p-orbitals (l = 1, ml = -1, 0, 1) a. 2px lies along the x-axis b. 2py lies along the y-axis c. 2pz lies along the z-axis 4. All three 2p orbitals have the same energy = degenerate 5. 3p, 4p, 5p, etc… h ...
... 2. 2p orbitals (n = 2, l = 1) have 2 lobes with a node at the nucleus 3. There are three different p-orbitals (l = 1, ml = -1, 0, 1) a. 2px lies along the x-axis b. 2py lies along the y-axis c. 2pz lies along the z-axis 4. All three 2p orbitals have the same energy = degenerate 5. 3p, 4p, 5p, etc… h ...
Basis Sets - unix.eng.ua.edu
... • The iterative SCF method is then used to solve for the energy, the wave function, and the associated coefficients. DRAWBACKS of HF SCF: 1. Electron correlation is still neglected 2. LCAO approach requires intensive four-index integrals (not shown here) 3. The # of four-index integrals calculated s ...
... • The iterative SCF method is then used to solve for the energy, the wave function, and the associated coefficients. DRAWBACKS of HF SCF: 1. Electron correlation is still neglected 2. LCAO approach requires intensive four-index integrals (not shown here) 3. The # of four-index integrals calculated s ...
Ch. 4-2 PowerPoint
... There are different types of orbitals….s, p, d, f which we will talk about more later. ...
... There are different types of orbitals….s, p, d, f which we will talk about more later. ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... simplicity of the trial function. The value of Z that minimize E can be interpreted as an effective charge. That fact that Z comes out to be less than 2 reflects the fact that each electron partially screens the nucleus from the other , so that net effective nuclear charge is reduced from 2 to 27/16 ...
... simplicity of the trial function. The value of Z that minimize E can be interpreted as an effective charge. That fact that Z comes out to be less than 2 reflects the fact that each electron partially screens the nucleus from the other , so that net effective nuclear charge is reduced from 2 to 27/16 ...
Document
... • Coupling between various angular momentum vectors – Gyroscopic forces disturb orbital motion of ...
... • Coupling between various angular momentum vectors – Gyroscopic forces disturb orbital motion of ...
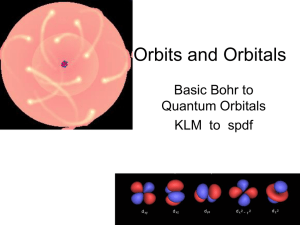
Orbits and Orbitals
... More rules • No orbital can have more than 2 e- in it. (one spin up, one spin down) • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
... More rules • No orbital can have more than 2 e- in it. (one spin up, one spin down) • Orbitals are half filled (with spins in the same direction) before they are doubly filled. • Orbitals are filled from lowest energy to highest energy. ...
General Introduction to Electronic Structure Theory
... • The electronic energy for an individual molecule shouldn’t change if we translate or rotate the molecule --- it only depends on the internal degrees of freedom • Each molecule has three translational degrees of freedom, and usually three rotational degrees of freedom (2 for linear molecules) • For ...
... • The electronic energy for an individual molecule shouldn’t change if we translate or rotate the molecule --- it only depends on the internal degrees of freedom • Each molecule has three translational degrees of freedom, and usually three rotational degrees of freedom (2 for linear molecules) • For ...
Chemistry 102 Summary June 25th - Bohr model only works for one
... Specific wave functions are called orbitals. Orbitals define the allowed energy states where electrons can reside. There are four basic shapes: s, p, d and f Shapes represent where an electron will reside 90 % of the time in that allowed energy state. From Heisenberg – the exact location cannot be d ...
... Specific wave functions are called orbitals. Orbitals define the allowed energy states where electrons can reside. There are four basic shapes: s, p, d and f Shapes represent where an electron will reside 90 % of the time in that allowed energy state. From Heisenberg – the exact location cannot be d ...
computational chemistry
... theory to explain the terminology used in later chapters. The core of this book is the description of the many computation techniques available and when to use them. Prioritizing which techniques work better or worse for various types of problems is a double-edged sword. This is certainly the type o ...
... theory to explain the terminology used in later chapters. The core of this book is the description of the many computation techniques available and when to use them. Prioritizing which techniques work better or worse for various types of problems is a double-edged sword. This is certainly the type o ...
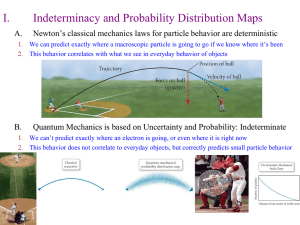
Quantum mechanics and electron structure
... The missing link in Bohr’s model was the quantum nature of the electron Quantum mechanics yields a viable model for electronic structure in all elements Quantum mechanics replaced the particle by the wave The extent to which it is physical reality or an abstract mathematical model remains a fascinat ...
... The missing link in Bohr’s model was the quantum nature of the electron Quantum mechanics yields a viable model for electronic structure in all elements Quantum mechanics replaced the particle by the wave The extent to which it is physical reality or an abstract mathematical model remains a fascinat ...
probability = ψ 2
... configurations of atoms in the corresponding atomic orbital theory. For example, an electron in H2 may be excited to any of the vacant orbitals of higher energy indicated in the energy level diagram. The excited molecule may return to its ground configuration with the emission of a photon. The energ ...
... configurations of atoms in the corresponding atomic orbital theory. For example, an electron in H2 may be excited to any of the vacant orbitals of higher energy indicated in the energy level diagram. The excited molecule may return to its ground configuration with the emission of a photon. The energ ...
Bohr Model, Quantum Mechanical Model
... b. energy is involved in moving an electron from one level to another. 4. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- It is impossible to know the momentum (mass of electron times velocity) of an electron and its position in space at the same time. One or the other. 5. Quantum Mechanical Model- a mathematical ...
... b. energy is involved in moving an electron from one level to another. 4. Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle- It is impossible to know the momentum (mass of electron times velocity) of an electron and its position in space at the same time. One or the other. 5. Quantum Mechanical Model- a mathematical ...
Nextnano_NEGF - Walter Schottky Institut
... Determination of wave functions and bound states OUTPUT ...
... Determination of wave functions and bound states OUTPUT ...