Document
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
CNS
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
Chapter 10 – Sensory Physiology
... 1. Distinguish between sensation and perception. (Sensation is depolarization of sensory receptor and sending the action potentials to brain. Primary Sensory Cortex receives the input and the perception is integration by Association area. It means we do not taste food on activation of gustatory cell ...
... 1. Distinguish between sensation and perception. (Sensation is depolarization of sensory receptor and sending the action potentials to brain. Primary Sensory Cortex receives the input and the perception is integration by Association area. It means we do not taste food on activation of gustatory cell ...
Popular Links
... sounds, touch, tastes, and smells) from his or her environment is thought to affect development. Sensory processing and sensory integration are terms used interchangeably by clinicians to describe how a person reacts to sensory stimuli in their environment. Occupational therapists are often asked to ...
... sounds, touch, tastes, and smells) from his or her environment is thought to affect development. Sensory processing and sensory integration are terms used interchangeably by clinicians to describe how a person reacts to sensory stimuli in their environment. Occupational therapists are often asked to ...
sensory receptors, neuronal circuits for processing information
... Mechanoreceptors Specialized to Receive Tactile Information ...
... Mechanoreceptors Specialized to Receive Tactile Information ...
Unit 3 Guide: Sensation and Perception (Modules 8, 9) Module 8
... - Sound: what are the structures of the ear and how do they work to detect sound waves and change them into neural impulses? - Taste, Smell, Touch: how do receptor cells in the nose, tongue, and skin allow us to sense smells, tastes and touch? Terms to know: Sensation: - sensation: - top-down proces ...
... - Sound: what are the structures of the ear and how do they work to detect sound waves and change them into neural impulses? - Taste, Smell, Touch: how do receptor cells in the nose, tongue, and skin allow us to sense smells, tastes and touch? Terms to know: Sensation: - sensation: - top-down proces ...
Savage Science AP Biology
... Savage Science AP Biology Special senses 50 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system ...
... Savage Science AP Biology Special senses 50 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system ...
A synaptic memory trace for cortical receptive field plasticity
... Neural networks of the cerebral cortex continually change throughout life, allowing us to learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordinati ...
... Neural networks of the cerebral cortex continually change throughout life, allowing us to learn from our sensations of the world. While the developing cortex is readily altered by sensory experience, older brains are less plastic. Adult cortical plasticity seems to require more widespread coordinati ...
Sensation and Perception - Shannon Deets Counseling
... Sensation and Perception • Sense- a system that translates outside information into activity in the nervous system • Sensation- the stimulus message coming from the senses • Transduction- process of converting stimuli • Perception- the process of giving meaning to that message ...
... Sensation and Perception • Sense- a system that translates outside information into activity in the nervous system • Sensation- the stimulus message coming from the senses • Transduction- process of converting stimuli • Perception- the process of giving meaning to that message ...
General Sensory Reception
... Receptor adaptation • Tonic receptors -- slow acting, -- no adaptation: continue to for impulses as long as the stimulus is there (e.g., proprioreceptors) • Phasic receptors -- quick acting, adapt: stop firing when stimuli are constant (e.g., smell) ...
... Receptor adaptation • Tonic receptors -- slow acting, -- no adaptation: continue to for impulses as long as the stimulus is there (e.g., proprioreceptors) • Phasic receptors -- quick acting, adapt: stop firing when stimuli are constant (e.g., smell) ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas
... The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas specialized for detecting and processing sensory signals from the eyes and ears and from receptors for touch, taste, and smell. Differences between these sensory areas may reflect variations in the rate of evolution of the five s ...
... The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas specialized for detecting and processing sensory signals from the eyes and ears and from receptors for touch, taste, and smell. Differences between these sensory areas may reflect variations in the rate of evolution of the five s ...
Two Point Discrimination Lab
... fingers are very large and the arms and back are small. This type of picture is called a homunculus, literally, "little man" or person. All sensory systems feed information into the cerebral cortex in orderly maps, even though the other peripheral sensory receptors, unlike those of the touch or tact ...
... fingers are very large and the arms and back are small. This type of picture is called a homunculus, literally, "little man" or person. All sensory systems feed information into the cerebral cortex in orderly maps, even though the other peripheral sensory receptors, unlike those of the touch or tact ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Receptive fields overlap, so each area of skin is monitored by multiple neurons. ...
... Receptive fields overlap, so each area of skin is monitored by multiple neurons. ...
Slide ()
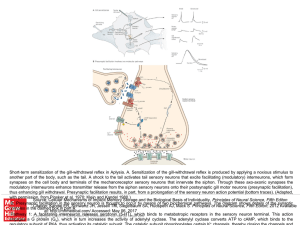
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Document
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
Ch 9 Sensory System
... Several sensory systems exist that detect external changes rapidly. These systems include: the somatosensory (touch, pressure, pain etc) system, visual system, auditory and vestibular system, olfactory (smell) system, and gustatory (taste) system. A major objective of this section is to look at how ...
... Several sensory systems exist that detect external changes rapidly. These systems include: the somatosensory (touch, pressure, pain etc) system, visual system, auditory and vestibular system, olfactory (smell) system, and gustatory (taste) system. A major objective of this section is to look at how ...
Chapter 5: SENSATION - Charles Best Library
... optic nerve. When individual ganglion cells register information in their region of the visual field, they send signals to the visual cortex. In the cortex, individual neurons respond to specific features of a visual stimulus. ...
... optic nerve. When individual ganglion cells register information in their region of the visual field, they send signals to the visual cortex. In the cortex, individual neurons respond to specific features of a visual stimulus. ...