PochPHYS104-Obj_Chapt23Sp13
... identify the distinguishing characteristics of each and apply to a practical situation, i.e. effect on parallel light rays, thickness in the center, sign convention, etc. draw a ray diagram for an image given the object’s distance and focal length of the lens and describe the image’s character, i.e. ...
... identify the distinguishing characteristics of each and apply to a practical situation, i.e. effect on parallel light rays, thickness in the center, sign convention, etc. draw a ray diagram for an image given the object’s distance and focal length of the lens and describe the image’s character, i.e. ...
GRADE 10 SA2 PHYSICS revision worksheet-2
... 8.(a) An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula of determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. 9.(a) An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a ...
... 8.(a) An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula of determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm. 9.(a) An object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a ...
Physics 161 Lecture 26 Mirrors and Lenses December 6, 2016
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
Physics_AP_B_Evans_Day_36_Period_2
... whose radius of curvature is 10.20 cm. Find the location and size of the image. ...
... whose radius of curvature is 10.20 cm. Find the location and size of the image. ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
... the surface!!! Your angles are formed by the light ray and the normal line!!! ...
... the surface!!! Your angles are formed by the light ray and the normal line!!! ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... To an eye on the right-hand side, these diverging rays will Appear to be coming from the point F’: the second focal point. ...
... To an eye on the right-hand side, these diverging rays will Appear to be coming from the point F’: the second focal point. ...
Ray Box Lab - Iona Physics
... 3. Adjust the position of the lens so that the rays are parallel to each other. 4. Trace the ray box, the plano-convex lens and the light rays on the worksheet. 5. Place an optical component in the path of the light rays and adjust it to locate the focus. 6. On the worksheet trace the optical compon ...
... 3. Adjust the position of the lens so that the rays are parallel to each other. 4. Trace the ray box, the plano-convex lens and the light rays on the worksheet. 5. Place an optical component in the path of the light rays and adjust it to locate the focus. 6. On the worksheet trace the optical compon ...
Paraxial Formulas - CVI Laser Optics
... of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray that enters the first principal point of the system exits the system from the second principal point parallel to its original direction (i.e., its ...
... of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray that enters the first principal point of the system exits the system from the second principal point parallel to its original direction (i.e., its ...
pupil function - UCT Digital Image Processing
... derived. It is useful to define the pupil function as the function that takes on a value of one inside the aperture, and zero outside. There are two cases: • Coherent illumination: If the point sources being imaged vary in synchrony, then stable patterns of constructive and destructive interference ...
... derived. It is useful to define the pupil function as the function that takes on a value of one inside the aperture, and zero outside. There are two cases: • Coherent illumination: If the point sources being imaged vary in synchrony, then stable patterns of constructive and destructive interference ...
The Very Basics of Geometric Optics 5.1.2 Basic Geometric Optics
... measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus produce "dark" pictures. The solution might be aspherical lenses but usually combinations of spherical lenses are used ...
... measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus produce "dark" pictures. The solution might be aspherical lenses but usually combinations of spherical lenses are used ...
Light Sources
... l, the light spreads out after passing through the aperture. (The smaller the aperture, the more it spreads out.) • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some inf ...
... l, the light spreads out after passing through the aperture. (The smaller the aperture, the more it spreads out.) • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some inf ...
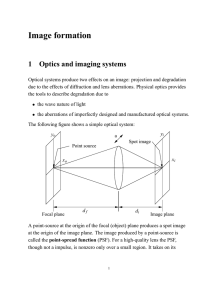
Image formation with broad bundles of rays
... Suppose all rays starting from O that travel through the optical system intersect again at O’. Wave surfaces near O for rays passing through O are spheres. Same for O’. Wave surfaces are surfaces of constant phase. The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two give ...
... Suppose all rays starting from O that travel through the optical system intersect again at O’. Wave surfaces near O for rays passing through O are spheres. Same for O’. Wave surfaces are surfaces of constant phase. The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two give ...
The Wave-Front Aberration Polynomial
... Here is the wave-front aberration polynomial written with terms up to order 4 (i + j = 4) … W(H,cos) ...
... Here is the wave-front aberration polynomial written with terms up to order 4 (i + j = 4) … W(H,cos) ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.