![Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001686639_1-accaddf9a4bef8f1f5e508cc8efafb82-300x300.png)
Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]
... 1. Place Theory – we can determine pitch by detecting how far up the basilar membrane the vibration travels. Higher pitched sounds travel lower down the basilar membrane, while low pitched sounds travel further up the basilar membrane. Accounts well for high pitched sounds. 2. Frequency Theory – the ...
... 1. Place Theory – we can determine pitch by detecting how far up the basilar membrane the vibration travels. Higher pitched sounds travel lower down the basilar membrane, while low pitched sounds travel further up the basilar membrane. Accounts well for high pitched sounds. 2. Frequency Theory – the ...
A. Sensation
... tendons, and joints; and in the inner ear sensory receptors here are distributed unevenly highest density areas – tip of tongue, lips, fingertips somatic sensations that result from stimulating the skin surface are called cutaneous sensations are of four modalities: tactile, thermal, pain propriocep ...
... tendons, and joints; and in the inner ear sensory receptors here are distributed unevenly highest density areas – tip of tongue, lips, fingertips somatic sensations that result from stimulating the skin surface are called cutaneous sensations are of four modalities: tactile, thermal, pain propriocep ...
The Nervous System
... Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of ...
... Example: Poison blocks muscle movement Acetylcholine (Ach) – Enables muscle action, learning, and memory **Brains of those suffering from Alzheimer’s have deteriorating Achproducing neurons Endorphins – natural neurotransmitters linked to pain control and pleasure **”Runner’s High” is an example of ...
Can an Injured Spinal Cord Be Fixed?
... Auditory association area Somatosensory association area (reading, speech) Visual association area ...
... Auditory association area Somatosensory association area (reading, speech) Visual association area ...
Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Sensory Receptors Martin Paré
... specific area, which defines the receptor’s receptive field. When action potentials are elicited from a sensory neuron, the neuron’s receptive field codes the stimulus location. ...
... specific area, which defines the receptor’s receptive field. When action potentials are elicited from a sensory neuron, the neuron’s receptive field codes the stimulus location. ...
Retina Rods retina receptors that detect black, white, and gray
... Frequency theory= place theory explains hearing upper ranges of pitch only. Lower tones are sensed by the rate at which cells fire. We hear pitch because hair cells fire at diff. rates (frequency) in cochlea ...
... Frequency theory= place theory explains hearing upper ranges of pitch only. Lower tones are sensed by the rate at which cells fire. We hear pitch because hair cells fire at diff. rates (frequency) in cochlea ...
Reflex and autonomic nervous system
... things that the sensory receptors might collect from the internal and external environment. ...
... things that the sensory receptors might collect from the internal and external environment. ...
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
... area in a normal monkey cortex. The individual digit representation can be revealed using single unit recording. If the two fingers of one hand are sewn together, months later the cortical maps change such that the sharp border once present between the sewn fingers is now blurred. (Gazzaniga, ...
... area in a normal monkey cortex. The individual digit representation can be revealed using single unit recording. If the two fingers of one hand are sewn together, months later the cortical maps change such that the sharp border once present between the sewn fingers is now blurred. (Gazzaniga, ...
Marina Florack
... o Complete sensation but incomplete perception Absolute Threshold: min. stimulation needed to detect a stimulus 50% of the time Difference Threshold: min. difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time (JND- just noticeable difference) o Subliminal: stimulus below ones abs ...
... o Complete sensation but incomplete perception Absolute Threshold: min. stimulation needed to detect a stimulus 50% of the time Difference Threshold: min. difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time (JND- just noticeable difference) o Subliminal: stimulus below ones abs ...
Sprint Adaptive Swimwear - Post
... machine is not good for use by polio survivors, because it can stimulate nerve endings and possibly result in further damage to already over-exhausted neurons. Is this true? ANSWER: Since TENS only stimulates the sensory nerve endings and does not stimulate the motor nerves,* it does not cause muscl ...
