Anatomy and Physiology
... Also allows you to estimated the amount of force needed to do something (lifting a bag of feathers or a bag of rocks). Receptors adapt very little if at all (you constantly need that information). ...
... Also allows you to estimated the amount of force needed to do something (lifting a bag of feathers or a bag of rocks). Receptors adapt very little if at all (you constantly need that information). ...
File
... Arousal is a state of awareness of the external world Sleep is a state in which external stimuli are received but not consciously perceived Sleep is also an active state Although sleep is essential for survival, we still know very little about its function, one hypothesis is that sleep and dreams ar ...
... Arousal is a state of awareness of the external world Sleep is a state in which external stimuli are received but not consciously perceived Sleep is also an active state Although sleep is essential for survival, we still know very little about its function, one hypothesis is that sleep and dreams ar ...
Nervous System
... Definition: the process by which organisms keep internal conditions relatively constant despite changes in their external environments Requires the integration of all organ systems at the same time Nervous system in conjunction with the endocrine system (hormones) is responsible for this integration ...
... Definition: the process by which organisms keep internal conditions relatively constant despite changes in their external environments Requires the integration of all organ systems at the same time Nervous system in conjunction with the endocrine system (hormones) is responsible for this integration ...
The Mechanical Senses: Vestibular and Somatosensation
... SOMATOSENSATION: sensation of the body/skin Sensory Neuron (or “Sensory Receptor”) Types 1) Tactile: response to being touched (“light” and “deep” touch) Ruffini ending, Meissner’s corpuscle, Pacinian corpuscle The axons from these receptors are myelinated! 2) Pain: response to noxious stimulus 3) ...
... SOMATOSENSATION: sensation of the body/skin Sensory Neuron (or “Sensory Receptor”) Types 1) Tactile: response to being touched (“light” and “deep” touch) Ruffini ending, Meissner’s corpuscle, Pacinian corpuscle The axons from these receptors are myelinated! 2) Pain: response to noxious stimulus 3) ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
Sensory system
... Each tract mediates specific modalities of sensation, somatotopic organization in tracts and cortex ...
... Each tract mediates specific modalities of sensation, somatotopic organization in tracts and cortex ...
Unit 4 Sensation
... Place Theory: Theory that the pitch we hear is associated with the place where the basilar membrane is stimulated. Best for explaining high-pitched tones. Frequency Theory: Theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of the tone we are hearing. Best f ...
... Place Theory: Theory that the pitch we hear is associated with the place where the basilar membrane is stimulated. Best for explaining high-pitched tones. Frequency Theory: Theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of the tone we are hearing. Best f ...
Early Brain Development and Its Implications for
... Sub-cortical Functions - involve involuntary responses characterized by unintentional and undifferentiated reactions to internal and external experiences often shown through such behaviors as posture, tone, respiration, palloring and so forth ...
... Sub-cortical Functions - involve involuntary responses characterized by unintentional and undifferentiated reactions to internal and external experiences often shown through such behaviors as posture, tone, respiration, palloring and so forth ...
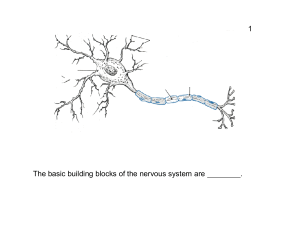
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Receptor Cells
... receptor cells in the cochlea that change sound vibrations into neural impulses ...
... receptor cells in the cochlea that change sound vibrations into neural impulses ...
Early Brain Development and Its Implications for
... Sub-cortical Functions - involve involuntary responses characterized by unintentional and undifferentiated reactions to internal and external experiences often shown through such behaviors as posture, tone, respiration, palloring and so forth ...
... Sub-cortical Functions - involve involuntary responses characterized by unintentional and undifferentiated reactions to internal and external experiences often shown through such behaviors as posture, tone, respiration, palloring and so forth ...
sensation.
... Sensation & Perception To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from the environment and convert it into neural signals. The process by which sensory systems and the nervous system receive stimuli from the environment is sensation. ...
... Sensation & Perception To represent the world, we must detect physical energy (a stimulus) from the environment and convert it into neural signals. The process by which sensory systems and the nervous system receive stimuli from the environment is sensation. ...
Nervous System
... • Neurons that carry sensory information • Neurons carrying motor information • Interneurons • Receptor ...
... • Neurons that carry sensory information • Neurons carrying motor information • Interneurons • Receptor ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... It is a building block of all proteins, but a high affinity transport system is required to get it through the ____ _____________________________________, thereby its concentration in brain fluids is also maintained at a fairly constant level. It is also synthetized in the CNS by the enzyme ________ ...
... It is a building block of all proteins, but a high affinity transport system is required to get it through the ____ _____________________________________, thereby its concentration in brain fluids is also maintained at a fairly constant level. It is also synthetized in the CNS by the enzyme ________ ...
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION
... experience the world in three-dimensions 1. Interposition – closer objects block the view of things further away 2. Relative Size – the object producing a larger image on the retina is perceived as closer 3. Height in the Visual Field – more distant objects are higher in the visual field 4. Texture ...
... experience the world in three-dimensions 1. Interposition – closer objects block the view of things further away 2. Relative Size – the object producing a larger image on the retina is perceived as closer 3. Height in the Visual Field – more distant objects are higher in the visual field 4. Texture ...
Nervous System
... Neurons that carry information about stimuli to the CNS-Central Nervous system ...
... Neurons that carry information about stimuli to the CNS-Central Nervous system ...
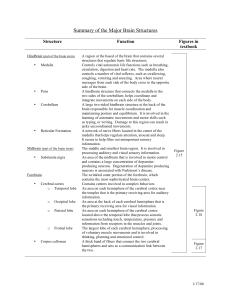
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... two sides of the cerebellum; helps coordinate and integrate movements on each side of the body. A large two-sided hindbrain structure at the back of the brain responsible for muscle coordination and maintaining posture and equilibrium. It is involved in the learning of automatic movements and motor ...
... two sides of the cerebellum; helps coordinate and integrate movements on each side of the body. A large two-sided hindbrain structure at the back of the brain responsible for muscle coordination and maintaining posture and equilibrium. It is involved in the learning of automatic movements and motor ...
Biology 232
... Sensory and Motor Pathways sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect ...
... Sensory and Motor Pathways sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect ...
ORAL SCIENCE I
... Nervous System • Reception- stimuli • Transmission- Sensory input- from area to brain Afferent • Integration- sums up input to allow brain to ...
... Nervous System • Reception- stimuli • Transmission- Sensory input- from area to brain Afferent • Integration- sums up input to allow brain to ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, redu ...
... Brandeis University, Waltham, MA The fine-tuning of circuits in sensory cortex requires sensory experience during an early critical period. Visual deprivation (VD) during the critical period has atastrophic effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, redu ...