Document
... Sensory systems Sensory info is received Nerve impulse or action potential All or nothing response Response depends on part of brain that receives the info ...
... Sensory systems Sensory info is received Nerve impulse or action potential All or nothing response Response depends on part of brain that receives the info ...
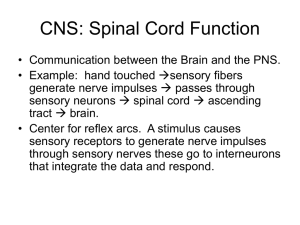
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... pineal gland. Thalamus receives all sensory input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information fro ...
... pineal gland. Thalamus receives all sensory input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information fro ...
Document
... • All neural structures outside the brain • Sensory receptors • Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia • Motor endings ...
... • All neural structures outside the brain • Sensory receptors • Peripheral nerves and associated ganglia • Motor endings ...
Sensory organs and perception
... many were temporarily distorted, and their brain-wave patterns, which had slowed down during the experiment, took several hours to return to normal. ...
... many were temporarily distorted, and their brain-wave patterns, which had slowed down during the experiment, took several hours to return to normal. ...
Exam 4
... -Describe preganglionic and postganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system. -Compare the anatomical components of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. -Describe the neurotransmitters and receptors involved in autonomic responses. -Describe the major ...
... -Describe preganglionic and postganglionic neurons of the autonomic nervous system. -Compare the anatomical components of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. -Describe the neurotransmitters and receptors involved in autonomic responses. -Describe the major ...
Glossary of commonly used Occupational Therapy terms
... Tactile Defensiveness: The tendency to react negatively and emotionally to unexpected. Light touch sensations. Tactile Sense: The sensory system that receives sensations of pressure, vibration, movement, temperature and pain, primarily through receptors in the skin. Tracking: Following a moving obje ...
... Tactile Defensiveness: The tendency to react negatively and emotionally to unexpected. Light touch sensations. Tactile Sense: The sensory system that receives sensations of pressure, vibration, movement, temperature and pain, primarily through receptors in the skin. Tracking: Following a moving obje ...
Module 4 - the Brain
... Pons: bridge for messages from the spinal cord to brain, also makes sleep chemicals Medulla: controls vital reflexes such as breathing, heart rate and blood pressure Cerebellum: coordinates motor movements (but does not initiate them), timed motor movements, and reflexive learning ...
... Pons: bridge for messages from the spinal cord to brain, also makes sleep chemicals Medulla: controls vital reflexes such as breathing, heart rate and blood pressure Cerebellum: coordinates motor movements (but does not initiate them), timed motor movements, and reflexive learning ...
The Brain ppt module 4
... Pons: bridge for messages from the spinal cord to brain, also makes sleep chemicals Medulla: controls vital reflexes such as breathing, heart rate and blood pressure Cerebellum: coordinates motor movements (but does not initiate them), timed motor movements, and reflexive learning ...
... Pons: bridge for messages from the spinal cord to brain, also makes sleep chemicals Medulla: controls vital reflexes such as breathing, heart rate and blood pressure Cerebellum: coordinates motor movements (but does not initiate them), timed motor movements, and reflexive learning ...
Sensory Systems
... __________________: respond to movement, pressure, and tension. Photoreceptors: respond to variations of light Chemoreceptors: respond to ______________ Thermoreceptors: respond to changes in temperature Pain receptors respond to tissue ____________ ...
... __________________: respond to movement, pressure, and tension. Photoreceptors: respond to variations of light Chemoreceptors: respond to ______________ Thermoreceptors: respond to changes in temperature Pain receptors respond to tissue ____________ ...
chapter 3 – sensation and perception
... b. Gravitation and movement 1) Utricle – 2) Saccule – 4. Travel on auditory nerve – D. Sensation of Motion 1. Motion sickness – 2. Can be completely overwhelmed – E. The Skin Senses 1. Sense organs with 2. 13 different types of 3. To brain through 4. Cutaneous sensation – 5. Meissner Corpuscles – ...
... b. Gravitation and movement 1) Utricle – 2) Saccule – 4. Travel on auditory nerve – D. Sensation of Motion 1. Motion sickness – 2. Can be completely overwhelmed – E. The Skin Senses 1. Sense organs with 2. 13 different types of 3. To brain through 4. Cutaneous sensation – 5. Meissner Corpuscles – ...
Lesson1 Powerpoint
... external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
Document
... external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
Chapter 22 Thalamus
... conscious perception is of a specific stimulus Receptors are selective not only in what drives them but also in the postsynaptic targets with which they communicate Orderly relay from receptor to ganglion cell to CNS makes up labeled line Modality: all sensory information arising from a single ...
