AP Revision Guide Ch 18
... Uranium-235 is the only naturally occurring fissile isotope. A large nucleus may be considered like an oscillating liquid drop. If the nucleus oscillates too much, it can divide into two parts which repel each other electrostatically. The two fragments gain kinetic energy and also release two or thr ...
... Uranium-235 is the only naturally occurring fissile isotope. A large nucleus may be considered like an oscillating liquid drop. If the nucleus oscillates too much, it can divide into two parts which repel each other electrostatically. The two fragments gain kinetic energy and also release two or thr ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... • Radioactive Isotopes: unstable atoms, due to a nucleus with too many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons. • No amount of neutrons can hold a nucleus together once it has more that 82 protons. All of the elements with an atomic number greater than 82 have only unstable isotopes. • ...
... • Radioactive Isotopes: unstable atoms, due to a nucleus with too many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons. • No amount of neutrons can hold a nucleus together once it has more that 82 protons. All of the elements with an atomic number greater than 82 have only unstable isotopes. • ...
The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus
... β-particle The b-particle is a much lighter particle than the a-particle and although they travel much faster (up to 0.9 c) they cause less intense ionisation than the a -particle. They have a charge of only – e so they are less reactive. The b particle travels about 1 m in air before it is absorbed ...
... β-particle The b-particle is a much lighter particle than the a-particle and although they travel much faster (up to 0.9 c) they cause less intense ionisation than the a -particle. They have a charge of only – e so they are less reactive. The b particle travels about 1 m in air before it is absorbed ...
nuclear physics - review
... β-particle The b-particle is a much lighter particle than the a-particle and although they travel much faster (up to 0.9 c) they cause less intense ionisation than the a -particle. They have a charge of only – e so they are less reactive. The b particle travels about 1 m in air before it is absorbed ...
... β-particle The b-particle is a much lighter particle than the a-particle and although they travel much faster (up to 0.9 c) they cause less intense ionisation than the a -particle. They have a charge of only – e so they are less reactive. The b particle travels about 1 m in air before it is absorbed ...
Atomic and Nuclear Terms
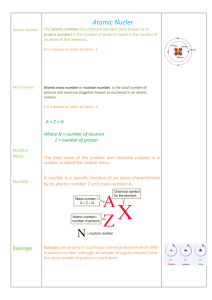
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
Chapter 29
... between protons • These forces should cause the nucleus to fly apart • The nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range force, called the nuclear force • This is an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles • The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulo ...
... between protons • These forces should cause the nucleus to fly apart • The nuclei are stable because of the presence of another, short-range force, called the nuclear force • This is an attractive force that acts between all nuclear particles • The nuclear attractive force is stronger than the Coulo ...
Atomic and Nuclear Terms
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
... ► Nuclear Reactions – A reaction that occurs whenever the number of protons or neutrons changes. • Nuclear reactions include natural and artificial transmutation, fission, and fusion. ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontan ...
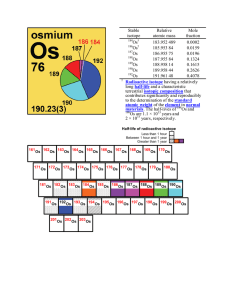
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction Os 183.952 489
... gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that ...
... gamma rays (gamma radiation) – a stream of high-energy electromagnetic radiation given off by an atomic nucleus undergoing radioactive decay. The energies of gamma rays are higher than those of X-rays; thus, gamma rays have greater penetrating power. half-life (radioactive) – the time interval that ...