... machine is not good for use by polio survivors, because it can stimulate nerve endings and possibly result in further damage to already over-exhausted neurons. Is this true? ANSWER: Since TENS only stimulates the sensory nerve endings and does not stimulate the motor nerves,* it does not cause muscl ...
Chapter 6
... Sensory Receptors: Transducers Transduction – the process on converting stimulus energy into electrical impulses that can be sent to the CNS Sensory receptors – sensory nerve endings that responds to changes in the environment around them by transducing stimuli into electrical impulses Ion channels ...
... Sensory Receptors: Transducers Transduction – the process on converting stimulus energy into electrical impulses that can be sent to the CNS Sensory receptors – sensory nerve endings that responds to changes in the environment around them by transducing stimuli into electrical impulses Ion channels ...
Sher`s Neurology Pre-Quiz Quiz
... 28. Unconscious 29. False – they can not be improved. Work with what you/re born with. 30. 1)Segmental response rule: for every stimulus there is a reflex, and 2.) The brain is always informed about what’s occurring. 31. D – all of them apply 32. Simple multisynaptic 33. Gray commissure, opposite 34 ...
... 28. Unconscious 29. False – they can not be improved. Work with what you/re born with. 30. 1)Segmental response rule: for every stimulus there is a reflex, and 2.) The brain is always informed about what’s occurring. 31. D – all of them apply 32. Simple multisynaptic 33. Gray commissure, opposite 34 ...
File
... • Sends information/messages from sensory receptors (such as skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARDS the CNS. • Sensory neurons have specialised endings that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the ...
... • Sends information/messages from sensory receptors (such as skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARDS the CNS. • Sensory neurons have specialised endings that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the ...
Topic: Nervous system Reading: Chapter 38 Main concepts
... • Damage to skin, blood vessels, and small nerves cause the release of potassium ions, stimulating pain receptors. • Other chemicals are involved in this response, some of which are blocked by pain medications. • Synesthesia: What might be called “cross-sensory perception.” The most common forms are ...
... • Damage to skin, blood vessels, and small nerves cause the release of potassium ions, stimulating pain receptors. • Other chemicals are involved in this response, some of which are blocked by pain medications. • Synesthesia: What might be called “cross-sensory perception.” The most common forms are ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... Anticipated Results: I expect to be able to map the retinotopic representations of the different ring sizes before and after acquisition and use this map to determine if conditioning causes a change in representation. I also anticipate being able to determine if there is a correlation between the am ...
... Anticipated Results: I expect to be able to map the retinotopic representations of the different ring sizes before and after acquisition and use this map to determine if conditioning causes a change in representation. I also anticipate being able to determine if there is a correlation between the am ...
Sensation
... stimulus information into electrochemical signals – neural activity – the only language the brain ...
... stimulus information into electrochemical signals – neural activity – the only language the brain ...
Chapters 13, and 14
... Vision is dependent on the eyes and the brain. About a third of the cerebral cortex takes part in processing visual information. Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye The eye has three layers. The outer layer, the sclera, can be seen as the white of the eye; it also becomes the transparent bulge in the ...
... Vision is dependent on the eyes and the brain. About a third of the cerebral cortex takes part in processing visual information. Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye The eye has three layers. The outer layer, the sclera, can be seen as the white of the eye; it also becomes the transparent bulge in the ...
Document
... • When 2 objects make the same size image on the retina, and we judge one to be farther away than the other, we assume that the more distant one is larger. ...
... • When 2 objects make the same size image on the retina, and we judge one to be farther away than the other, we assume that the more distant one is larger. ...
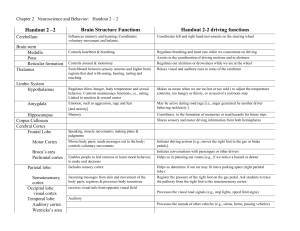
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...
... Frontal Lobe Motor Cortex Broca’s area Prefrontal cortex ...