* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optics Observations
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction topography wikipedia , lookup
Fiber-optic communication wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Fourier optics wikipedia , lookup
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Interferometry wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
Passive optical network wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
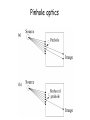
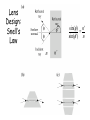
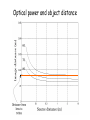
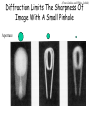
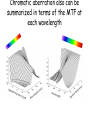
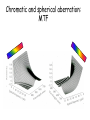
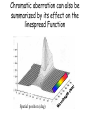
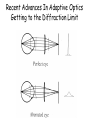
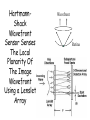
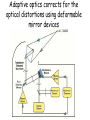
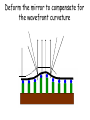
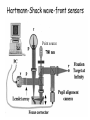
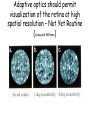
Optics Observations • Pinholes, apertures and diffraction • Lenses, lensmaker and depth of focus • Two-dimensions and asymmetries • Chromatic aberration of the human eye • Adaptive optics, H-S • Encoding Pinhole optics Lens Design: Snell’s Law sin( ) n ' sin( ') n Lensmaker’s Equation 1 1 1 d s di f d s source dist d i image dist f focal length Optical power and object distance (From Jenkins and White, I think) Diffraction Limits The Sharpness Of Image With A Small Pinhole Aperture The Diffraction Pattern Of A Disk Has A Formula Based on Bessel Functions That Can Be Calculated From First Principles Airy Some Animals Have Non-Circular Pupils: Cat Eye Pupil Size Changes With Mean Luminance, Influencing Acuity Pupil diameter (mm) (From Wyszecki and Stiles, 1982) Log luminance (Trolands) The Pointspread Function Is The Generalization of the Linespread Astigmatism Measures The Orientation of the Pointspread Function Chromatic (A) aberration is a differences Stimulus in optical focus that varies with (B) wavelength Stimulus -0.3 0.3 Position Chromatic Aberration Can Be Summarized By The Optical Power At Various Wavelengths; Very Constant Across People Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength Relative intensity 0.4 0.3 580nm 0.2 0.1 430nm 0 -1 -0.5 0 0.5 Position (deg) 1 Chromatic aberration also can be summarized in terms of the MTF at each wavelength Chromatic and spherical aberration: MTF Chromatic aberration can also be summarized by its effect on the linespread Function Spatial position (deg) Recent Advances In Adaptive Optics Getting to the Diffraction Limit HartmannShack Wavefront Sensor Senses The Local Planarity Of The Image Wavefront Using a Lenslet Array Wavefront Retina Artal, Guirao, Berrio & Williams Journal of Vision Example H-S displacement images at the CCD sensor Adaptive optics corrects for the optical distortions using deformable mirror devices Wavefront phase corrector priniciple Deformable mirror arrays Compensate For the Measured Aberrations Deform the mirror to compensate for the wavefront curvature Real deformable mirror arrays Hartmann-Shack wave-front sensors Point source Adaptive Optics compensate for aberrations in the optical path, the MTF approaches the diffraction limit The MTF approaches the diffraction limit Adaptive optics should permit visualization of the retina at high spatial resolution – Not Yet Routine (Liang and Williams) End Reading for next Tuesday Liang and Williams paper Roorda and Williams paper Who wants to lead the discussion? Anyone have other papers to discuss? Application: Seeing The Arrangement of Cone Classes in the Human Eye ( Roorda and Williams) mm Zernicke Polynomials (Not Harmonics) Are Used To Model Transmission Through The Lens The Zernike polynomials are a set of functions that are orthogonal over the unit circle. They are useful for describing the shape of an aberrated wavefront in the pupil of an optical system. Project idea: Implement a set of Matlab functions for these polynomials. Explain their use in optics characterization. Review the human literature pertaining to measurements of wavefront aberrations in the human eye.