Sensation and Perception
... contains receptor cells that are sensitive to the physical energy of light. The most important sense to humans Light is one of many different kinds of magnetic energy that travels in the form of waves Other forms of electromagnetic energy include X-rays, the microwave oven, and ultraviolet light ...
... contains receptor cells that are sensitive to the physical energy of light. The most important sense to humans Light is one of many different kinds of magnetic energy that travels in the form of waves Other forms of electromagnetic energy include X-rays, the microwave oven, and ultraviolet light ...
Somatosensory 2
... Pain (Nociception) The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimu ...
... Pain (Nociception) The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimu ...
Peripheral NS: Sensory processing & receptors
... Sensory Receptors Specialized structures which respond to changes in their environment (stimuli) Some receptors are simply ends of sensory nerve fibers. Other receptors are cells adjacent to sensory nerrve fibers. Other receptors are sensory nerve fiber endings plus specialized supporting cells and ...
... Sensory Receptors Specialized structures which respond to changes in their environment (stimuli) Some receptors are simply ends of sensory nerve fibers. Other receptors are cells adjacent to sensory nerrve fibers. Other receptors are sensory nerve fiber endings plus specialized supporting cells and ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... producing a graded depolarization that can lead to action potentials. Information from olfactory receptors is transmitted directly to the cerebral cortex instead of being relayed through the thalamus. 5. As the head accelerates in one direction, inertia causes structures in the vestibular apparatus ...
... producing a graded depolarization that can lead to action potentials. Information from olfactory receptors is transmitted directly to the cerebral cortex instead of being relayed through the thalamus. 5. As the head accelerates in one direction, inertia causes structures in the vestibular apparatus ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... • Parietal toe) • Temporal • Occipital Motor speech area (Broca’s • Insula area) Occipital lobe, vision from retina ...
... • Parietal toe) • Temporal • Occipital Motor speech area (Broca’s • Insula area) Occipital lobe, vision from retina ...
The somatic sensory system
... From Sensation to Perception Sensation: the awareness of changes in the internal and external environment Perception: the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
... From Sensation to Perception Sensation: the awareness of changes in the internal and external environment Perception: the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
Sensory pathways
... LEARNING OBJECTIVES. • At the end of lecture, students should be able to know: • Sensory pathways and receptors. • Spinothalamic pathway. • Spinothalamic damage. • Dorsal column pathway. • Dorsal column damage. • Spinocerebellar pathway. • Spinocerebellar tract damage. ...
... LEARNING OBJECTIVES. • At the end of lecture, students should be able to know: • Sensory pathways and receptors. • Spinothalamic pathway. • Spinothalamic damage. • Dorsal column pathway. • Dorsal column damage. • Spinocerebellar pathway. • Spinocerebellar tract damage. ...
sensory neurone
... a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector ...
... a) receptor-->sensory neurone-->relay neurone-->motor neurone--> effector b) receptor--> motor neurone-->relay neurone-->sensory neurone-->effector ...
PsychScich04
... • Ventral stream appears to be specialized for the perception and recognition of objects • Dorsal stream seems to be specialized for spatial perception (determining where an object is) • These two processing streams are therefore known as the “what” stream and the “where” stream ...
... • Ventral stream appears to be specialized for the perception and recognition of objects • Dorsal stream seems to be specialized for spatial perception (determining where an object is) • These two processing streams are therefore known as the “what” stream and the “where” stream ...
Anatomy of the Sensory organs
... All sensory receptors send info to the CNS via an action potential… • At the CNS, info is routed according to the stimulus and its location • The stronger the stimulus, the higher the frequency of action potentials • Some receptors adapt, that is their sensitivity to a stimulus is reduced if the st ...
... All sensory receptors send info to the CNS via an action potential… • At the CNS, info is routed according to the stimulus and its location • The stronger the stimulus, the higher the frequency of action potentials • Some receptors adapt, that is their sensitivity to a stimulus is reduced if the st ...
The Somatic Sensory System and Touch
... temperature, pain, and basic touch information to your cerebrum Spinocerebellar tract carries information about posture and position to your cerebellum ...
... temperature, pain, and basic touch information to your cerebrum Spinocerebellar tract carries information about posture and position to your cerebellum ...
Chapters Five and Six – Sensation and Perception
... Theories of color vision o Explain the difference between the YoungHelmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Opponent Processing Theory Hearing Amplitude vs. Frequency Anatomy of the ear Activity – Sound localization Types of hearing loss Touch, Taste and Smell Body position and movement Ves ...
