Light and Optics - Mayfield City Schools
... • Step 1: Draw a light ray passing through the center of the lens. • Step 2: Draw a light ray that starts parallel to the axis and bends at the lens to pass through the far focal point. • Step 3: Draw a light ray passing through the near focal point. ...
... • Step 1: Draw a light ray passing through the center of the lens. • Step 2: Draw a light ray that starts parallel to the axis and bends at the lens to pass through the far focal point. • Step 3: Draw a light ray passing through the near focal point. ...
Chapt23_VG0
... Different colors are associated with light of different wavelengths. However, color is a perception, and most of that perception is based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original compo ...
... Different colors are associated with light of different wavelengths. However, color is a perception, and most of that perception is based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original compo ...
lecture 31 - magnifier, telescope
... telescopes. Which list contains the largest telescopes overall, and why are the largest telescopes all that variety? a. Reflecting is much larger. The glass in large refracting telescopes would sag so they use mirrors instead since they can support the back of them. b. reflecting telescopes are larg ...
... telescopes. Which list contains the largest telescopes overall, and why are the largest telescopes all that variety? a. Reflecting is much larger. The glass in large refracting telescopes would sag so they use mirrors instead since they can support the back of them. b. reflecting telescopes are larg ...
The Resolving Power Of a Microscope and Telescope
... When a point object is imaged using a circular opening (or aperture) like a lens or the iris of our eye, the image formed is not a point but a diffraction pattern. This is true particularly when the size of the object is comparable to the wavelength of light. Just as in single slit diffraction (clic ...
... When a point object is imaged using a circular opening (or aperture) like a lens or the iris of our eye, the image formed is not a point but a diffraction pattern. This is true particularly when the size of the object is comparable to the wavelength of light. Just as in single slit diffraction (clic ...
Lecture - Galileo
... The ray approximation states that light travels in straight lines until it is reflected or refracted and then travels in straight lines again. The wavelength of light must be small compared to the size of the objects or else diffractive effects occur. ...
... The ray approximation states that light travels in straight lines until it is reflected or refracted and then travels in straight lines again. The wavelength of light must be small compared to the size of the objects or else diffractive effects occur. ...
F - DCS Physics
... What would be the value of the angle θ so that the ray of light emerges parallel to the side of the glass block? Calculate the speed of light as it passes through the glass. ...
... What would be the value of the angle θ so that the ray of light emerges parallel to the side of the glass block? Calculate the speed of light as it passes through the glass. ...
OPTICS
... a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appear to come to a single point. ...
... a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appear to come to a single point. ...
February 6 pptx
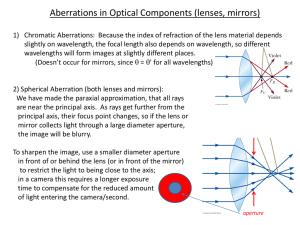
... Aberrations in Optical Components (lenses, mirrors) 1) Chromatic Aberrations: Because the index of refraction of the lens material depends slightly on wavelength, the focal length also depends on wavelength, so different wavelengths will form images at slightly different places. (Doesn’t occur for m ...
... Aberrations in Optical Components (lenses, mirrors) 1) Chromatic Aberrations: Because the index of refraction of the lens material depends slightly on wavelength, the focal length also depends on wavelength, so different wavelengths will form images at slightly different places. (Doesn’t occur for m ...
ECEN 4616/5616 Optoelectronic Design
... When we block those rays with a lens, say, the real image is no longer formed, but becomes a virtual object for that lens, which may create a real image at another location: ...
... When we block those rays with a lens, say, the real image is no longer formed, but becomes a virtual object for that lens, which may create a real image at another location: ...
the optical (light) microscope
... down to the edge of the field of view. A second adjustable-iris diaphragm, the aperture diaphragm, is placed in the light path before the vertical illuminator. Opening or closing this diaphragm alters the amount of light and the angle of the cone of light entering the objective lens. The optim ...
... down to the edge of the field of view. A second adjustable-iris diaphragm, the aperture diaphragm, is placed in the light path before the vertical illuminator. Opening or closing this diaphragm alters the amount of light and the angle of the cone of light entering the objective lens. The optim ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.