* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch14 Review
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction grating wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Photographic film wikipedia , lookup
Transparency and translucency wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
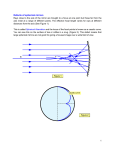
Chapter 14 Objectives: Identify the components of the electromagnetic spectrum. Calculate the frequency or wavelength of electromagnetic radiation. Recognize that light has a finite speed. Describe how the brightness of a light source is affected by distance. Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Calculate distances and focal lengths using the mirror equation for concave and convex spherical mirrors. Draw ray diagrams to find the image distance and magnification for concave and convex spherical mirrors. Distinguish between real and virtual images. Describe how parabolic mirrors differ from spherical mirrors. Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields with different wavelengths. The relationship between the frequency, wavelength, and speed of electromagnetic radiation is given by the equation: c=fλ The brightness of light is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the light source. Light obeys the law of reflection, which states that the incident and reflected angles of light are equal. Flat mirrors form virtual images that are the same distance from the mirror’s surface as the object is. The mirror equation relates object distance, image distance, and focal length of a spherical mirror. The magnification equation relates image height or distance to object height or distance, respectively. Light of different colors can be produced by adding light consisting of the primary additive colors (red, green, blue). Pigments can be produced by combining subtractive colors (magenta, yellow, cyan). Light can be linearly polarized by transmission, reflection, or scattering. Key Terms Angle of incidence, angle of reflection, concave spherical mirror, convex spherical mirror, electromagnetic wave, linear polarization, real image, reflection, virtual image