* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrons in the Atom
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen-vacancy center wikipedia , lookup
Hartree–Fock method wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
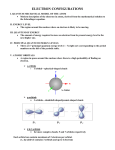
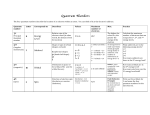
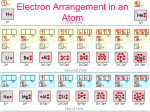
Electrons in the Atom What do we know about electrons? 1. What is the basic information about electrons (charge, mass, location)? 2. Explain the Bohr model structure. Draw a model for carbon. Label the valence electrons. Draw a Lewis dot structure for carbon. 3. What is the energy released when a hydrogen electron moves from n=6 to n=2? 4. What is the difference between ground state and excited state? How do electrons move between these two states? 5. What does it mean for an atom to become an ion? How does the charge relate to the change in electrons? Quantum Mechanics • Using a mathematical description of the wavelike behavior of particles on the atomic level • Electrons are located in orbitals (spaces where they have a high probability of being found) • Each orbital is described by three quantum numbers Atomic Orbitals • Region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron • Principal quantum number, n • Angular momentum quantum number l • Magnetic quantum number ml Principal Energy levels • Quantum number, n • Orbitals with the same value of n are in the same shell Energy level n Max number • n= 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. electrons 1 2 2 8 3 18 4 32 Angular Momentum quantum number l • Orbitals with the same value of n and l are in the same subshell • Different shaped spaces within the sublevels • s is spherical (1 orbital) • p is dumbbell (3 orbitals) • d varies (5 orbitals) • f more complex (7 orbitals) • (2 electrons per orbital) Summary of Principal Energy Levels, Sublevels, and Orbitals Energy level n Number of sublevels Type of sublevel 1 1 1s 2 2 2s, 2p 3 3 3s, 3p, 3d 4 4 4s, 4p, 4d, 4f Magnetic quantum number ml • Distinguishes orbitals of given n and l, of given energy and shape but having different orientation in space • Values are integers from -1 to +1 Magnetic quantum number ms • Refers to the two possible orientations of the spin axis of an electron • Values are +1/2 and -1/2 • Each orbital can contain two electrons with opposite spins • “Up” • “Down” • Spintronics Keeping Track of Electrons • All this information about electrons is very hard to visualize and understand • Electron configuration and orbital diagrams can help • Electron configuration: description of the orbitals occupied by electrons Three rules and electron configuration • • • • Aufbau PrinciplePauli Exclusion Principal – Hund’s Rule – (Page 133-134) Three rules and electron configuration • Aufbau Principle- fill lowest energy level first • Pauli Exclusion Principal – 2 electrons per orbital with opposite spin • Hund’s Rule – Bus Seat, electrons occupy orbitals in the same energy level going in the same spin direction • (Page 133-134) Energy Levels & Orbitals Energy Levels Sublevels Orbitals 16 Aufbau diagram Orbital diagram Electron configuration 1s22s22p63s1 Sodium • Electron Configuration Video • Periodic Table Song