Chromatic and Monochromatic Aberrations
... Everything you have learned about object and image formation is an approximation. When light is refracted by spherical surfaces the rays do not all converge to a point, even if they are of one wavelength. Monochromatic aberrations can arise from surfaces with irregularities (The human eye is a good ...
... Everything you have learned about object and image formation is an approximation. When light is refracted by spherical surfaces the rays do not all converge to a point, even if they are of one wavelength. Monochromatic aberrations can arise from surfaces with irregularities (The human eye is a good ...
Training modules for an advanced interactive course on
... Note that the only areas where the spherical aberration falls to zero are in the upper right and lower left corners of the graph. These correspond to the two classical “aplanats,” with one surface at which the incident and refracted marginal ray angles are proportional to the refractive indices, and ...
... Note that the only areas where the spherical aberration falls to zero are in the upper right and lower left corners of the graph. These correspond to the two classical “aplanats,” with one surface at which the incident and refracted marginal ray angles are proportional to the refractive indices, and ...
Aberrations
... So far, we haven’t asked what the functional form of W might be. If we restrict ourselves to rotationally symmetric optical systems, we can limit the possible forms W might take. If we assume a 2-Dimensional polynomial form for W, and eliminate all terms and combination of terms that are not rotatio ...
... So far, we haven’t asked what the functional form of W might be. If we restrict ourselves to rotationally symmetric optical systems, we can limit the possible forms W might take. If we assume a 2-Dimensional polynomial form for W, and eliminate all terms and combination of terms that are not rotatio ...
RAY OPTICS notes
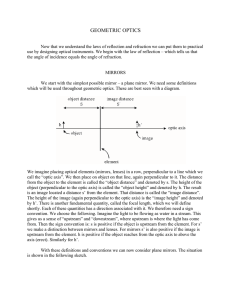
... The image is real if the rays actually converge to the point; it is virtual if the rays do not actually meet but appear to diverge from the point when produced backwards. ...
... The image is real if the rays actually converge to the point; it is virtual if the rays do not actually meet but appear to diverge from the point when produced backwards. ...
N - Purdue Physics
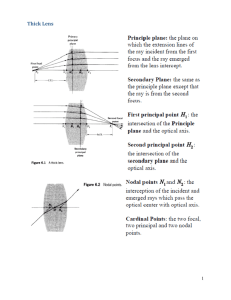
... to the optical axis by both surfaces of the lens – Rays parallel to the optical axis are refracted through the focal point – For a thin lens, we can draw the point where refraction occurs in a common plane – For a thick lens, refraction for the two types of rays can occur at different planes ...
... to the optical axis by both surfaces of the lens – Rays parallel to the optical axis are refracted through the focal point – For a thin lens, we can draw the point where refraction occurs in a common plane – For a thick lens, refraction for the two types of rays can occur at different planes ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 27 – Geometric Optics
... to the optical axis by both surfaces of the lens – Rays parallel to the optical axis are refracted through the focal point – For a thin lens, we can draw the point where refraction occurs in a common plane – For a thick lens, refraction for the two types of rays can occur at different planes ...
... to the optical axis by both surfaces of the lens – Rays parallel to the optical axis are refracted through the focal point – For a thin lens, we can draw the point where refraction occurs in a common plane – For a thick lens, refraction for the two types of rays can occur at different planes ...
Exam 2 Phy 116 study guide
... description of the situation, from ray diagrams and from equations. You should also be able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mirror or through a lens for different situations and materials? What would you pr ...
... description of the situation, from ray diagrams and from equations. You should also be able to explain the coordinate system(s). Can you describe in words or by drawing a picture what one would see when looking into a mirror or through a lens for different situations and materials? What would you pr ...
Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
... b) If the object is 8.50 mm tall, how tall is the image? Is it erect or inverted? c) Draw a principal ray diagram. L02. A photographic slide is to the left of a lens. The lens projects an image of the slide onto a wall 6.00 m to the right of the slide. The image is 80.0 times the size of the slide. ...
... b) If the object is 8.50 mm tall, how tall is the image? Is it erect or inverted? c) Draw a principal ray diagram. L02. A photographic slide is to the left of a lens. The lens projects an image of the slide onto a wall 6.00 m to the right of the slide. The image is 80.0 times the size of the slide. ...
D - Purdue Physics
... - harder to make (need large diameter to collect more light) - focal length depends on wavelength: n=n() ...
... - harder to make (need large diameter to collect more light) - focal length depends on wavelength: n=n() ...
Lab 11 - Optical Ray Tracing
... compare it to the theoretical value. (Note: The rms value will not attain perfect zero due to spherical aberration.) B. Spherical Aberration In the previous exercise, the phenomenon of spherical aberration was observed as a slight divergence at the ideal focal point. This is due to the fact that ra ...
... compare it to the theoretical value. (Note: The rms value will not attain perfect zero due to spherical aberration.) B. Spherical Aberration In the previous exercise, the phenomenon of spherical aberration was observed as a slight divergence at the ideal focal point. This is due to the fact that ra ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.