File
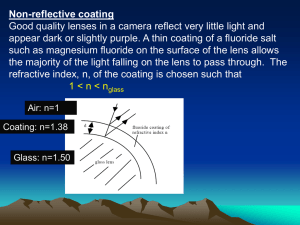
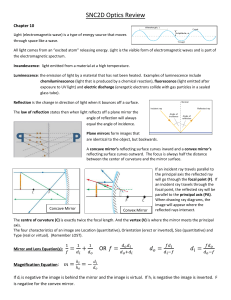
... Good quality lenses in a camera reflect very little light and appear dark or slightly purple. A thin coating of a fluoride salt such as magnesium fluoride on the surface of the lens allows the majority of the light falling on the lens to pass through. The refractive index, n, of the coating is chose ...
... Good quality lenses in a camera reflect very little light and appear dark or slightly purple. A thin coating of a fluoride salt such as magnesium fluoride on the surface of the lens allows the majority of the light falling on the lens to pass through. The refractive index, n, of the coating is chose ...
d - Madison Public Schools
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
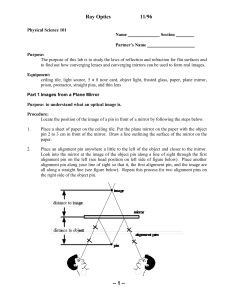
Lab #8 Ray Optics
... Part 2 Light Refraction through a Prism Purpose: to show that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors and that each color of light interacts with the prism material differently. When light travels through a transparent object its speed is reduced relative to its speed in a vacuum. This chang ...
... Part 2 Light Refraction through a Prism Purpose: to show that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors and that each color of light interacts with the prism material differently. When light travels through a transparent object its speed is reduced relative to its speed in a vacuum. This chang ...
Ray Diagram PRELAB LAB
... Converging Lenses A convex lens is a converging lens which bends light rays into focus. The focal length, f, is the distance to the focal point where parallel rays converge as shown. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light rays reflected off an object to visualize how images are fo ...
... Converging Lenses A convex lens is a converging lens which bends light rays into focus. The focal length, f, is the distance to the focal point where parallel rays converge as shown. A Ray Diagram is a simple picture using only 2 or 3 light rays reflected off an object to visualize how images are fo ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. Any other spots appearing on the card indicate the presence of other spatial frequencies. Remove the card ...
... Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. Any other spots appearing on the card indicate the presence of other spatial frequencies. Remove the card ...
Interference I - Galileo and Einstein
... of the magnifying glass discussed above. • The simplest compound microscope has two convex lenses: the first (objective) forms a real (inverted) image, the second (eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to examine that image. • The total magnification is a product of the two: the eyepiece is N/fe, N = ...
... of the magnifying glass discussed above. • The simplest compound microscope has two convex lenses: the first (objective) forms a real (inverted) image, the second (eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to examine that image. • The total magnification is a product of the two: the eyepiece is N/fe, N = ...
Some Issues from Advanced Lithography General
... have been realized, but this is already pushing it quite a bit. The ArF excimer laser has been used from about 2003, so it is still in its infancy. It is expected to cover the "65 nm node", and possibly also the 45 nm node. That will be the end. After that, the age of "EUV" (extreme ultraviolet) mig ...
... have been realized, but this is already pushing it quite a bit. The ArF excimer laser has been used from about 2003, so it is still in its infancy. It is expected to cover the "65 nm node", and possibly also the 45 nm node. That will be the end. After that, the age of "EUV" (extreme ultraviolet) mig ...
Lecture-7-Optics
... conversely if h1, h2 < 0 then H1, H2 is to the left of V1,V2 Again, H1 and H2 refer to axial points through the principal planes. Now, consider a compound lens consisting of two thick lenses L1 and L2, with the usual parameters so1, si1, f1 and so2, si2 and f2, as shown on the next slide. si, so are ...
... conversely if h1, h2 < 0 then H1, H2 is to the left of V1,V2 Again, H1 and H2 refer to axial points through the principal planes. Now, consider a compound lens consisting of two thick lenses L1 and L2, with the usual parameters so1, si1, f1 and so2, si2 and f2, as shown on the next slide. si, so are ...
5.2 Optical Instruments Optical systems Camera Limitations of Lens
... Nearsighted eye cannot focus on objects far away (further than the far point < infinity) The lens retina distance is too long and/or the lens is too converging. ...
... Nearsighted eye cannot focus on objects far away (further than the far point < infinity) The lens retina distance is too long and/or the lens is too converging. ...
How do eye glasses work? BUT first, let`s review!
... They travel as vibrations in electrical and ...
... They travel as vibrations in electrical and ...
Word
... on the _______. Think about one letter of the print in front of you. Light enters your eye from each part of the letter. Your eye bends the light so that all the light from one point on the letter is focused onto one point of the retina. The light from each part of the letter is thus _______ on the ...
... on the _______. Think about one letter of the print in front of you. Light enters your eye from each part of the letter. Your eye bends the light so that all the light from one point on the letter is focused onto one point of the retina. The light from each part of the letter is thus _______ on the ...
Optical aberration
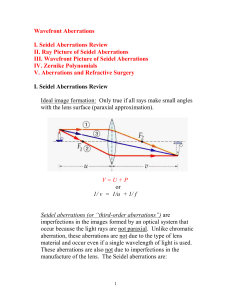
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.