
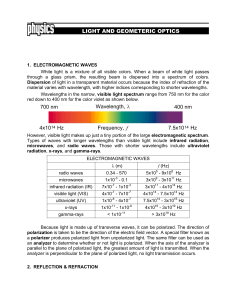
Ray Optics
... The image of the first lens is treated as the object of the second lens Then a ray diagram is drawn for the second lens The image formed by the second lens is the final image of the system If the image formed by the first lens lies on the back side of the second lens, then the image is treated a ...
... The image of the first lens is treated as the object of the second lens Then a ray diagram is drawn for the second lens The image formed by the second lens is the final image of the system If the image formed by the first lens lies on the back side of the second lens, then the image is treated a ...
10-SNC2D-ConcaveContinued-10
... of curvature is reflected back into itself. 3. A ray through the focus will reflect parallel to the principal axis. 4. A ray aimed at the vertex will follow through the law of reflection. ...
... of curvature is reflected back into itself. 3. A ray through the focus will reflect parallel to the principal axis. 4. A ray aimed at the vertex will follow through the law of reflection. ...
f - Uplift Education
... edges of the lens is subject to this departure from the expected or proper course for the ideal lens. This manifests itself as a blurring of the image. Lenses in which closer-to-ideal, non-spherical surfaces are used are called aspheric lenses. object ...
... edges of the lens is subject to this departure from the expected or proper course for the ideal lens. This manifests itself as a blurring of the image. Lenses in which closer-to-ideal, non-spherical surfaces are used are called aspheric lenses. object ...
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... of the track parallel to each other (schematic shown below). A semiconductor laser with a vacuum wavelength of 0.79-μm is focussed to a spot (also shown) within this track. By spinning the CD, the laser spot is made to scan along the track. As it passes over a bump, roughly half of the spot is refle ...
... of the track parallel to each other (schematic shown below). A semiconductor laser with a vacuum wavelength of 0.79-μm is focussed to a spot (also shown) within this track. By spinning the CD, the laser spot is made to scan along the track. As it passes over a bump, roughly half of the spot is refle ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2013 Semester Lecture 30 – Geometric Optics
... An object is placed in front of two thin symmetrical coaxial lenses (lens 1 & lens 2) with focal lengths f1=+24 cm & f2=+9.0 cm, with a lens separation of L=10.0 cm. The object is 6.0 cm from lens 1. Where is the image of the object? Lens 1: ...
... An object is placed in front of two thin symmetrical coaxial lenses (lens 1 & lens 2) with focal lengths f1=+24 cm & f2=+9.0 cm, with a lens separation of L=10.0 cm. The object is 6.0 cm from lens 1. Where is the image of the object? Lens 1: ...
Images in Lenses
... 5. A real image is never formed because the emergent rays from a divergent lens always spread apart. A real image can only be formed if the emergent refracted rays cross or converge. The human brain interprets diverging light from this type of lens as if it were coming from a single focus point, cr ...
... 5. A real image is never formed because the emergent rays from a divergent lens always spread apart. A real image can only be formed if the emergent refracted rays cross or converge. The human brain interprets diverging light from this type of lens as if it were coming from a single focus point, cr ...
RESOLVING POWER AND MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION
... When the modulation drops below the minimum that can be detected, the target ist not resolved. (b) The system represented by (a) will produce a superior image, although both (a) and (b) have the same limiting resolution. (Ref. 1) ...
... When the modulation drops below the minimum that can be detected, the target ist not resolved. (b) The system represented by (a) will produce a superior image, although both (a) and (b) have the same limiting resolution. (Ref. 1) ...
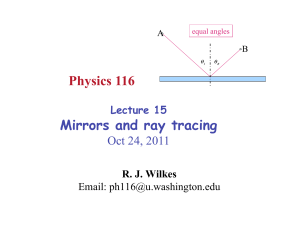
Refraction
... • Lenses form images by refraction, rather than by reflection. • Lenses can create real or virtual images. • A real image is formed when rays of light actually intersect to form an image. • A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to come from a point that they don’t actually come ...
... • Lenses form images by refraction, rather than by reflection. • Lenses can create real or virtual images. • A real image is formed when rays of light actually intersect to form an image. • A virtual image is formed when light rays appear to come from a point that they don’t actually come ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.

















![13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008538239_1-d1798f6d27c8a2d8c0931d41a70fff89-300x300.png)


