Chapter 25 Optical Instruments
... • Circles of confusion involve objects not in focus forming circles of non-focused images…not all distances of objects can be in focus at one time. • A smaller lens opening will cause there to be a wider range of in-focus object distances. • See normal lens, telephoto lens, wide-angle lens, zoom len ...
... • Circles of confusion involve objects not in focus forming circles of non-focused images…not all distances of objects can be in focus at one time. • A smaller lens opening will cause there to be a wider range of in-focus object distances. • See normal lens, telephoto lens, wide-angle lens, zoom len ...
Lecture 14 Images Chapter 34
... The ray approximation states that light travels in straight lines until it is reflected or refracted and then travels in straight lines again. The wavelength of light must be small compared to the size of the objects or else diffractive effects occur. ...
... The ray approximation states that light travels in straight lines until it is reflected or refracted and then travels in straight lines again. The wavelength of light must be small compared to the size of the objects or else diffractive effects occur. ...
Quiz 8
... larger than the critical angle undergo total internal reflection, thus it is enough to block the rays with an angle of incidence smaller the critical angle. When the diameter is minimal, the light ray incident on the water surface at the critical angle strikes the edge of the raft. Therefore, we hav ...
... larger than the critical angle undergo total internal reflection, thus it is enough to block the rays with an angle of incidence smaller the critical angle. When the diameter is minimal, the light ray incident on the water surface at the critical angle strikes the edge of the raft. Therefore, we hav ...
Converging Lens
... telescopes. The refractive telescope that Galileo constructed, for instance, uses two converging lenses in series. Telescopes that use mirrors as their objective are called reflective telescopes. Sir Issac Newton was the first to figure out that mirrors could be used to focus light instead of lenses ...
... telescopes. The refractive telescope that Galileo constructed, for instance, uses two converging lenses in series. Telescopes that use mirrors as their objective are called reflective telescopes. Sir Issac Newton was the first to figure out that mirrors could be used to focus light instead of lenses ...
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... Brewster's Angle--The light ray incident obliquely to a surface contains a reflective beam of light polarized parallel to the plane of the reflecting surface. ...
... Brewster's Angle--The light ray incident obliquely to a surface contains a reflective beam of light polarized parallel to the plane of the reflecting surface. ...
optical quality standards
... ƛ is the wavelength of light to be used t is the geometrical thickness along the optical path n is the average refractive index for material in visible δ is the Peak to Valley departure for flatness of one surface 2(n-1) is the worst case contribution of both surfaces ...
... ƛ is the wavelength of light to be used t is the geometrical thickness along the optical path n is the average refractive index for material in visible δ is the Peak to Valley departure for flatness of one surface 2(n-1) is the worst case contribution of both surfaces ...
General Introduction of Optical
... • f or D decreases the flux area • f or D increases the flux area ...
... • f or D decreases the flux area • f or D increases the flux area ...
Optics in Confocal Microscopy
... which fluoresce both red and green (available from Polysciences at 1 mm and 2 mm diameter. If you make a z-section through these beads, even the best objective lenses are likely to show image duplication. In the merged image of red and green emission channels, the upper part of each bead is likely t ...
... which fluoresce both red and green (available from Polysciences at 1 mm and 2 mm diameter. If you make a z-section through these beads, even the best objective lenses are likely to show image duplication. In the merged image of red and green emission channels, the upper part of each bead is likely t ...
File
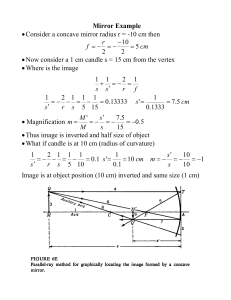
... • A light source radiates millions of light rays in all directions, but you are only concerned with the rays that actually strike the mirror and are reflected into your eyes, with the angle of incidence being equal to the angle of reflection. • In an image, the distance from the object to the mirror ...
... • A light source radiates millions of light rays in all directions, but you are only concerned with the rays that actually strike the mirror and are reflected into your eyes, with the angle of incidence being equal to the angle of reflection. • In an image, the distance from the object to the mirror ...
N15_Geom_Optics - University of Arizona
... prisms, blue light bends more than red light. So the same effect must happen in lenses—where one assumes that ray paths are independent of color. The first picture below shows how lenses will have slightly different focal lengths for different colors. This effect is called “chromatic aberration” and ...
... prisms, blue light bends more than red light. So the same effect must happen in lenses—where one assumes that ray paths are independent of color. The first picture below shows how lenses will have slightly different focal lengths for different colors. This effect is called “chromatic aberration” and ...
Modulation Transfer Function
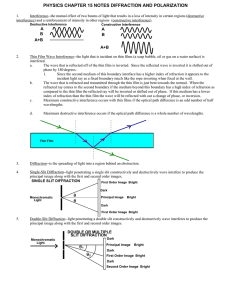
... Figure 1: Illustration of diffraction of light passing through an aperture, seen as wavefronts. Diffraction follows from the wave nature of light, and implies that any concentration of light, like a beam or light passing through an aperture, will spread. It places a fundamental limit on the spot siz ...
... Figure 1: Illustration of diffraction of light passing through an aperture, seen as wavefronts. Diffraction follows from the wave nature of light, and implies that any concentration of light, like a beam or light passing through an aperture, will spread. It places a fundamental limit on the spot siz ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.