... conscious perception is of a specific stimulus Receptors are selective not only in what drives them but also in the postsynaptic targets with which they communicate Orderly relay from receptor to ganglion cell to CNS makes up labeled line Modality: all sensory information arising from a single ...
Hair cells
... -Hair cells with associated sensory neurons & stereocilia -Tectorial membrane: Overhanging, gelatinous membrane (holds top of stereocilia in place) Stereocilia of hair cells bend in response to vibrations of the basilar membrane -Hair cells are depolarized or hyperpolarized and signals are sent to b ...
... -Hair cells with associated sensory neurons & stereocilia -Tectorial membrane: Overhanging, gelatinous membrane (holds top of stereocilia in place) Stereocilia of hair cells bend in response to vibrations of the basilar membrane -Hair cells are depolarized or hyperpolarized and signals are sent to b ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... Information about the external and internal environments presents itself as different forms of energy (sound, light) The sensory receptors respond to these stimuli; the rest of the nervous system responds chiefly to neurotransmitters The process by which a stimulus is transformed into an electrical ...
... Information about the external and internal environments presents itself as different forms of energy (sound, light) The sensory receptors respond to these stimuli; the rest of the nervous system responds chiefly to neurotransmitters The process by which a stimulus is transformed into an electrical ...
Skeletal System
... Information about the external and internal environments presents itself as different forms of energy (sound, light) The sensory receptors respond to these stimuli; the rest of the nervous system responds chiefly to neurotransmitters The process by which a stimulus is transformed into an electrical ...
... Information about the external and internal environments presents itself as different forms of energy (sound, light) The sensory receptors respond to these stimuli; the rest of the nervous system responds chiefly to neurotransmitters The process by which a stimulus is transformed into an electrical ...
semicircular canals
... Optic Disk (blind spot): area on retina where neurons leave and form optic nerve. No photoreceptors are found here. ...
... Optic Disk (blind spot): area on retina where neurons leave and form optic nerve. No photoreceptors are found here. ...
principles and techniques of the examination of the trigeminal nerve
... of cotton or the edge of a tissue. One may also use a light brush of the fingertips against the skin of the face. If reliability is in doubt, the patient should be asked to close the eyes and then indicate each touch. Although the most sensitive test is to compare the sense of light touch on one sid ...
... of cotton or the edge of a tissue. One may also use a light brush of the fingertips against the skin of the face. If reliability is in doubt, the patient should be asked to close the eyes and then indicate each touch. Although the most sensitive test is to compare the sense of light touch on one sid ...
Somatic Sensory System
... S2 and Parietal Posterior Cortex • S2 is lateral to S1 and is association area • PPC is posterior to S1 and is involved in perception/recognition of sensation • Neurons in S2 and PPC have complex receptive fields which can include sensory information as well as attention and visual and movement pla ...
... S2 and Parietal Posterior Cortex • S2 is lateral to S1 and is association area • PPC is posterior to S1 and is involved in perception/recognition of sensation • Neurons in S2 and PPC have complex receptive fields which can include sensory information as well as attention and visual and movement pla ...
Nervous System
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
... homeostasis & processes information Accepts sensory signals & channels them to cerebrum for interpretation (e.g. thalmus may have a consciousness of pain but does not know the location of the pain – the cerebrum interprets the signal and we know where it hurts) ...
Somatic Sensory Systems
... mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and chemoreceptors. I discussed the chemoreceptors of the general sensory system when we covered gustation. Each of these four types of receptors can be further divided into subcategories, which were reviewed in lecture and you should know each type and subtype. Yo ...
... mechanoreceptors, thermoreceptors, and chemoreceptors. I discussed the chemoreceptors of the general sensory system when we covered gustation. Each of these four types of receptors can be further divided into subcategories, which were reviewed in lecture and you should know each type and subtype. Yo ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... the synapse is chemical Neurotransmitters include ACh, GABA, serotonin ...
... the synapse is chemical Neurotransmitters include ACh, GABA, serotonin ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
... ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
Construction of mental model in mechanics through sensory
... + Department of Education in Technology and Science, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology Research topic: Construction of mental model in mechanics through sensory interaction in computerized environment Abstract: The research focuses on construction of physics understanding through sensory inter ...
... + Department of Education in Technology and Science, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology Research topic: Construction of mental model in mechanics through sensory interaction in computerized environment Abstract: The research focuses on construction of physics understanding through sensory inter ...