Fraunhofer diffraction from gratings In this exercise we use a two
... blue-green and blue-violet lines at 656.3 nm, 486.1 nm and 434.1 nm. ...
... blue-green and blue-violet lines at 656.3 nm, 486.1 nm and 434.1 nm. ...
Here
... – When the dimensions of the system are large compared to the wavelength of the light and the effects of diffraction become less important, we have the domain of Geometric Optics. • A lens is a refracting device ie. a disconinuity in the prevailing medium that reconfigures the transmitted energy dis ...
... – When the dimensions of the system are large compared to the wavelength of the light and the effects of diffraction become less important, we have the domain of Geometric Optics. • A lens is a refracting device ie. a disconinuity in the prevailing medium that reconfigures the transmitted energy dis ...
Chapter 33E Worksheet - Rose
... bowl to keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid blinding the fish, which might swim into the focal point of the parallel rays from the sun. Is the focal point actually within the bowl? ...
... bowl to keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid blinding the fish, which might swim into the focal point of the parallel rays from the sun. Is the focal point actually within the bowl? ...
Waves & Oscillations Geometric Optics Physics 42200 3/20/2016
... – Given an optical system, what are the properties of the image that is formed (if any)? – What configuration of optical elements (if any) will produce an image with certain desired characteristics? ...
... – Given an optical system, what are the properties of the image that is formed (if any)? – What configuration of optical elements (if any) will produce an image with certain desired characteristics? ...
Reflection - E. R. Greenman
... The angle the incident ray makes with the mirror The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray ...
... The angle the incident ray makes with the mirror The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray ...
Geometrical Optics
... Aberrations are imperfections in the optical image formed by a spherical lens (or optical mirror). There are five main aberrations: 1. Chromatic aberration. The refractive index of glass varies with wavelength. This results in different focal lengths and image magnifications for different colours. ...
... Aberrations are imperfections in the optical image formed by a spherical lens (or optical mirror). There are five main aberrations: 1. Chromatic aberration. The refractive index of glass varies with wavelength. This results in different focal lengths and image magnifications for different colours. ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... A lens is an optical device consisting of two refracting surfaces The simplest lens has two spherical surfaces close enough together that we can neglect the distance between the surfaces (i.e., thin) Consider two spherical surfaces (with radii of curvature R1 and R2), separating three materials of i ...
... A lens is an optical device consisting of two refracting surfaces The simplest lens has two spherical surfaces close enough together that we can neglect the distance between the surfaces (i.e., thin) Consider two spherical surfaces (with radii of curvature R1 and R2), separating three materials of i ...
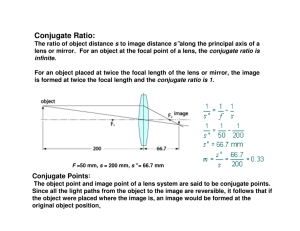
Conjugate Ratio:
... Seidel developed a method of calculating aberrations resulting from the θ3/3! term. The resultant third-order lens aberrations are therefore called Seidel aberrations. Seidel put the aberrations of an optical system into several different classifications: In monochromatic light they are spherical a ...
... Seidel developed a method of calculating aberrations resulting from the θ3/3! term. The resultant third-order lens aberrations are therefore called Seidel aberrations. Seidel put the aberrations of an optical system into several different classifications: In monochromatic light they are spherical a ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.