... Theories of color vision o Explain the difference between the YoungHelmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Opponent Processing Theory Hearing Amplitude vs. Frequency Anatomy of the ear Activity – Sound localization Types of hearing loss Touch, Taste and Smell Body position and movement Ves ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves The Brain
... Sulcus is the Primary Somesthetic Area • Sensory information from the entire body comes into this gyrus • The fraction of this gyrus that functions for any particular area of the body is an indication of how important that region is to sensory input ...
... Sulcus is the Primary Somesthetic Area • Sensory information from the entire body comes into this gyrus • The fraction of this gyrus that functions for any particular area of the body is an indication of how important that region is to sensory input ...
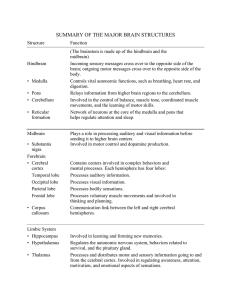
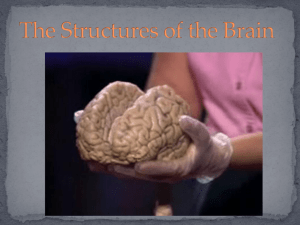
The Structures of the Brain
... with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the ...
... with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the ...
Touch is complicated
... Active Tactile = directed & dynamic contact of body surface (skin) with object surface Movement intended to produce or enhance sensations by changing part of body making contact or making contact with adjacent areas of body – usually 1dimensional pressing or 2-dimensional sweeping Haptic perc ...
... Active Tactile = directed & dynamic contact of body surface (skin) with object surface Movement intended to produce or enhance sensations by changing part of body making contact or making contact with adjacent areas of body – usually 1dimensional pressing or 2-dimensional sweeping Haptic perc ...
Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory
... • One input variable: Stimulus • One output measure: unit recording from region of interest • One anatomical map and one functional map • Receptive fields: naturally occurring stimulus modality to which the neuron is most responsive ...
... • One input variable: Stimulus • One output measure: unit recording from region of interest • One anatomical map and one functional map • Receptive fields: naturally occurring stimulus modality to which the neuron is most responsive ...
Lecture 5 - TeachLine
... Introduction to Sensory Systems Mapping the receptive field of visual system neurons using small spots of light or dark. Very effective in RGC & LGN. Very problematic for Visual Cortex. ...
... Introduction to Sensory Systems Mapping the receptive field of visual system neurons using small spots of light or dark. Very effective in RGC & LGN. Very problematic for Visual Cortex. ...
Neuron Powerpoint
... • The phenomenon of sensory adaptation focuses our attention on informative changes in stimulation by diminishing our sensitivity to constant or routine odors, sounds, and touches ...
... • The phenomenon of sensory adaptation focuses our attention on informative changes in stimulation by diminishing our sensitivity to constant or routine odors, sounds, and touches ...
Nervous System III – Senses
... Example: Perception occurs when the brain interprets sensory impulses (realizing that the pain is a result of stepping on a tack). ...
... Example: Perception occurs when the brain interprets sensory impulses (realizing that the pain is a result of stepping on a tack). ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Somatic Sensory System
... mechanoreceptors Provide information about touch, pressure, vibration, and skin tension. Four major types of encapsulated mechanoreceptors: • Meissner’s corpuscle • Pacinian corpuscle • Merkel’s disk • Ruffini’s corpuscle. Called low-threshold because even weak stimulation causes action potentials. ...
... mechanoreceptors Provide information about touch, pressure, vibration, and skin tension. Four major types of encapsulated mechanoreceptors: • Meissner’s corpuscle • Pacinian corpuscle • Merkel’s disk • Ruffini’s corpuscle. Called low-threshold because even weak stimulation causes action potentials. ...
HUMAN INFORMATION PROCESSING
... It took three weeks of adaptation for correct answers to appear, suggesting that a new imagined hand representation was emerging; the volunteers said they could visualize their own hands in two ways and could even choose between the two images. Brain scans associated activity with these new hand im ...
... It took three weeks of adaptation for correct answers to appear, suggesting that a new imagined hand representation was emerging; the volunteers said they could visualize their own hands in two ways and could even choose between the two images. Brain scans associated activity with these new hand im ...